A brief discussion on DOM core operations in JavaScript
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a standard programming interface recommended by the W3C organization for processing extensible markup language (HTML or XML).

W3C has defined a series of DOM interfaces through which the content, structure and style of web pages can be changed.
1. For JavaScript, in order to enable JavaScript to operate HTML, JavaScript has its own DOM programming interface;
2. For HTML, DOM makes HTML form a DOM tree, including documents, elements, and nodes.
Document: The entire page is a document;
Element: All tags in the page are called elements;
Node: All content on the page is a node. Document node (ducument object), element node (element object), attribute node (attribute object), text node (text object) , comment node (comment object), The line break between codes is also a node.
All DOM elements we obtain are an object.
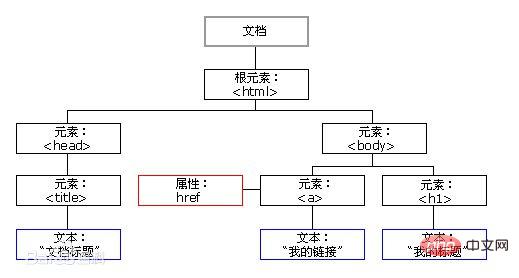
For DOM operations, we mainly focus on elements Operations mainly include create, add, delete, modify, check, attribute operations, and event operations.
1. Creating
mainly includes three types:
1. document.write
Features: If the page document flow is loaded (that is, all codes are executed), calling this sentence again will cause the page to be redrawn (That is, a new html page is created for us, and everything we wrote before is gone). (Rarely used)
2. innerHTML: Writing content to a DOM node will not cause the entire page to be redrawn.
3. createElement: It will not cause the page to be redrawn.
InnerHTML and createElement efficiency comparison:
①innerHTML splicing efficiency test:
<script>
function fn() {
var d1 = +new Date();
var str = '';
for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
document.body.innerHTML += '<div style="width:100px; height:2px; border:1px solid blue;"></div>';
}
var d2 = +new Date();
console.log(d2 - d1);
}
fn();
</script>The execution results are as follows
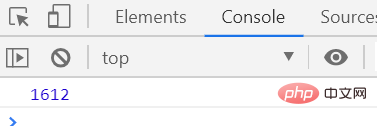
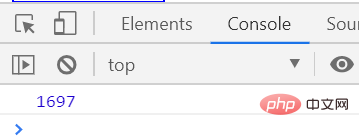
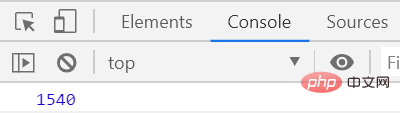
##The execution speed is about 1600 milliseconds
②createElement efficiency test
<script>
function fn() {
var d1 = +new Date();
for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
var div = document.createElement('div');
div.style.width = '100px';
div.style.height = '2px';
div.style.border = '1px solid red';
document.body.appendChild(div);
}
var d2 = +new Date();
console.log(d2 - d1);
}
fn();
</script>The execution results are as follows
执行速度为十几秒
③innerHTML数组效率测试
<script>
function fn() {
var d1 = +new Date();
var array = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
array.push('<div style="width:100px; height:2px; border:1px solid blue;"></div>');
}
document.body.innerHTML = array.join('');
var d2 = +new Date();
console.log(d2 - d1);
}
fn();
</script>执行结果如下
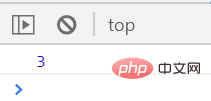
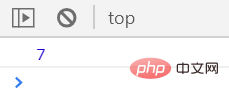
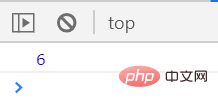
执行速度为个位数秒
结果分析:
执行效率:innerHTML数组效率 > createElement效率 > innerHTML拼接效率
所以创建多个元素时innerHTML效率更高(不要拼接字符串,采用数组形式拼接),结构稍微复杂麻烦一些。
createElement()创建多个元素时效率稍微低一些,但结构清晰。
二、增
主要包括两种:
1、appendChild:node.appendChild(child)是在后面追加元素
2、insertBefore:node.insertBefore(child)是添加到最前面
三、删
removeChild:node.removeChild(child)删除父节点中的一个子节点,并返回被删除的节点。
四、改
主要是修改dom元素的属性,dom元素的内容、属性,表单的值等。
1、修改元素属性:src、href、title等。可以直接修改,这些属性都是可读写的。
2、修改普通元素内容:innerText、innerHTML。(两者都是可读写的)
element.innerText:读取时,只读取标签里面的内容,不会少文字,但不会读取里边的标签、空格和换行。(非标准)
element.innerHTML:读取时,整个读取出来,包括html标签,同时保留空格和换行。(W3C标准,常用)
3、修改表单元素:value(表单里边的内容)、type(表单类型)、disabled(是否被使用)等。
4、修改元素样式:style、className。可以直接通过style修改属性,如果需要修改的属性较多或者为了方便操作,建议修改className。
五、查
主要获取查询dom的元素
1、DOM提供的API方法:getEementById、getElementsByTagName等古老的方法。
2. New methods provided by H5: querySelector, querySelectorAll. (Advocate)
3. Use node operations to obtain elements: parent (parentNode), child (children), brother (previousElementSibling, nextElementSibling). (Advocate)
6. Attribute operation
Main For custom attributes
1, setAttribute: Set the attribute value of dom. element.setAttribute('attribute', 'value'); Mainly for custom attributes
##2. getAttribute: Get the attribute value of dom
There are two ways to get the attribute value of dom: element.attribute and element.getAttribute('attribute')
Difference:
element.Attribute gets the built-in attribute value (the attribute that comes with the element itself);
element.getAttribute('attribute') mainly gets the Custom attributes (attributes added by ourselves).
3. removeAttribute: Remove the attribute. removeAttribute('attribute')
7. Event operation
give The element registers an event, taking: event source. event type = event handler
onclick: left mouse button click event.
onmouseover: Triggered when the mouse passes over.
onmouseout: Triggered when the mouse leaves.
onfocus: Triggered by getting mouse focus.
onblur: Triggered when mouse focus is lost.
dblclick: Left mouse button double-click event.
onmousemove: Triggered by mouse movement.
onmousedown: Triggered when the mouse button is pressed.
onmouseup: Triggered when the pressed mouse button is released.
Recommended learning: JavaScript video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion on DOM core operations in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).






