

Change the root password
The root account does not have a password by default. For security reasons, initialize one first
passwd
Create Linux administrator account
When using a Linux server, try not to use the root account. To handle daily operations, we create a new administrator account.
First, add a user group (my customized admin here).
addgroup admin
Then, add a new user (assumed to be www).
useradd -d /home/www -s /bin/bash -m www
In the above command, the parameter d specifies the user's home directory, the parameter s specifies the user's shell, and the parameter m indicates that if the directory does not exist, create the directory.
Free learning video tutorial sharing: linux video tutorial
Next, set the password of the new user.
passwd www
Add new user (www) to user group (admin).
usermod -a -G admin www
Next, set sudo permissions for the new user.
sudo vi /etc/sudoers
Find the following line.
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
Below this line, add another line.
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL www ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
The above NOPASSWD means that you do not need to enter a password when switching sudo. For security reasons, a password can also be enforced.
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL www ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
Finally, log out as the root user first, and then log in as the new user.
Configure SSH service
Save your computer’s ssh public key to the server’s ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file
Use the following command directly
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@123.456.78
Then, enter the server and edit the SSH configuration file /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
sudo cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config ~ (备份,复原时使用) sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
In the configuration file, change the default port 22 of SSH. Suppose you use 25000
Port 25000
Then, check whether several settings are set as follows, making sure to remove the # sign in front.
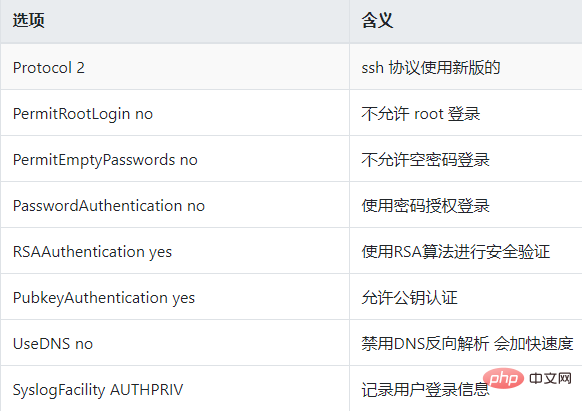
The above mainly prohibits root user login and password login.
After saving, exit file editing.
Next, change the permissions of the authorized_keys file.
sudo chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys && chmod 700 ~/.ssh/
Restart SSHD
sudo service ssh restart
or
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
Running environment configuration
Check the regional settings of the server.
locale
If the result is not en_US.UTF-8, it is recommended to set it to it.
sudo locale-gen en_US en_US.UTF-8 en_CA.UTF-8 sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales
Then, update the software
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Finally, make some security settings as needed, such as setting up a firewall and closing ports other than HTTP, HTTPs, and SSH.
Recommended related articles and tutorials: linux tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Linux server initialization configuration process. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!