A brief discussion on regular expressions on the front end

1. Overview
In JavaScript, use // You can create a regular expression object, of course you can also use new RegExp()
Commonly used methods related to regular expressions include match, test and replace.
Among them, match and replace are methods on strings, and test is a method on regular objects.
[Related course recommendations: JavaScript video tutorial]
Look at the specific illustrations below:

2. Match single characters
-
[]/reg/can directly match specific stringsreg. The square brackets in -
in##/[arzy]/means matching any single character inarzyThe dash- /[f-h]/represents matchingftoin alphabetical order Any single character in h- ##/[1-3]/
represents matching numbers 1 to 3

3. Regular optionsThe regular object can also be followed by options,
JavaScript Commonly used options in are:
- i
- represents ignoring case
- m
- Represents multi-line matching
- g
- Represents global matching (can match multiple times)

4. Boundary matching
- ^
- represents the beginning of the matching string
- $
- Represents the end of the matched string
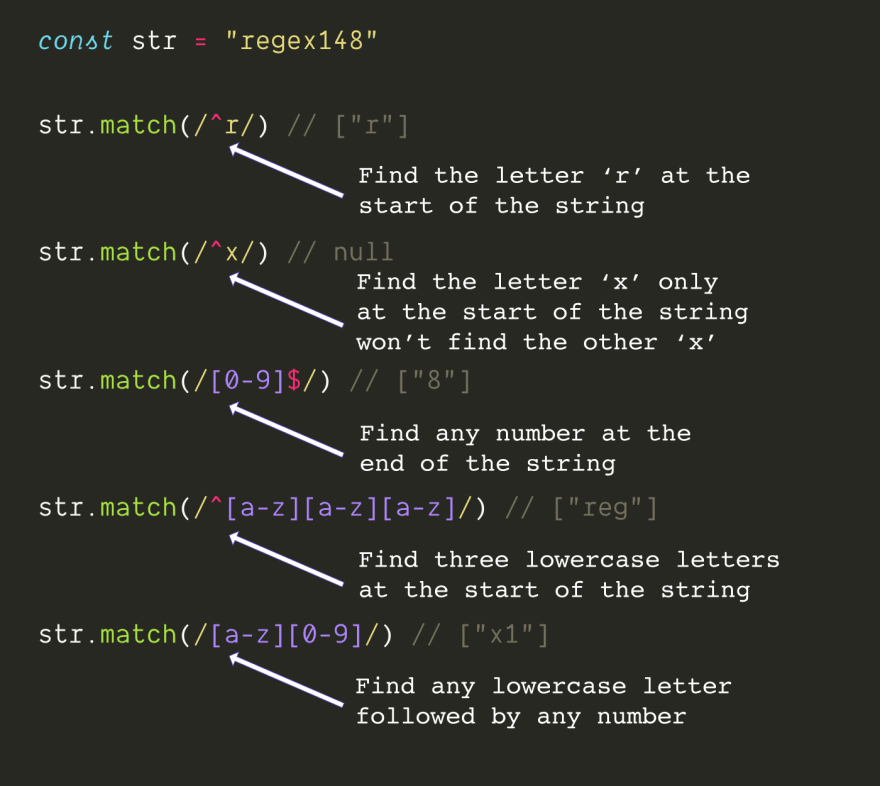
5. Character matching
- .
- - can match any character except newline characters
- - can match Any number
- - can match any
non-number \s - - matches any whitespace character
- - matches any
non-whitespace character \n - - matches newline
- - It is actually equivalent to
[A-Za-z0-9_], which matches alphanumeric underscores
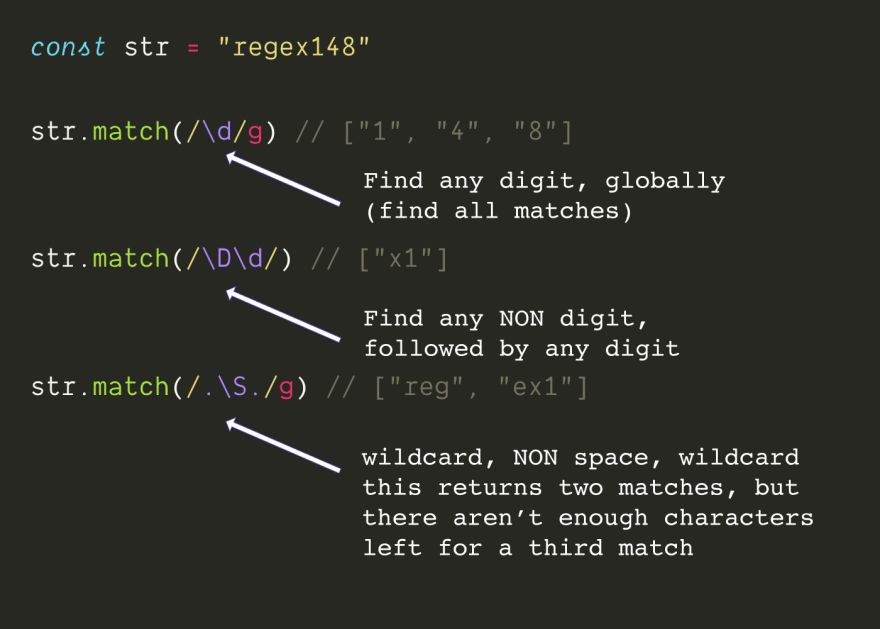
6. Quantifier matching
- *
- - Match 0 or more times
- - Match 1 or more times
- - Match 0 or 1 times
- - Match 3 times
- - Matches 2, 3 or 4 times
- - Matches 2 or more times

7. Grouping
() Parentheses represent grouping in regular expressions, usually in The match method is used to return full matches plus multiple grouping results. If the g option is used, only full matches are returned. In parentheses you can use the pipe symbol
, which stands for or
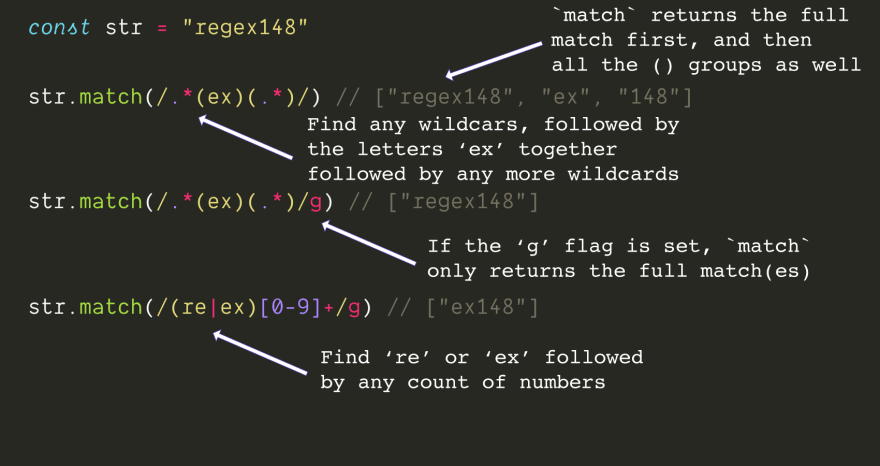
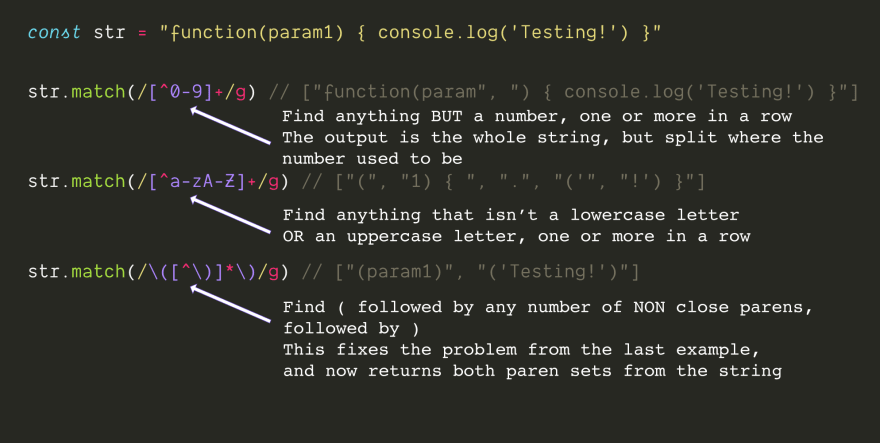
When matching special symbols, you need to add a backslash\
The special characters in JS are ^ $ \ . * ? () [] {} |
So if you need to match the asterisk *
\*

match except a certain character Any characters need to be used in square brackets []
^So far ^
- If used inside square brackets []
- , it represents Matches other than this character
 ##10. End
##10. End
The above only introduces the basic usage of regular expressions, which is basically enough for daily development. For more in-depth usage, such as Regular rules are very Powerful, but cannot be abused. If you write a very complicated regular expression that only you can understand, a better approach is to implement it without using regular expressions~ Reference link ● Intro to Regex for Web Developers This article comes from the js tutorial column, welcome to learn! Greedy and Lazy, Zero-width Assertion and Capture, interested friends can learn by themselves~
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion on regular expressions on the front end. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.






