What does file system mean?

What is the file system?
File system is the method and data structure used by the operating system to identify files on storage devices (commonly disks, but also solid-state drives based on NAND Flash) or partitions; That is, a method of organizing files on a storage device.
The software organization responsible for managing and storing file information in the operating system is called the file management system, or file system for short.
The file system consists of three parts: the file system interface, a collection of software for object manipulation and management, and objects and attributes. From a system perspective, the file system is a system that organizes and allocates the space of file storage devices, is responsible for file storage, and protects and retrieves stored files.
Specifically, it is responsible for creating files for users, storing, reading, modifying, and dumping files, controlling file access, and revoking files when the user no longer uses them.
Function
1. The file system is the method and data structure used by the operating system to identify files on the disk or partition; that is, the method of organizing files on the disk . Also refers to the disk or partition used to store files, or the type of file system. Therefore, it can be said that "I have 2 file systems" means that he has 2 partitions, one to store files, or he uses an "extended file system", which means the type of file system.
2. The difference between the disk or partition and the file system it contains is very important. A few programs (including most legitimately those that generate file systems) operate directly on the raw sectors of a disk or partition; this may corrupt an existing file system. Most programs operate based on file systems and cannot work on different file systems.
3. Before a partition or disk is used as a file system, it needs to be initialized and the record data structure written to the disk. This process is called creating a file system.
4. Most UNIX file system types have a similar general structure, even if the details vary. The central concepts are superblock, i-node inode, data block, directory block, and indirect block indirection block. The superblock contains general information about the file system, such as size (its exact information depends on the file system). The i-node contains all information about a file except the name. The name is stored in the directory together with the number of i-nodes. The directory entry includes the file name and the number of i-nodes of the file. The i-node contains the number of several data blocks used to store the file's data. There is only space for a small number of data blocks in the i-node. If more are needed, pointer space pointing to the data blocks will be dynamically allocated. These dynamically allocated blocks are indirect blocks; in order to find the data block, the name indicates that it must first find the indirect block number.
5. UNIX file systems usually allow holes in files, which means that the file system pretends that there is a special location in the file with only 0 bytes, but does not reserve actual disk space for this location in the file. This happens frequently with small binaries, Linux shared libraries, some databases and some other special cases.
6. Holes have certain uses. On my system, a simple measurement tool showed a savings of about 4MB out of 200MB of disk space used due to holes. In this system, there are relatively few programs and no database files.
7. The functions of the file system include: managing and scheduling the storage space of files, providing the logical structure, physical structure and storage method of files; realizing the mapping of files from identification to actual addresses, and realizing file control operations and Access operations realize the sharing of file information and provide reliable file confidentiality and protection measures, and provide file security measures.
8. The logical structure of the file is to organize the file structure according to the logical relationship of the content of the file. The logical structure of files can be divided into streaming files and recorded files.
9. Streaming file: The data in the file is a stream of characters without structure.
10. Record file: It is composed of several logical records, and each record is composed of the same data items. The length of the data items can be determined or uncertain.
Main defects: poor data association, data inconsistency, and redundancy.
The above is the detailed content of What does file system mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
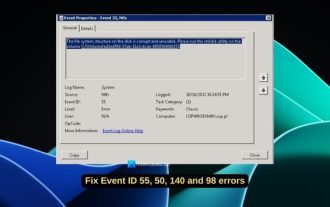 Fix event ID 55, 50, 98, 140 disk error in event viewer
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:43 AM
Fix event ID 55, 50, 98, 140 disk error in event viewer
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:43 AM
If you find event ID 55, 50, 140 or 98 in the Event Viewer of Windows 11/10, or encounter an error that the disk file system structure is damaged and cannot be used, please follow the guide below to resolve the issue. What does Event 55, File system structure on disk corrupted and unusable mean? At session 55, the file system structure on the Ntfs disk is corrupted and unusable. Please run the chkMSK utility on the volume. When NTFS is unable to write data to the transaction log, an error with event ID 55 is triggered, which will cause NTFS to fail to complete the operation unable to write the transaction data. This error usually occurs when the file system is corrupted, possibly due to the presence of bad sectors on the disk or the file system's inadequacy of the disk subsystem.
 How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems
Jun 29, 2023 pm 04:05 PM
How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems
Jun 29, 2023 pm 04:05 PM
How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems Introduction: With the continuous development of computer technology, the stability and reliability of the operating system are becoming more and more important. However, although Linux systems are widely regarded as a stable and reliable operating system, there is still the possibility of file system corruption. A file system crash may lead to serious consequences such as data loss and system abnormalities. Therefore, this article will introduce how to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems to help users better protect their data and systems.
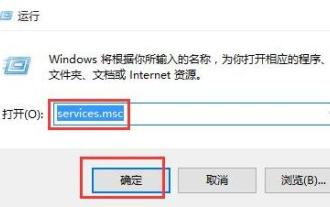 How to handle file system error 2147416359 in WIN10
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How to handle file system error 2147416359 in WIN10
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:31 AM
1. Press win+r to enter the run window, enter [services.msc] and press Enter. 2. In the service window, find [windows license manager service] and double-click to open it. 3. In the interface, change the startup type to [Automatic], and then click [Apply → OK]. 4. Complete the above settings and restart the computer.
 fstab(File System Table)
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
fstab(File System Table)
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
fstab (FileSystemTable) is a configuration file in the Linux system, used to define the rules for mounting file systems when the system starts. The fstab file is located in the /etc directory and can be created manually or modified by an editor. Each line specifies a file system to be mounted. Each line has six fields, and their meanings are as follows: The file system device file or UUID can be used to specify the device of the file system to be mounted. The UUID is a unique identifier. The UUID of the device can be obtained through the blkid command. 2. Mount point: Specify the directory to which the file system is to be mounted, which can be an absolute path (such as /mnt/data) or a relative path (such as ../data). 3. File system class
 The Difference: NTFS vs. FAT32
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:18 PM
The Difference: NTFS vs. FAT32
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:18 PM
NTFS and FAT32 are two common file systems used to organize and manage data on your computer's hard drive. While they all share some common functions and features, there are also some important differences in many ways. This article will explore several key differences between NTFS and FAT32. Functions and performance: NTFS (New Technology File System) is a newer file system in Microsoft Windows operating system. It has many advanced functions, such as data compression, file encryption,
 A complete list of Linux system commands.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:54 PM
A complete list of Linux system commands.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:54 PM
The following is a list of common Linux system commands (arranged in alphabetical order): alias: set command alias awk: text processing tool, used to extract and manipulate text data cat: connect files and print to standard output cd: change the current working directory chmod: Modify the permissions of a file or directory chown: Modify the owner and group of a file or directory chroot: Change the root file system directory cp: Copy a file or directory cron: A scheduled task management tool curl: A command line tool for downloading or uploading files cut :Extract text data by columns date:Display or set the system date and time dd:Copy and convert files df:Display the disk usage of the file system diff:Compare files or destinations
 In-depth understanding of Linux's standard file system (Ext2/Ext3/Ext4)
Dec 31, 2023 pm 10:18 PM
In-depth understanding of Linux's standard file system (Ext2/Ext3/Ext4)
Dec 31, 2023 pm 10:18 PM
The full name of Ext is Linux extended file system, extfs, which is the Linux extended file system. Ext2 represents the second generation file extension system, Ext3/Ext4 and so on. They are all upgraded versions of Ext2, but they add the log function and are backward compatible with each other. So Ext2 is called an indexed file system, and Ext3/Ext4 is called a journaled file system. Note: Linux supports many file systems, including Network File System (NFS) and Windows’ Fat file system. View the file systems supported by Linux: ls-l/lib/modules/$(uname-r)/kernel/fs view
 Common performance problems and solutions for Linux file systems
Jun 30, 2023 am 08:03 AM
Common performance problems and solutions for Linux file systems
Jun 30, 2023 am 08:03 AM
As a common operating system, Linux is widely used in servers, embedded devices and personal computers. However, when using a Linux system, we may encounter some file system performance problems, such as slow response speed, slow file reading and writing, etc. This article will introduce some common file system performance problems and provide corresponding solutions. Disk Fragmentation Disk fragmentation is a common file system performance problem. When files in the file system are frequently created, modified, and deleted, the files on the disk will be scattered.



