Detailed explanation of Java generics (summary of knowledge points)

Concept
Source: Java was not universal until the design started, until it was introduced in JDK 1.5. Java generics are implemented through erasure. Do you know what erasure is? Look down.
Concept: Regular classes and methods can only use specific types; basic types or custom classes. If you want to write code that can be applied to many types of code, this strict restriction will impose a lot of constraints on the code. Generics implement the concept of parameterized types, allowing code to be applied to multiple types. When generics emerged in programming languages, their original purpose was to enable classes and methods to have broad expressive power.
[Recommended learning: java video tutorial]
Simple generics
There are many reasons why generics appear, one of the most important reasons is Create container class. We don't specify the type yet, but decide what type to use later. To achieve this, type parameters need to be used after the class name, enclosed in angle brackets. Then, when this class is used, parameters of this type will be replaced with the actual type. In the example below, t is a type parameter. The code is as follows:
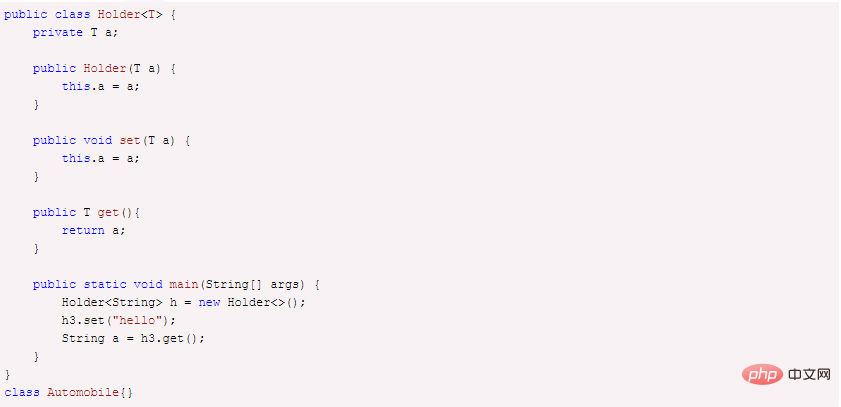
# However, in many source codes, some generic classes have multiple generic parameters, such as Java. UTIL function. Double function, with three types of parameters t, u, r.
Generic methods
Generic methods make methods independent of classes. When writing generic code, the basic guideline is to use generic methods whenever possible. This means that if you can use generic methods instead of generic methods for the entire class, then you can use generic methods because they make things clearer. Additionally, for static methods, the type parameters of a generic class cannot be accessed, so if static methods need to use generalization capabilities, they must be made into generic methods.
Generic erasure
When I read the "Mysteries of Deletion" section in the general chapter of Java Programming Thoughts, I was particularly dizzy, and then when I looked down, I became increasingly confused. Especially when you look at boundaries and wildcards, it's a little confusing. First let’s look at what erasure is. In generic code, information about generic parameter types is not available. Java generics are implemented through erasure, which means that when using generics, any specific type is erased and the only thing you know about it is using objects. Since generics were not originally introduced in Java, it was designed to be compatible with older versions of the JDK. ErAcess is a compromise between Java's generic implementations. So when you run, list

Boundaries of generics
Generics in Java, when compiled, T represents a type. If no boundary is specified, it is equal to the object. . We can specify boundaries for generics using the extends keyword. To be able to call f(), we can help the generic class given a generic class boundary, telling the compiler that it must accept types behind the boundary. Extended keywords are used here. Change the above code to

Summary
Java generics features are widely used in many open source frameworks. This needs to be understood in depth. I think as the years of coding begin, I will have a different understanding in the future. Now I can only know so much through reading books.
This article comes from the java introduction column, welcome to learn!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Java generics (summary of knowledge points). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




