What is a mirror?

What is the mirror?
Mirroring is a form of file storage and a type of redundancy. The data on one disk has an identical copy on another disk, which is a mirror. You can make many files into a mirror file, put it on the same disk with programs such as GHOST, and open it with software such as GHOST, and then restore it to many files. RAID 1 and RAID 10 use mirroring. Common image file formats include ISO, BIN, IMG, TAO, DAO, CIF, and FCD.
Overview
The so-called image file is actually similar to a ZIP compressed package. It makes a specific series of files into a single file in a certain format to facilitate users to download and use, such as a beta version of an operating system, game, etc. The image file not only has the "synthesis" function of a ZIP compressed package, but its most important feature is that it can be recognized by specific software and can be burned directly to a disc.
In fact, the image file in the usual sense can be expanded and contain more information.
For example, system files, boot files, partition table information, etc., so that the image file can contain all the information of a partition or even a hard disk. The classic software that uses this type of image file is Ghost. It also has a burning function, but its burning only saves the image file itself on the disc. In general, burning software can directly save the image file contained in the supported image file. Content is burned to disc.
For more programming related content, please pay attention to the Programming Introduction column on the php Chinese website!
The above is the detailed content of What is a mirror?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 ao3 mirror official website entrance
Feb 24, 2024 am 11:34 AM
ao3 mirror official website entrance
Feb 24, 2024 am 11:34 AM
ao3 mirror is a platform for creating fan fiction, but most friends don’t know where the official website of ao3 mirror is. Click on the https://ao3.cubeart.club/ link to enter the ao3 mirror website. The next step is The editor brings users an introduction to the latest official website entrance of ao3 mirror 2024. Interested users come and take a look! ao3 mirror official website entrance: https://ao3.cubeart.club/ 1. Download address 1. AO3: Click to download》》 2. AO3 latest version: Click to download》》 2. Enter the website method 1. Copy the website to View it in the browser and click [LogIn] in the upper right corner of the page to enter; 2. Account
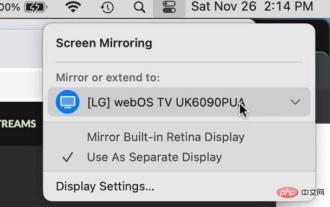 How to turn off AirPlay on Mac
Apr 16, 2023 am 09:49 AM
How to turn off AirPlay on Mac
Apr 16, 2023 am 09:49 AM
Turn off AirPlay on Mac via Control Center You can quickly turn off AirPlay in Mac OS Ventura 13 or later by doing the following: On a Mac with AirPlay enabled, go to Control Center in the upper right corner by clicking the two switch appearance icon and select " "Screen Mirroring" From the menu that appears, select the screen your Mac is AirPlay mirroring to. This will disconnect AirPlay and turn it off. You can also turn on ScreenMirroring and AirPlay this way, which you probably already know by now if you enabled it in the first place. . Disconnect AirPla on Mac via system settings
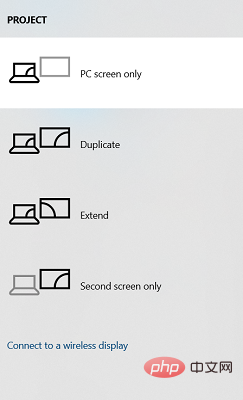 Easily mirror your Acer laptop screen to TV with these steps
Apr 13, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Easily mirror your Acer laptop screen to TV with these steps
Apr 13, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Screen mirroring is the best option when you want to view or display content from a small screen to a large screen (for example, from a laptop to a TV). While you may have heard of the option to mirror your smartphone screen to your TV or laptop, you can also mirror your laptop screen to your TV. This will allow you to view the content on a larger screen. The process of mirroring your laptop screen to your TV can be done in a variety of ways, including wired and wireless. It's up to you which option you want to continue using. On the one hand, the wired approach gives you a reliable mirroring experience with low latency. However, the wireless method eliminates the need to find a compatible cable for mirroring and can be done between two supported devices. The only downside is that you'll experience some lag and sometimes low-resolution mirroring
 CentOS7 various version image download addresses and version descriptions (including Everything version)
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:20 AM
CentOS7 various version image download addresses and version descriptions (including Everything version)
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:20 AM
When loading CentOS-7.0-1406, there are many optional versions. For ordinary users, they don’t know which one to choose. Here is a brief introduction: (1) CentOS-xxxx-LiveCD.ios and CentOS-xxxx- What is the difference between bin-DVD.iso? The former only has 700M, and the latter has 3.8G. The difference is not only in size, but the more essential difference is that CentOS-xxxx-LiveCD.ios can only be loaded into the memory and run, and cannot be installed. Only CentOS-xxx-bin-DVD1.iso can be installed on the hard disk. (2) CentOS-xxx-bin-DVD1.iso, Ce
 AtomHub, an open source container mirroring center jointly created by Huawei, Inspur and other units, announced that it is officially open for public testing and can stably download domestic services.
Jan 02, 2024 pm 03:54 PM
AtomHub, an open source container mirroring center jointly created by Huawei, Inspur and other units, announced that it is officially open for public testing and can stably download domestic services.
Jan 02, 2024 pm 03:54 PM
According to Huawei’s official news, the Open Atomic Developer Conference, with the theme of “Everything for Developers”, was held in Wuxi for two days, from December 16 to 17. The conference was led by the Open Atomic Open Source Foundation, Huawei, and Inspur. , DaoCloud, Xieyun, Qingyun, Hurricane Engine, as well as the OpenSDV Open Source Alliance, openEuler community, OpenCloudOS community and other member units jointly initiated the construction of the AtomHub Trusted Mirror Center, which is officially open for public testing. AtomHub adheres to the concepts of co-construction, co-governance, and sharing, and aims to provide open source organizations and developers with a neutral, open and co-constructed trusted open source container mirror center. In view of the instability and uncontrollability of image warehouses such as DockerHub, and some
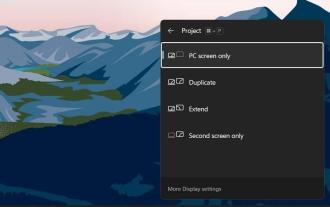 Miracast not working in Windows 11? Fix now
Apr 16, 2023 pm 11:46 PM
Miracast not working in Windows 11? Fix now
Apr 16, 2023 pm 11:46 PM
Receiving error codes or error messages on Windows operating systems is very common, almost all of us have encountered one while using Microsoft operating systems. Windows 11 is no different from other Windows operating systems. A common error encountered by many Windows 11 users is related to Miracast not working properly. Miracast is a Windows service from Microsoft that allows you to cast your screen to other monitors. This feature is built into Windows 11, and you need to connect your device and other monitors to the same Wi-Fi connection to cast content. If you want to tell your friends or
 Golang image manipulation: how to mirror, rotate and flip images
Aug 25, 2023 pm 10:31 PM
Golang image manipulation: how to mirror, rotate and flip images
Aug 25, 2023 pm 10:31 PM
Golang image manipulation: How to mirror, rotate and flip images 1. Introduction Image processing is one of the needs we often encounter in many development scenarios. In Golang, we can use the image package to operate and process images. This article will focus on how to use Golang to mirror, rotate and flip images, and provide corresponding code examples. 2. Mirroring operation Mirroring a picture is to change the left and right layout of the picture. In Golang, you can use Fli of the draw package
 Where to download win7iso image
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Where to download win7iso image
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
win7 has always been loved by everyone for its stability and good compatibility, but many friends don’t know where to download the win7 iso image. Today, the editor brings the download method and download and installation steps. The specific solution is as follows Get up and take a look. Win7iso image download and installation tutorial 1. Baidu website, download the win7ISO image. The first step of the installation steps: Download the system and click the download button (you can choose Thunder download, network disk download, China Telecom, China Mobile or China Unicom download), and then select the location where the download file is stored, for example: E drive. Finally, click the "Download Now" button to download. Step 2: Unzip the file, open the E drive, right-click the compressed package (Windows7X64.iso), and select "Extract to W



