How to change the language setting in centos to Chinese

View the current language package of the system
locale
View the language package the system has
locale -a
(zh_CN.UTF-8 is Simplified Chinese, if there is no zh_CN. UTF-8, just install the language pack. If it exists, you can set it directly)
Install the Simplified Chinese language pack
yum install kde-l10n-Chinese
(Recommended tutorial: centos usage tutorial)
Set to Chinese
Temporary modification, the previous settings will be restored after restarting the server
LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8" #修改为中文 LANG="en_US.UTF-8" #修改为英文
Permanent modification requires writing the configuration into the file.
Method (1)
vi /etc/locale.conf ##加下面内容到第一行,设置中文 LANG=zh_CN.UTF8
Method (2)
localectl set-locale.UTF8
Related video tutorial sharing: linux video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of How to change the language setting in centos to Chinese. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to input Chinese in centos
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
How to input Chinese in centos
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Methods for using Chinese input in CentOS include: using the fcitx input method: install and enable fcitx, set shortcut keys, press the shortcut keys to switch input methods, and input pinyin to generate candidate words. Use iBus input method: Install and enable iBus, set shortcut keys, press the shortcut keys to switch input methods, and input pinyin to generate candidate words.
 How to read USB disk files in centos7
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:18 PM
How to read USB disk files in centos7
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:18 PM
To read U disk files in CentOS 7, you need to first connect the U disk and confirm its device name. Then, use the following steps to read the file: Mount the USB flash drive: mount /dev/sdb1 /media/sdb1 (replace "/dev/sdb1" with the actual device name) Browse the USB flash drive file: ls /media/sdb1; cd /media /sdb1/directory; cat file name
 What to do if you forget your password to log in to centos
Apr 07, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
What to do if you forget your password to log in to centos
Apr 07, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
Solutions for forgotten CentOS passwords include: Single-user mode: Enter single-user mode and reset the password using passwd root. Rescue Mode: Boot from CentOS Live CD/USB, mount root partition and reset password. Remote access: Use SSH to connect remotely and reset the password with sudo passwd root.
 SCP usage tips-recursively exclude files
Apr 22, 2024 am 09:04 AM
SCP usage tips-recursively exclude files
Apr 22, 2024 am 09:04 AM
One can use the scp command to securely copy files between network hosts. It uses ssh for data transfer and authentication. Typical syntax is: scpfile1user@host:/path/to/dest/scp -r/path/to/source/user@host:/path/to/dest/scp exclude files I don't think you can when using scp command Filter or exclude files. However, there is a good workaround to exclude the file and copy it securely using ssh. This page explains how to filter or exclude files when copying directories recursively using scp. How to use rsync command to exclude files The syntax is: rsyncav-essh-
 How to enable root permissions in centos7
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:03 PM
How to enable root permissions in centos7
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:03 PM
CentOS 7 disables root permissions by default. You can enable it by following the following steps: Temporarily enable it: Enter "su root" on the terminal and enter the root password. Permanently enabled: Edit "/etc/ssh/sshd_config", change "PermitRootLogin no" to "yes", and restart the SSH service.
 How to obtain root permissions in centos7
Apr 07, 2024 pm 07:57 PM
How to obtain root permissions in centos7
Apr 07, 2024 pm 07:57 PM
There are several ways to gain root privileges in CentOS 7: 1. Run the command using "su". 2. Use "sudo" to run a single command. 3. Enable the root user and set a password. NOTE: Be cautious when using root privileges as they may damage the system.
 How to enter root permissions in centos
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
How to enter root permissions in centos
Apr 07, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
There are two ways to perform tasks with root privileges in CentOS: 1) Use the sudo command to temporarily obtain root privileges; 2) Log in directly using the root user password. Extreme caution should be used when using root privileges and it is recommended to only use them when necessary.
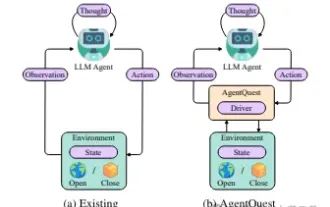 Exploring the boundaries of agents: AgentQuest, a modular benchmark framework for comprehensively measuring and improving the performance of large language model agents
Apr 11, 2024 pm 08:52 PM
Exploring the boundaries of agents: AgentQuest, a modular benchmark framework for comprehensively measuring and improving the performance of large language model agents
Apr 11, 2024 pm 08:52 PM
Based on the continuous optimization of large models, LLM agents - these powerful algorithmic entities have shown the potential to solve complex multi-step reasoning tasks. From natural language processing to deep learning, LLM agents are gradually becoming the focus of research and industry. They can not only understand and generate human language, but also formulate strategies, perform tasks in diverse environments, and even use API calls and coding to Build solutions. In this context, the introduction of the AgentQuest framework is a milestone. It not only provides a modular benchmarking platform for the evaluation and advancement of LLM agents, but also provides researchers with a Powerful tools to track and improve the performance of these agents at a more granular level






