

1. What is an exception
Exception is an abnormal phenomenon that occurs during the running of the program.
try: Wrap the code where exceptions may occur. When an exception occurs, throw the exception
catch: Catch the exception and handle it
finally: Regardless of whether an exception occurs, it will be executed
throw: Manually raise an exception
throws: Define exceptions for any called methods
Online learning video recommendation:java online video
##2. Reasons for exceptions
User input errors; Code errors; Environmental factors; The exception mechanism ensures the robustness of the program!3. Classification of exceptions
NullPointerExceptionNull reference exception
IndexOutOfBoundExceptionSubscript out-of-bounds exception
4. Obtain exception information
When an exception occurs in the program, the program will be executed directly from the try to the catch statement block and will not continue to execute here.public class text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main开始执行");
text3 a=new text3();
a.text();
System.out.println("main执行结束");
}
public void text() {
int a;
try {
a=2/0;
System.out.println(a);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("程序发生了异常");
}
}
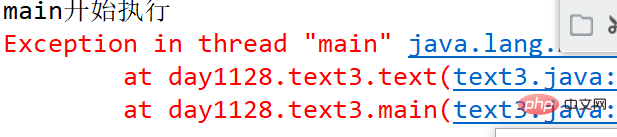
}public class text3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main开始执行");
text3 a=new text3();
a.text();
System.out.println("main执行结束");
}
public void text() {
int a;
//try {
a=2/0;
System.out.println(a);
//}catch(ArithmeticException e){
//System.out.println("程序发生了异常");
//}
}
}
5. Manually throw exceptions
throw exception; The parameter exception represents the exception object to be thrown. This object is a subclass of the throwable class and can only be one.public void text1() throws ArithmeticException{
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Text t=new Text();
try {
t.text();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public void text() throws Exception {
//手动抛出异常
throw new Exception("这是手动抛出来的");
}
}6. Nested use of try catch finally
public class Textthrow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a=Math.random();
try {
if(a>0.5) {
System.out.println(a+"程序不报错");
}
else {
throw new Exception();
}
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("这是外层捕获的对象"+e);
try {
a=1/0;
}catch(ArithmeticException e1) {
System.out.println("这是内层捕获的对象"+e1);
}finally {
System.out.println("这是内层的finally块");
}
}finally {
System.out.println("这是外层的finally块 ");
}
}
}7. Exception chain
Definition: two or Multiple different exceptions appear in the same program, and nested throwing occurs, which is called an exception chain.public class ExceptionChainText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator c=new Calculator();
try {
c.chufa(1, 0);
}catch(NumberCalculateExcetption e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("错误原因"+e);
}
}
}
class Calculator{
public int chufa(int i,int j) throws NumberCalculateExcetption {
if(j==0) {
NumberCalculateExcetption e = new
NumberCalculateExcetption ("计算错误");
NegativeNumberException e1= new
NegativeNumberException("除数不能为0");
e.initCause(e1);//由e1引起的异常
throw e;
}
return 0;
}
}
class NegativeNumberException extends Exception{
public NegativeNumberException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
class NumberCalculateExcetption extends Exception{
public NumberCalculateExcetption(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}The above is the detailed content of An overview of exceptions in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!