2020 New Java Interview Questions - Multi-Threading (3)

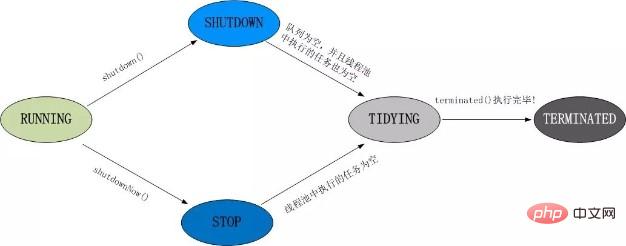
1. What are the states of the thread pool?
The thread pool has 5 states: Running, ShutDown, Stop, Tidying, and Terminated.
Thread pool state switching frame diagram:
(Video tutorial recommendation: java video)
2. What is the difference between the submit() and execute() methods in the thread pool?
The parameters received are different
submit has a return value, but execute does not
submit facilitates Exception handling
3. How to ensure the safety of multi-threaded operations in java programs?
Thread safety is reflected in three aspects:
Atomicity: Provides mutually exclusive access, only one thread can operate on data at the same time, (atomic, synchronized);
Visibility: One thread's modifications to main memory can be seen by other threads in time, (synchronized, volatile);
Ordering: One thread observes the order of instruction execution in other threads ,Due to instruction reordering, this observation is generally ,disordered (happens-before principle).
(Related tutorial recommendations: java introductory program)
4. What is the principle of upgrading multi-thread locks?
In Java, there are four lock states. The levels from low to high are: stateless lock, biased lock, lightweight lock and heavyweight lock state. These states will change with time. As the competition gradually escalates. Locks can be upgraded but not downgraded.
Illustrated process of lock upgrade:
5. What is a deadlock?
Deadlock refers to a blocking phenomenon caused by two or more processes competing for resources or communicating with each other during execution. Without external force, they will all Unable to proceed. At this time, the system is said to be in a deadlock state or the system has a deadlock. These processes that are always waiting for each other are called deadlock processes.
Recommended tutorial: java interview questions
The above is the detailed content of 2020 New Java Interview Questions - Multi-Threading (3). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is




)


