centos7 host only mode settings
Host-only mode:
(1) Host-only mode is used to establish an internal network isolated from the outside world to improve network security and can only communicate with the host.
() Host-only mode (H) is NAT mode, removes the virtual NAT device, and then uses VMware Network Adapter The VMnet1 virtual network card connects to the VMnet1 virtual switch to communicate with the virtual machine. It is host-only isolated, making the virtual machine an independent system and only communicates with the host.
Experiment: node-1 and node-5 use vmnet4 host-only mode to communicate
node-1:172.16.1.1
node-5: 172.16.1.2
Result: The virtual machine can successfully ping the host machine, that is, ping the VMNet4, and the host machine can also ping the virtual machine successfully.
----
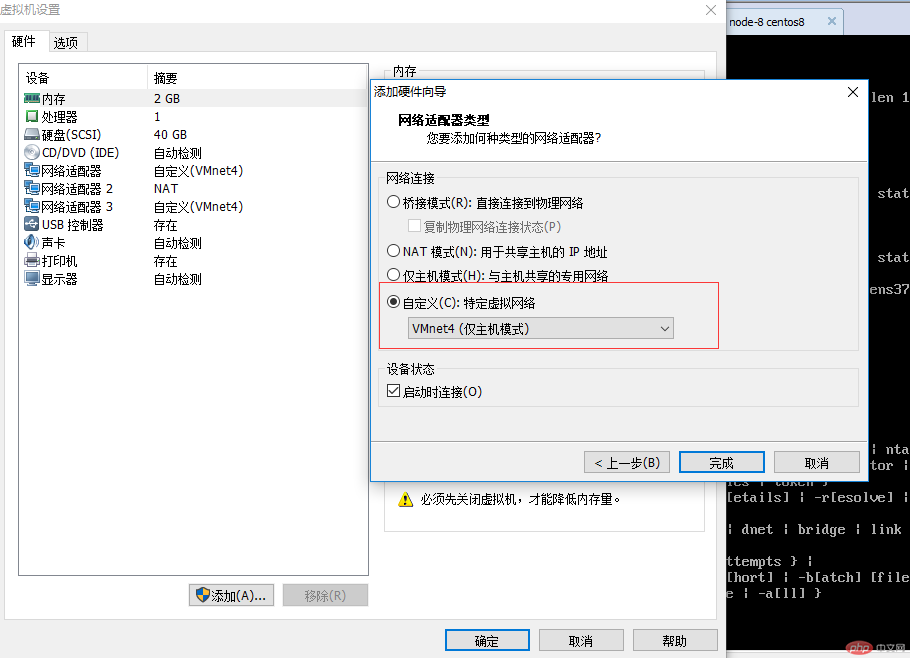
Add a network card to node-1
Select the CentOS virtual machine in the VMware main interface> right-click the mouse> select settings
Under the hardware options bar> Left-click the single-machine mouse to select the network adapter> Click on host-only mode> Finally click OK
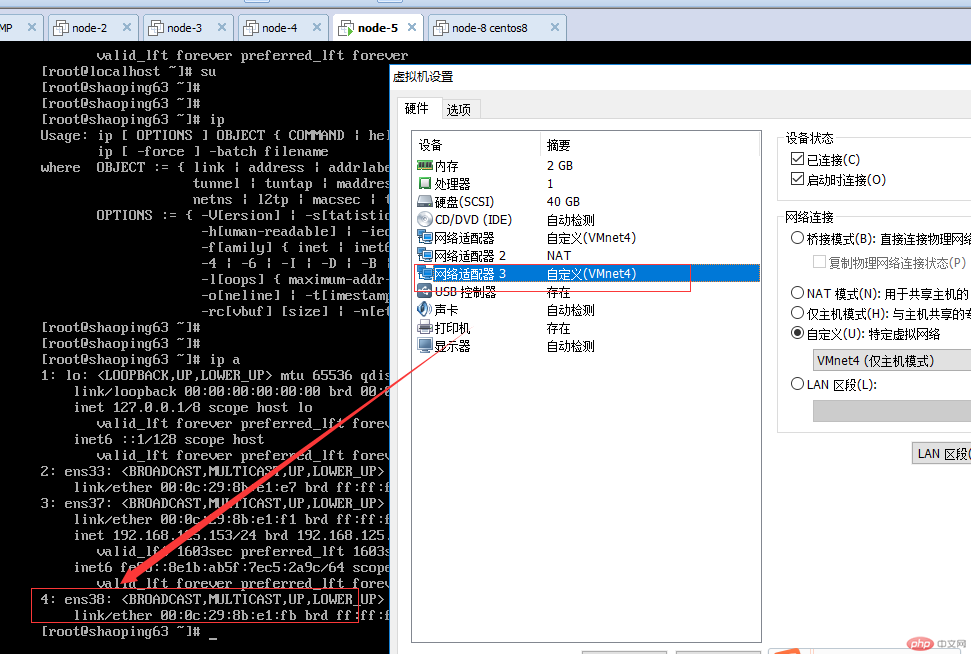
Check VMNet4 with ipconfig /all on the host machine. It serves as a gateway. Represents the host in host-only mode, because it uses this gateway to communicate with the host, rather than using the gateway connected to the external network.
Temporary configuration:
[root@shaoping63 ~]# ifconfig ens38 172.16.2.1/24 //Restart Will be lost later
Permanent configuration:
A graphical interface configuration
[root@shaoping63 ~]# nmtui
B How to modify the configuration file
Note: Anything starting with ifcfg- will be considered a network card configuration file. If you need to back it up, be sure not to keep this part. For example, the backup is called ifcfg_bak-eth0
[root@shaoping63 network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens38
[root@shaoping63 network-scripts]# uuidgen ifcfg-ens38
ba8527c8-89ed-4a83- bd84-be7918fcc50d
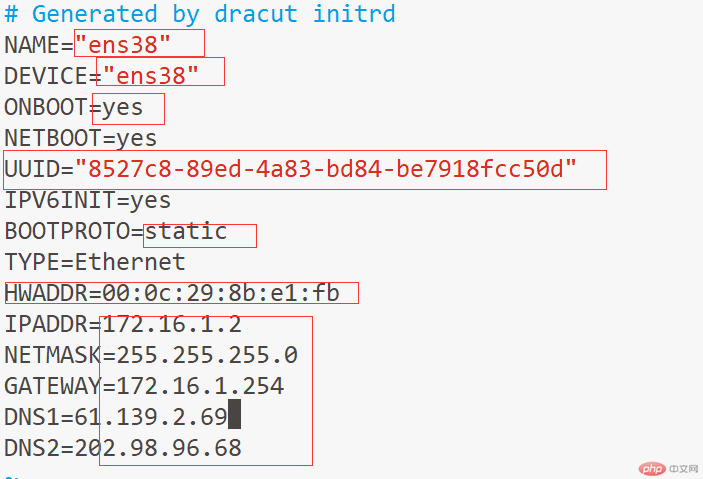
[root@shaoping63 network-scripts]# ifdown ens38
[root@shaoping63 network-scripts]# ifup ens38
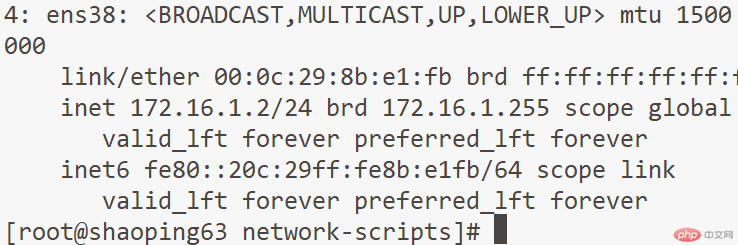
[root@client network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-ens37
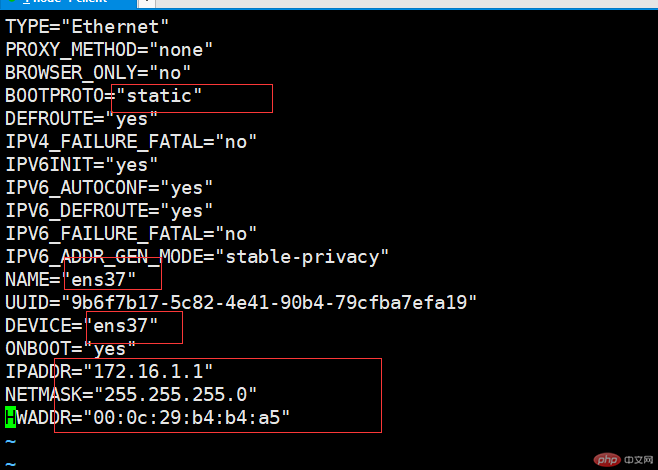
[root@client network-scripts]# systemctl restart network //Restart the network card

Note: If you use remote tools to connect to a virtual machine in host-only mode and fail to connect successfully, it is very likely that It is affected by DNS, turn it off in the file /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
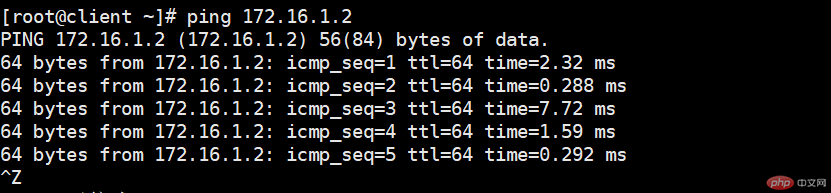
Test results show that the virtual machine can successfully ping the host machine, that is, ping the VMNet4, and the host machine can also ping the virtual machine successfully. The setting is successful!
The above is the detailed content of centos7 host only mode settings. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How do I configure log rotation in CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:43 PM
How do I configure log rotation in CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:43 PM
The article explains how to configure log rotation in CentOS using logrotate, detailing installation, configuration, and benefits like disk space management and security.
 How do I install and configure MySQL/MariaDB on CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:35 PM
How do I install and configure MySQL/MariaDB on CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:35 PM
Article discusses installation, configuration, and troubleshooting of MySQL/MariaDB on CentOS, including system requirements and security measures.(159 characters)
 How do I use Logical Volume Management (LVM) in CentOS to manage storage?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
How do I use Logical Volume Management (LVM) in CentOS to manage storage?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
The article discusses using Logical Volume Management (LVM) in CentOS for efficient storage management, detailing steps for setup, extension, and backup/restore processes, and highlighting LVM's advantages over traditional partitioning.
 How do I manage system services with systemd in CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:38 PM
How do I manage system services with systemd in CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:38 PM
The article explains how to manage system services using systemd on CentOS, covering starting, stopping, enabling at boot, and troubleshooting services.
 How do I monitor system performance in CentOS using tools like top, htop, and vmstat?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:41 PM
How do I monitor system performance in CentOS using tools like top, htop, and vmstat?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:41 PM
The article discusses monitoring CentOS system performance using top, htop, and vmstat, detailing their features, differences, and customization for effective system analysis.
 How do I perform a minimal installation of CentOS?
Mar 14, 2025 pm 03:51 PM
How do I perform a minimal installation of CentOS?
Mar 14, 2025 pm 03:51 PM
The article details steps for a minimal CentOS installation, covering download, boot media creation, and system setup. It discusses benefits like reduced resource use and enhanced security, and explains post-installation software management using yum
 How do I use yum or dnf to manage software packages in CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
How do I use yum or dnf to manage software packages in CentOS?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
The article discusses using yum and dnf for package management in CentOS, detailing their commands, differences, and troubleshooting. Key differences include speed, dependency resolution, and modularity, with dnf being the default in CentOS 8 .
 How do I set up a firewall in CentOS using firewalld?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:44 PM
How do I set up a firewall in CentOS using firewalld?
Mar 17, 2025 pm 04:44 PM
The article provides a comprehensive guide on setting up and managing firewalld on CentOS, including installation, enabling, basic commands, and troubleshooting steps.




