What are the differences between centos6 and centos7?

The differences are as follows:
1. System initialization technology evolution-boot startup process
CentOS 6: Using INIT technology, the entire boot process is Self-check BIOS - MBR boot - GRUB loading - load kernel - start INIT process - read INITTAB configuration file, and start process services in order according to the mode specified in the configuration file. INIT technology makes the startup process very clear and relies on SHELL scripts. Because the processes are started one by one in sequence, the speed is slow and the system startup may be affected because a certain service is stuck.
CentOS 7: Using systemd technology. This is a new technology that replaces INIT. It uses a parallel method to start the process, so the startup speed is faster, and it is compatible with INIT commands to reduce migration costs.
2. Changes in network setting methods
The familiar ipconfig in CentOS 6 was replaced by the ip command in CentOS 7; the graphical network configuration tool nmtui replaced setup.
(Recommended tutorial: centos tutorial)
3. Host name and character set
You can modify the host name in CentOS 6 By editing the /etc/sysconfig/network file, but this method has been abandoned in CentOS 7 and the /etc/hostname file is used. The method of temporarily modifying the host name remains unchanged, and the hostname command is still used. And a new hostname management tool hostnamectl has been added to CentOS 7 (the file name modifications made by this tool are permanent).
For the modification of the character set, CentOS 7 uses the new configuration file /etc/locale.conf to replace /etc/sysconfig/i18n. If you want to temporarily modify the character set, the method remains the same, modify the LANG variable, such as LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8. A new character set management tool, localectl, has the same effect as hostnamectl.
4. Compatible with /etc/rc.local
The /etc/rc.local file records commands that need to be automatically executed after booting. Although this file has been abandoned in CentOS 7, However, it can also be used with compatibility. You only need to give the file executable permissions:
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
5. The difference between runlevels
The /etc/inittab file in CentOS 6 is based on init technology. , so naturally it cannot be used in CentOS 7, but the file is still retained, but the content has been replaced with boot content to let users know how to switch run levels now. Since this is not commonly used, I will not continue to describe it.
6. Service Management
This is the most unpleasant modification for users. It adds the systemctl tool and integrates the functions of the service and chkconfig commands.
Recommended related video tutorials: linux video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of What are the differences between centos6 and centos7?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 CentOS7 various version image download addresses and version descriptions (including Everything version)
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:20 AM
CentOS7 various version image download addresses and version descriptions (including Everything version)
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:20 AM
When loading CentOS-7.0-1406, there are many optional versions. For ordinary users, they don’t know which one to choose. Here is a brief introduction: (1) CentOS-xxxx-LiveCD.ios and CentOS-xxxx- What is the difference between bin-DVD.iso? The former only has 700M, and the latter has 3.8G. The difference is not only in size, but the more essential difference is that CentOS-xxxx-LiveCD.ios can only be loaded into the memory and run, and cannot be installed. Only CentOS-xxx-bin-DVD1.iso can be installed on the hard disk. (2) CentOS-xxx-bin-DVD1.iso, Ce
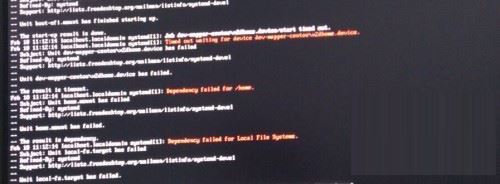 Steps to enter CentOS 7 emergency repair mode
Jan 13, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Steps to enter CentOS 7 emergency repair mode
Jan 13, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Open the centos7 page and appear: welcome to emergency mode! afterloggingin, type "journalctl -xb" to viewsystemlogs, "systemctlreboot" toreboot, "systemctldefault" to tryagaintobootintodefaultmode. giverootpasswordformaintenance(??Control-D???): Solution: execute r
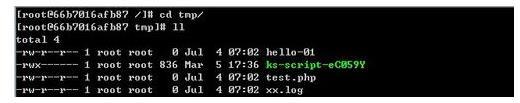 How to access and clean junk files in /tmp directory in CentOS 7?
Dec 27, 2023 pm 09:10 PM
How to access and clean junk files in /tmp directory in CentOS 7?
Dec 27, 2023 pm 09:10 PM
There is a lot of garbage in the tmp directory in the centos7 system. If you want to clear the garbage, how should you do it? Let’s take a look at the detailed tutorial below. To view the list of files in the tmp file directory, execute the command cdtmp/ to switch to the current file directory of tmp, and execute the ll command to view the list of files in the current directory. As shown below. Use the rm command to delete files. It should be noted that the rm command deletes files from the system forever. Therefore, it is recommended that when using the rm command, it is best to give a prompt before deleting the file. Use the command rm-i file name, wait for the user to confirm deletion (y) or skip deletion (n), and the system will perform corresponding operations. As shown below.
 How to set password rules in centos7? How to set password rules in centos7
Jan 07, 2024 pm 01:17 PM
How to set password rules in centos7? How to set password rules in centos7
Jan 07, 2024 pm 01:17 PM
Set password rules for security reasons Set the number of days after which passwords expire. User must change password within days. This setting only affects created users, not existing users. If setting to an existing user, run the command "chage -M (days) (user)". PASS_MAX_DAYS60#Password expiration time PASS_MIN_DAYS3#Initial password change time PASS_MIN_LEN8#Minimum password length PASS_WARN_AGE7#Password expiration prompt time Repeat password restriction use [root@linuxprobe~]#vi/etc/pam.d/system-auth#nearline15:
 How to install Mysql in CentOS7 and set it to start automatically at boot
Jun 02, 2023 pm 08:36 PM
How to install Mysql in CentOS7 and set it to start automatically at boot
Jun 02, 2023 pm 08:36 PM
Centos7 does not have a mysql database. The default database is mariadb (a branch of mysql). You can install the mysql database manually by following the steps below. 1. Download the rpm installation file wgethttp://repo.mysql.com/mysql-community-release-el7.rpm 2. Execute rpm to install rpm-ivhmysql-community-release-el7.rpm. After the dependency resolution is completed, the following options appear: dependenciesresolved =================================
 How to install mbstring extension under CENTOS7?
Jan 06, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
How to install mbstring extension under CENTOS7?
Jan 06, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
1.UncaughtError:Calltoundefinedfunctionmb_strlen(); When the above error occurs, it means that we have not installed the mbstring extension; 2. Enter the PHP installation directory cd/temp001/php-7.1.0/ext/mbstring 3. Start phpize(/usr/local/bin /phpize or /usr/local/php7-abel001/bin/phpize) command to install php extension 4../configure--with-php-config=/usr/local/php7-abel
 Detailed explanation of decompression file command (zip) under centos7
Jan 07, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Detailed explanation of decompression file command (zip) under centos7
Jan 07, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
1. The compressed folder is a zip file [root@cgls]#zip-rmydata.zipmydata2. Unzip mydata.zip into the mydatabak directory [root@cgls]#unzipmydata.zip-dmydatabak3.mydata01 folder and mydata02.txt are compressed into mydata.zip[root@cgls]#zipmydata.zipmydata01mydata02.txt4. Decompress the mydata.zip file directly [root@cgls]#unzipmydata.zip5. View myd
 How to modify and set the default shortcut keys of CentOS7?
Jan 09, 2024 pm 06:14 PM
How to modify and set the default shortcut keys of CentOS7?
Jan 09, 2024 pm 06:14 PM
When the default shortcut keys conflict with the keys of the software you are using or you need to use the shortcut keys according to your own habits, you have to modify and set the default shortcut keys. How to modify the default shortcut keys of CentOS7? Let’s take a look at the detailed tutorial below. 1. Start the Centos7 system in the virtual machine and enter the desktop. 2. Click Applications->System Tools->Settings in the upper left corner. 3. Enter the setting interface and click the device. 4. Select Keyboard and click any item on the right. And press the shortcut key to be set on the keyboard to change its shortcut key (note that some cannot be changed!) 5. After the change, as shown below, finally click Settings, so that the shortcut key setting modification is completed.




