How to implement master-slave failover in Redis sentry mode

Redis Sentinel is a distributed system. You can run multiple Sentinel processes (progress) in an architecture. These processes use gossip protocols to receive information about whether the main server is offline information, and uses agreement protocols to decide whether to perform automatic failover and which slave server to select as the new master server.
Although Redis Sentinel is released as a separate executable file redis-sentinel, it is actually just a Redis server running in a special mode. You can start a normal Redis server by giving - -sentinel option to start Redis Sentinel.
The Sentinel system is used to manage multiple Redis servers (instances). The system performs the following three tasks:
1. Monitoring: Sentinel will continuously check your main server and Whether the slave server is operating normally.
2. Notification: When a problem occurs on a monitored Redis server, Sentinel can send notifications to the administrator or other applications through the API.
3. Automatic failover: When a master server cannot work properly, Sentinel will start an automatic failover operation. It will upgrade one of the slave servers of the failed master server to the new master. server, and let other slave servers of the failed master server change to replicate the new master server; when the client attempts to connect to the failed master server, the cluster will also return the address of the new master server to the client, so that the cluster can use the new master server Replace the failed server.
Configuration
When the master goes down, the slave takes over and becomes the new master. The downed master automatically becomes the slave after it starts. In fact, it is a dual master with Mysql. The mode is the same as mutual master-slave; redis sentinel needs to use the redis-sentinel program and sentinel.conf configuration file.
mkdir -p /usr/local/redis mkdir -p /usr/local/redis/6379 mkdir -p /usr/local/redis/6380 mkdir -p /usr/local/redis/redis_cluster
Main configuration
vim redis_6379.conf
daemonize yes pidfile /usr/local/redis/6379/redis_6379.pid port 6379 tcp-backlog 128 timeout 0 tcp-keepalive 0 loglevel notice logfile "" databases 16 save 900 1 ###save save 300 10 save 60 10000 stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes rdbcompression yes rdbchecksum yes dbfilename dump.rdb ###dbfile dir "/usr/local/redis/6379" masterauth "123456" requirepass "123456" slave-serve-stale-data yes slave-read-only yes repl-diskless-sync no repl-diskless-sync-delay 5 repl-disable-tcp-nodelay no slave-priority 100 appendonly yes appendfilename "appendonly.aof" appendfsync everysec no-appendfsync-on-rewrite no auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100 auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb aof-load-truncated yes lua-time-limit 5000 slowlog-log-slower-than 10000 slowlog-max-len 128 latency-monitor-threshold 0 notify-keyspace-events "" hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 hash-max-ziplist-value 64 list-max-ziplist-entries 512 list-max-ziplist-value 64 set-max-intset-entries 512 zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 zset-max-ziplist-value 64 hll-sparse-max-bytes 3000 activerehashing yes client-output-buffer-limit normal 0 0 0 client-output-buffer-limit slave 256mb 64mb 60 client-output-buffer-limit pubsub 32mb 8mb 60 hz 10 aof-rewrite-incremental-fsync yes
vim sentinel_1.conf
Sentinel file configuration
port 6000 dir "/usr/local/redis/sentinel" # 守护进程模式 daemonize yes protected-mode no logfile "/usr/local/sentinel/sentinel.log"
Slave configuration
vim redis_6380.conf
daemonize yes pidfile "/usr/local/redis/6380/redis_6380.pid" port 6380 tcp-backlog 128 timeout 0 tcp-keepalive 0 loglevel notice logfile "" databases 16 save 900 1 save 300 10 save 60 10000 stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes rdbcompression yes rdbchecksum yes dbfilename "dump.rdb" dir "/usr/local/redis/6380" masterauth "123456" requirepass "123456" slave-serve-stale-data yes slave-read-only yes repl-diskless-sync no repl-diskless-sync-delay 5 repl-disable-tcp-nodelay no slave-priority 100 appendonly yes appendfilename "appendonly.aof" appendfsync everysec no-appendfsync-on-rewrite no auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100 auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb aof-load-truncated yes lua-time-limit 5000 slowlog-log-slower-than 10000 slowlog-max-len 128 latency-monitor-threshold 0 notify-keyspace-events "" hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 hash-max-ziplist-value 64 list-max-ziplist-entries 512 list-max-ziplist-value 64 set-max-intset-entries 512 zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 zset-max-ziplist-value 64 hll-sparse-max-bytes 3000 activerehashing yes client-output-buffer-limit normal 0 0 0 client-output-buffer-limit slave 256mb 64mb 60 client-output-buffer-limit pubsub 32mb 8mb 60 hz 10 aof-rewrite-incremental-fsync yes
vim sentinel_2.conf
#sentinel端口 port 6000 #工作路径,注意路径不要和主重复 dir "/usr/local/sentinel" # 守护进程模式 daemonize yes protected-mode no # 指明日志文件名 logfile "/usr/local/sentinel/sentinel.log"
Note:
1. The application connects to Sentinel Port, connect to a specific master replica by specifying a different master name.
2. In the Sentinel configuration file, you only need to configure the master replica IP and port in the master-slave replication. When the master-slave switches, Sentinel will automatically modify the master replica IP in the Sentinel configuration file to the new master replica. ip.
3. A sentinel configuration file can be configured to monitor multiple master-slave replications at the same time.
4. A single sentinel can be used for master-slave fault monitoring, but if there is only one sentinel process, if this process runs incorrectly, or the network is blocked, then the master-slave switchover of the redis cluster will not be possible (single Question);
This 2 represents the number of votes. When two sentinels believe that a master is no longer available, a failover will be triggered, and then the master can truly be considered to be unavailable. (Each sentinel in the sentinel cluster also communicates with each other through the gossip protocol); therefore, a reasonable configuration should be to start multiple sentinel processes at the same time, and it is best to start them in different servers. 5. Note that the requirement of mymaster is unique in the entire network environment. Sentinels will automatically establish associations through mastername as long as the network environment is connected.
Start redis
1. Both master and slave must be started
src/redis-server redis.conf
2. Log in to 6380 to establish a master-slave relationship
redis-cli -p 6380 slaveof 192.168.137.40 6379
Configure Sentinel
Both master and slave sentinels must be started, and can also be started through redis-server, such as "redis-server sentinel.conf --sentinel"
1. Start the sentinel
src/redis-sentinel sentinel.conf
2. Log in to the sentry (both sentries need to log in to execute), add master-slave monitoring information
redis-cli -p 6000
sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.137.40 6379 2 sentinel set mymaster down-after-milliseconds 5000 sentinel set mymaster failover-timeout 15000 sentinel set mymaster auth-pass 123456
Start error processing
Error 1:
WARNING overcommit_memory is set to 0! Background save may fail under low memory condition. To fix this issue add 'vm.overcommit_memory = 1' to /etc/sysctl.conf and then reboot or run the command 'sysctl vm.overcommit_memory=1' for this to take effect.
Two solutions (overcommit_memory)
1. echo "vm.overcommit_memory=1" > ; /etc/sysctl.conf or vi /etcsysctl.conf , and then reboot to restart the machine
2. echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory It will take effect without starting the machine
overcommit_memory parameter description:
Set the memory allocation policy (optional, set according to the actual situation of the server)
/proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
Optional values: 0, 1, 2.
0 means that the kernel will check whether there is enough available memory for the application process; if there is enough available memory, the memory application is allowed; otherwise, the memory application fails and an error is returned to the application process.
1, indicates that the kernel allows all physical memory to be allocated regardless of the current memory status.
2, indicates that the kernel is allowed to allocate memory that exceeds the sum of all physical memory and swap space
注意:redis在dump数据的时候,会fork出一个子进程,理论上child进程所占用的内存和parent是一样的,比如parent占用 的内存为8G,这个时候也要同样分配8G的内存给child,如果内存无法负担,往往会造成redis服务器的down机或者IO负载过高,效率下降。所 以这里比较优化的内存分配策略应该设置为 1(表示内核允许分配所有的物理内存,而不管当前的内存状态如何)。
这里又涉及到Overcommit和OOM。
什么是Overcommit和OOM
在Unix中,当一个用户进程使用malloc()函数申请内存时,假如返回值是NULL,则这个进程知道当前没有可用内存空间,就会做相应的处理工作。许多进程会打印错误信息并退出。
Linux使用另外一种处理方式,它对大部分申请内存的请求都回复"yes",以便能跑更多更大的程序。因为申请内存后,并不会马上使用内存。这种技术叫做Overcommit。
当内存不足时,会发生OOM killer(OOM=out-of-memory)。它会选择杀死一些进程(用户态进程,不是内核线程),以便释放内存。
Overcommit的策略
Linux下overcommit有三种策略(Documentation/vm/overcommit-accounting):
0. 启发式策略。合理的overcommit会被接受,不合理的overcommit会被拒绝。
1. 任何overcommit都会被接受。
2. 当系统分配的内存超过swap+N%*物理RAM(N%由vm.overcommit_ratio决定)时,会拒绝commit。
overcommit的策略通过vm.overcommit_memory设置。
overcommit的百分比由vm.overcommit_ratio设置。
# echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
# echo 80 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_ratio
当oom-killer发生时,linux会选择杀死哪些进程
选择进程的函数是oom_badness函数(在mm/oom_kill.c中),该函数会计算每个进程的点数(0~1000)。
点数越高,这个进程越有可能被杀死。
每个进程的点数跟oom_score_adj有关,而且oom_score_adj可以被设置(-1000最低,1000最高)。
错误2:
WARNING: The TCP backlog setting of 511 cannot be enforced because /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn is set to the lower value of 128.
echo 511 > /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn
错误3:
16433:X 12 Jun 14:52:37.734 * Increased maximum number of open files to 10032 (it was originally set to 1024).
新装的linux默认只有1024,当负载较大时,会经常出现error: too many open files
ulimit -a:使用可以查看当前系统的所有限制值
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
在文件的末尾加上
* soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535
执行su或者重新关闭连接用户再执行ulimit -a就可以查看修改后的结果。
故障切换机制
1. 启动群集后,群集程序默认会在从库的redis文件中加入连接主的配置
# Generated by CONFIG REWRITE slaveof 192.168.137.40 6379
2.启动群集之后,群集程序默认会在主从的sentinel.conf文件中加入群集信息
主:
port 26379 dir "/usr/local/redis-6379" # 守护进程模式 daemonize yes # 指明日志文件名 logfile "./sentinel.log" sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.137.40 6379 1 sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000 sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 18000 sentinel auth-pass mymaster 123456 # Generated by CONFIG REWRITE sentinel config-epoch mymaster 0 sentinel leader-epoch mymaster 1 sentinel known-slave mymaster 192.168.137.40 6380 sentinel known-sentinel mymaster 192.168.137.40 26380 c77c5f64aaad0137a228875e531c7127ceeb5c3f sentinel current-epoch 1
从:
#sentinel端口 port 26380 #工作路径 dir "/usr/local/redis-6380" # 守护进程模式 daemonize yes # 指明日志文件名 logfile "./sentinel.log" #哨兵监控的master,主从配置一样,在进行主从切换时6379会变成当前的master端口, sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.137.40 6379 1 # master或slave多长时间(默认30秒)不能使用后标记为s_down状态。 sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000 #若sentinel在该配置值内未能完成failover操作(即故障时master/slave自动切换),则认为本次failover失败。 sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 18000 #设置master和slaves验证密码 sentinel auth-pass mymaster 123456 #哨兵程序自动添加的部分 # Generated by CONFIG REWRITE sentinel config-epoch mymaster 0 sentinel leader-epoch mymaster 1 ###指明了当前群集的从库的ip和端口,在主从切换时该值会改变 sentinel known-slave mymaster 192.168.137.40 6380 ###除了当前的哨兵还有哪些监控的哨兵 sentinel known-sentinel mymaster 192.168.137.40 26379 7a88891a6147e202a53601ca16a3d438e9d55c9d sentinel current-epoch 1
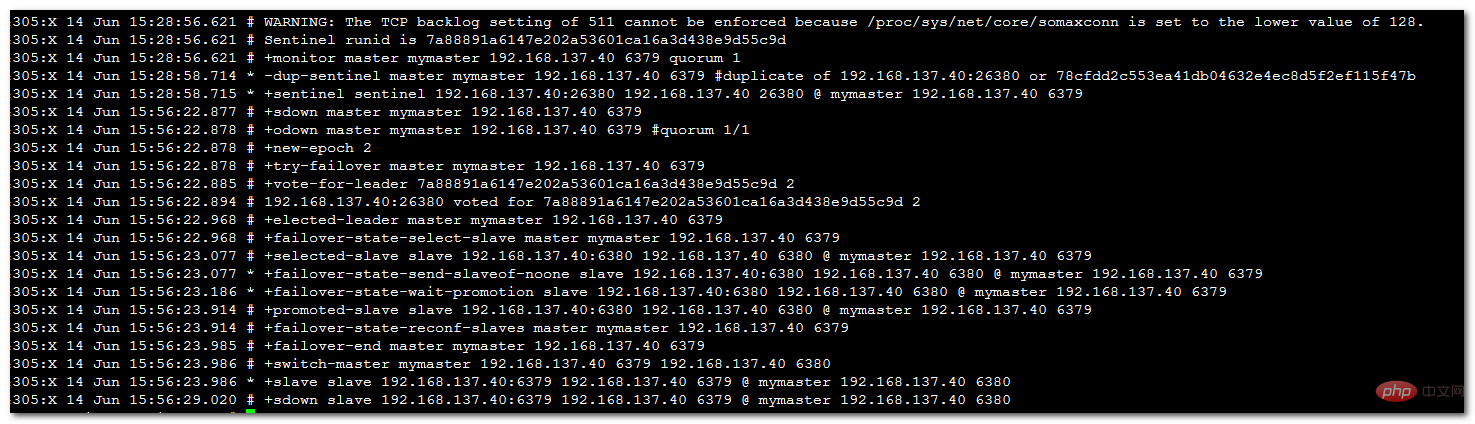
模拟主故障
[root@monitor redis-6380]# ps -ef|grep redis root 4171 1 0 14:20 ? 00:00:15 /usr/local/redis-6379/src/redis-server *:6379 root 4175 1 0 14:20 ? 00:00:15 /usr/local/redis-6380/src/redis-server *:6380 root 4305 1 0 15:28 ? 00:00:05 /usr/local/redis-6379/src/redis-sentinel *:26379 [sentinel] root 4306 1 0 15:28 ? 00:00:05 /usr/local/redis-6380/src/redis-sentinel *:26380 [sentinel] root 4337 4144 0 15:56 pts/1 00:00:00 grep redis [root@monitor redis-6380]# kill -9 4171 [root@monitor redis-6380]# ps -ef|grep redis root 4175 1 0 14:20 ? 00:00:15 /usr/local/redis-6380/src/redis-server *:6380 root 4305 1 0 15:28 ? 00:00:05 /usr/local/redis-6379/src/redis-sentinel *:26379 [sentinel] root 4306 1 0 15:28 ? 00:00:05 /usr/local/redis-6380/src/redis-sentinel *:26380 [sentinel] root 4339 4144 0 15:56 pts/1 00:00:00 grep redis [root@monitor redis-6380]#
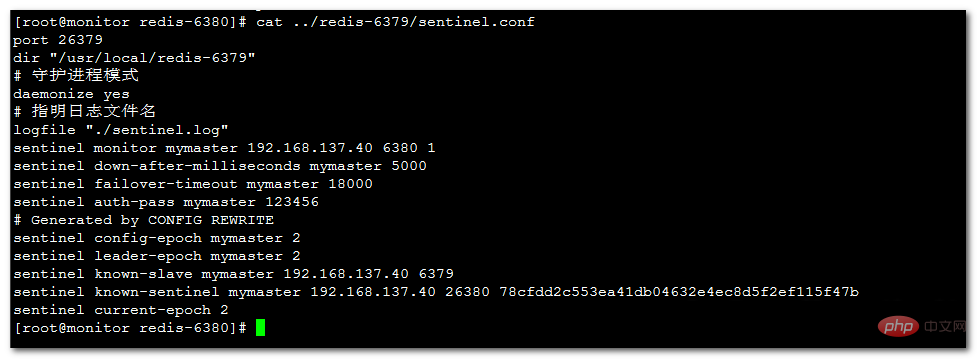
 从哨兵配置文件中可以看到当前的主库的已经发生了改变
从哨兵配置文件中可以看到当前的主库的已经发生了改变
总结
redis的哨兵端口26379、26380使用客户端软件无法连接,使用程序可以连接,客户端软件只能直接连接6379和6380端口。使用哨兵监控当主故障后会自动切换从为主,当主启动后就变成了从。有看到别人只配置单哨兵26379的这种情况,这种情况无法保证哨兵程序自身的高可用。
更多redis知识请关注redis数据库教程栏目。
The above is the detailed content of How to implement master-slave failover in Redis sentry mode. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Redis, as a message middleware, supports production-consumption models, can persist messages and ensure reliable delivery. Using Redis as the message middleware enables low latency, reliable and scalable messaging.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.




