Object-oriented practice in PHP - basic practice cases
Object-oriented practice in PHP - basic practice
(1) Basic practice
1. The concept of class
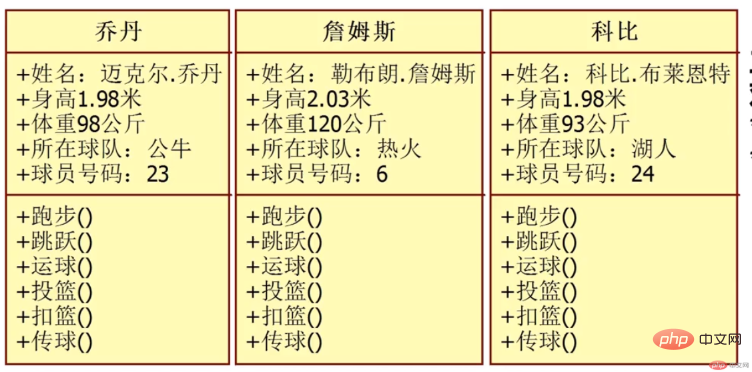
1. Common points:
all have the same attributes
all There are the same methods
2. Differences:
The specific values are different
3. Summary: They are all Objects of a class
Speaking of classes, let’s talk about the concept of classes
1) Class definition
-We say that things flock together and people divide into groups. Classify objects with similar characteristics into a class
So when we look at objects, try to compare their properties and methods. If their properties and methods are very similar, we can put They are classified into one class
-The class defines that these similar objects have the same properties and methods
For example: an NBA player is the definition of a class, which stipulates that as long as it is an NBA Players must have: age, name, height, weight, team, player number
and then they will also have the same skills:

But the question is, is there a specific height defined in this class, is there a specific name, is there a specific weight, none of them, but if we write all these attributes, will it become a specific one? Object
This is the relationship between classes and objects. Specifically, a class is a description of similar objects. This is called the definition of a class. A class is the blueprint or prototype of all these similar objects
For example, how did the object James come from? Just set the attribute value of this class.
The object of the class is an <strong>instance(Instance)</strong> of the class. This operation is also called instantiation of a class.
For example, James, Jordan, and Kobe are all instances of the NBA player class. The process of instantiating them is called instantiation of a class.
For classes, we can The understanding is that it is just an empty shelf. It only defines how objects are divided. As for objects, it is defined. For specific values, all attribute values must be written in detail.
Supplement A concept: We collectively refer to the objects and methods of a class as class members
2. The concept of instantiation
1) Definition of instantiation of a class
is to create a specific object through a class. This process is the instantiation of the class, which is equivalent to filling this empty shelf.
Example: For example, through the NBA player class we created James and Kobe Bryant , Jordan, among which the NBA player class was instantiated three times
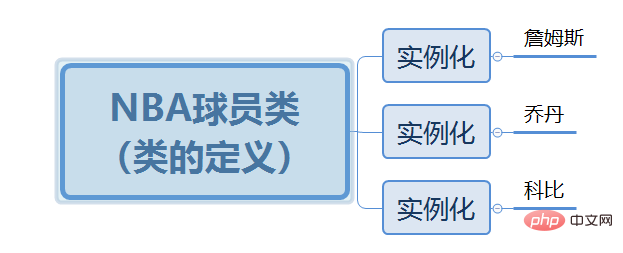
Summary: There is only one class, but it can be instantiated multiple times to obtain multiple specific Object
Tip: How to implement it, we will demonstrate it in the code later
2) Instantiation of the class
2) Example: Take Jordan as an example
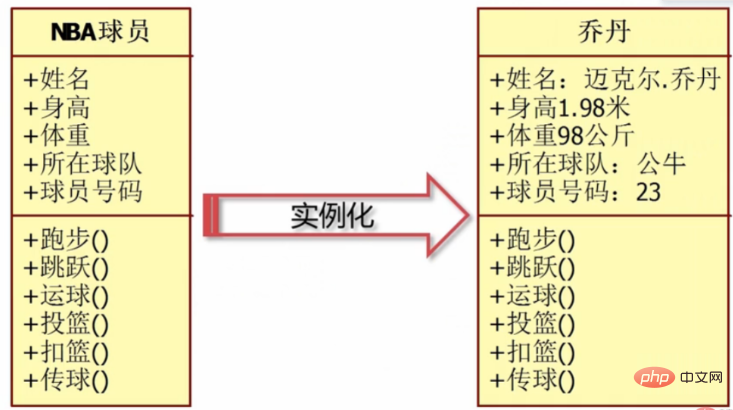
The left side is a class with no data, and the right side is Jordan. So how to instantiate it is to directly add these names, height, weight, team, and players If the values of the numbers are filled in specifically, then the Jordan object will be instantiated
Tip: Instantiation can be understood as making the class into a practical example
3. Specific cases
1) Case study objectives
1. How to define a class
2. How to instantiate a class
3. How to call a class Properties and methods
2) See the following code for details
<?php
/***
* 案例目标:
* 1.类的定义
* 2.类的实例化
* 3.属性的赋值
* 4.方法的调用
*
*/
/***定义一个类,类的名字叫NbaPlayer(中文=NBA球员)
* 提示:
* 1.定义类的过程:我们首先以class开始,然后写上类 名称:NbaPlayer,最后要写上一对{}
* 2.类的名字通常首字母要大写
* 3
*
***/
class NbaPlayer{
//定义属性
public $name = "";
public $height = "";
public $weight = "";
public $team = "";
public $playerName = "";
//定义方法
//定义跑的方法
//提示:
//方法定义的过程:
//1.写上方法的类型,public,表示公共的方法,可以被外部直接调用
//2.写上function
//3.定义方法的名称,然后写上一对(),最后{}结尾
//总结:
//方法定义和之前js中函数的定义是一样的,只是类中的方法多了一个public
public function run(){
//里面的代码我们称之为业务逻辑
echo "跑步<br/>";
}
//定义跳跃方法
public function jump(){
echo "跳跃<br/>";
}
//定义运球方法
public function dribble(){
echo "运球<br/>";
}
//定义投篮的方法
public function shoot(){
echo "投篮<br/>";
}
//定义扣篮方法
public function dunk(){
echo "扣篮<br/>";
}
//定义传球
public function pass(){
echo "传球<br/>";
}
}
//类到对象的实例化
/*总结:
1、类的实例化过程= 通过new 类名() 即可完成一个类的实例化过程
*/
//1.创建乔丹
$jordan = new NbaPlayer();//类的实例化
//类赋值
$jordan->name = "乔丹";
$jordan->height = "1.98米";
$jordan->weight = "98公斤";
$jordan->team = "公牛";
$jordan->playerName = "23";
//输出对象值
print_r("乔丹名称:".$jordan->name."<br/>");
print_r("乔丹身高:".$jordan->height."<br/>");
//总结:通过->可以调用对象里的属性
echo "<br/>";
//输出对象方法
$jordan->dribble();
$jordan->pass();
//总结:通过->符号可以调用对象的方法
?>The above is the detailed content of Object-oriented practice in PHP - basic practice cases. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to implement object-oriented event-driven programming using Go language
Jul 20, 2023 pm 10:36 PM
How to implement object-oriented event-driven programming using Go language
Jul 20, 2023 pm 10:36 PM
How to use Go language to implement object-oriented event-driven programming Introduction: The object-oriented programming paradigm is widely used in software development, and event-driven programming is a common programming model that realizes the program flow through the triggering and processing of events. control. This article will introduce how to implement object-oriented event-driven programming using Go language and provide code examples. 1. The concept of event-driven programming Event-driven programming is a programming model based on events and messages, which transfers the flow control of the program to the triggering and processing of events. in event driven
 What is the importance of @JsonIdentityInfo annotation using Jackson in Java?
Sep 23, 2023 am 09:37 AM
What is the importance of @JsonIdentityInfo annotation using Jackson in Java?
Sep 23, 2023 am 09:37 AM
The @JsonIdentityInfo annotation is used when an object has a parent-child relationship in the Jackson library. The @JsonIdentityInfo annotation is used to indicate object identity during serialization and deserialization. ObjectIdGenerators.PropertyGenerator is an abstract placeholder class used to represent situations where the object identifier to be used comes from a POJO property. Syntax@Target(value={ANNOTATION_TYPE,TYPE,FIELD,METHOD,PARAMETER})@Retention(value=RUNTIME)public
 Explore object-oriented programming in Go
Apr 04, 2024 am 10:39 AM
Explore object-oriented programming in Go
Apr 04, 2024 am 10:39 AM
Go language supports object-oriented programming through type definition and method association. It does not support traditional inheritance, but is implemented through composition. Interfaces provide consistency between types and allow abstract methods to be defined. Practical cases show how to use OOP to manage customer information, including creating, obtaining, updating and deleting customer operations.
 Analyzing the Flyweight Pattern in PHP Object-Oriented Programming
Aug 14, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
Analyzing the Flyweight Pattern in PHP Object-Oriented Programming
Aug 14, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
Analyzing the Flyweight Pattern in PHP Object-Oriented Programming In object-oriented programming, design pattern is a commonly used software design method, which can improve the readability, maintainability and scalability of the code. Flyweight pattern is one of the design patterns that reduces memory overhead by sharing objects. This article will explore how to use flyweight mode in PHP to improve program performance. What is flyweight mode? Flyweight pattern is a structural design pattern whose purpose is to share the same object between different objects.
 Analysis of object-oriented features of Go language
Apr 04, 2024 am 11:18 AM
Analysis of object-oriented features of Go language
Apr 04, 2024 am 11:18 AM
The Go language supports object-oriented programming, defining objects through structs, defining methods using pointer receivers, and implementing polymorphism through interfaces. The object-oriented features provide code reuse, maintainability and encapsulation in the Go language, but there are also limitations such as the lack of traditional concepts of classes and inheritance and method signature casts.
 PHP Advanced Features: Best Practices in Object-Oriented Programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
PHP Advanced Features: Best Practices in Object-Oriented Programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
OOP best practices in PHP include naming conventions, interfaces and abstract classes, inheritance and polymorphism, and dependency injection. Practical cases include: using warehouse mode to manage data and using strategy mode to implement sorting.
 Are there any class-like object-oriented features in Golang?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
Are there any class-like object-oriented features in Golang?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
There is no concept of a class in the traditional sense in Golang (Go language), but it provides a data type called a structure, through which object-oriented features similar to classes can be achieved. In this article, we'll explain how to use structures to implement object-oriented features and provide concrete code examples. Definition and use of structures First, let's take a look at the definition and use of structures. In Golang, structures can be defined through the type keyword and then used where needed. Structures can contain attributes
 In-depth understanding of PHP object-oriented programming: Debugging techniques for object-oriented programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
In-depth understanding of PHP object-oriented programming: Debugging techniques for object-oriented programming
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:50 PM
By mastering tracking object status, setting breakpoints, tracking exceptions and utilizing the xdebug extension, you can effectively debug PHP object-oriented programming code. 1. Track object status: Use var_dump() and print_r() to view object attributes and method values. 2. Set a breakpoint: Set a breakpoint in the development environment, and the debugger will pause when execution reaches the breakpoint, making it easier to check the object status. 3. Trace exceptions: Use try-catch blocks and getTraceAsString() to get the stack trace and message when the exception occurs. 4. Use the debugger: The xdebug_var_dump() function can inspect the contents of variables during code execution.




