How to set up LRU algorithm in redis
1. Set Redis to use the LRU algorithm
LRU (Least Recently Used) least recently used algorithm is one of many replacement algorithms. A sort of.
There is a maxmemory concept in Redis, mainly to limit the memory used to a fixed size. The LRU algorithm used by Redis is an approximate LRU algorithm.
(1) Set maxmemory
As mentioned above, maxmemory is to limit the maximum memory usage of Redis. There are several ways to set its size. One method is to set it through CONFIG SET, as follows:
127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET maxmemory 1) "maxmemory" 2) "0" 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG SET maxmemory 100MB OK 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET maxmemory 1) "maxmemory" 2) "104857600"
The other method is to modify the configuration file redis.conf:
maxmemory 100mb
Note that under 64bit systems, maxmemory is set to 0 Indicates that Redis memory usage is not limited. Under 32bit systems, maxmemory implicitly cannot exceed 3GB.
When Redis memory usage reaches the specified limit, you need to choose a replacement strategy.
(2) Replacement policy
When Redis memory usage reaches maxmemory, you need to select the set maxmemory-policy to replace the old data.
The following are the replacement strategies that can be selected:
noeviction: No replacement, which means that even if the memory reaches the upper limit, no replacement will be performed. All commands that can cause memory increase will return error
allkeys-lru: Prioritize deleting the keys that are least frequently used recently to save new data
volatile-lru: Only set the Select the least frequently used key among the expired keys to delete to save new data
allkeys-random: Randomly select some keys from all-keys. Delete to save new data
volatile-random: Only select some keys from the expired set keys to delete to save new data
volatile-ttl: Only select the key with the shortest survival time (TTL) from the expired set key to delete it to save new data
It should be noted that:
(1) The method of setting maxmemory-policy is similar to the method of setting maxmemory, which can be modified dynamically through redis.conf or CONFIG SET.
(2) If there is no matching key that can be deleted, then the volatile-lru, volatile-random and volatile-ttl strategies are the same as the noeviction replacement strategy - no keys will be replaced.
(3) It is very important to choose the appropriate replacement strategy, which mainly depends on the access mode of your application. Of course, you can also dynamically modify the replacement strategy and output it by using the Redis command - INFO The cache hit rate can then be used to tune the replacement strategy.
Generally speaking, there are some common experiences:
If all keys are most frequently used recently, then you need to select allkeys-lru to replace the most recent ones. The least frequently used key. If you are not sure which strategy to use, it is recommended to use allkeys-lru.
If the access probabilities of all keys are similar, you can use the allkeys-random strategy to replace the data.
If you have enough understanding of the data and can specify a hint for the key (specified through expire/ttl), you can choose volatile-ttl for replacement.
volatile-lru and volatile-random are often used when one Redis instance is used for both caching and persistence. However, it is better to use two Redis instances to solve the problem. this problem.
Setting the expiration time expire will occupy some memory, but with allkeys-lru there is no need to set the expiration time, thus making more effective use of memory.
(3) How the replacement strategy works
It is very important to understand how the replacement strategy is executed, such as:
The client executes a new command, causing the database to need to add data (such as set key value)
Redis will check the memory usage. If the memory usage exceeds maxmemory, it will be deleted according to the replacement strategy. Some keys
The new command is successfully executed
Our continuous writing of data will cause the memory to reach or exceed the upper limit maxmemory, but the replacement strategy will Memory usage drops below the upper limit.
If a lot of memory needs to be used at one time (such as writing a large set at once), then the memory usage of Redis may exceed the maximum memory limit for a period of time.
(4) Approximate LRU algorithm
LRU in Redis is not a strict LRU algorithm implementation, but an approximate LRU implementation, mainly to save memory occupy and improve performance. Redis has such a configuration - maxmemory-samples. Redis's LRU is to take out the configured number of keys, and then select the least frequently used key among them for replacement. The default is 5, as follows:
maxmemory-samples 5
Yes Gain advantages in speed or accuracy of the LRU replacement algorithm by adjusting the number of samples.
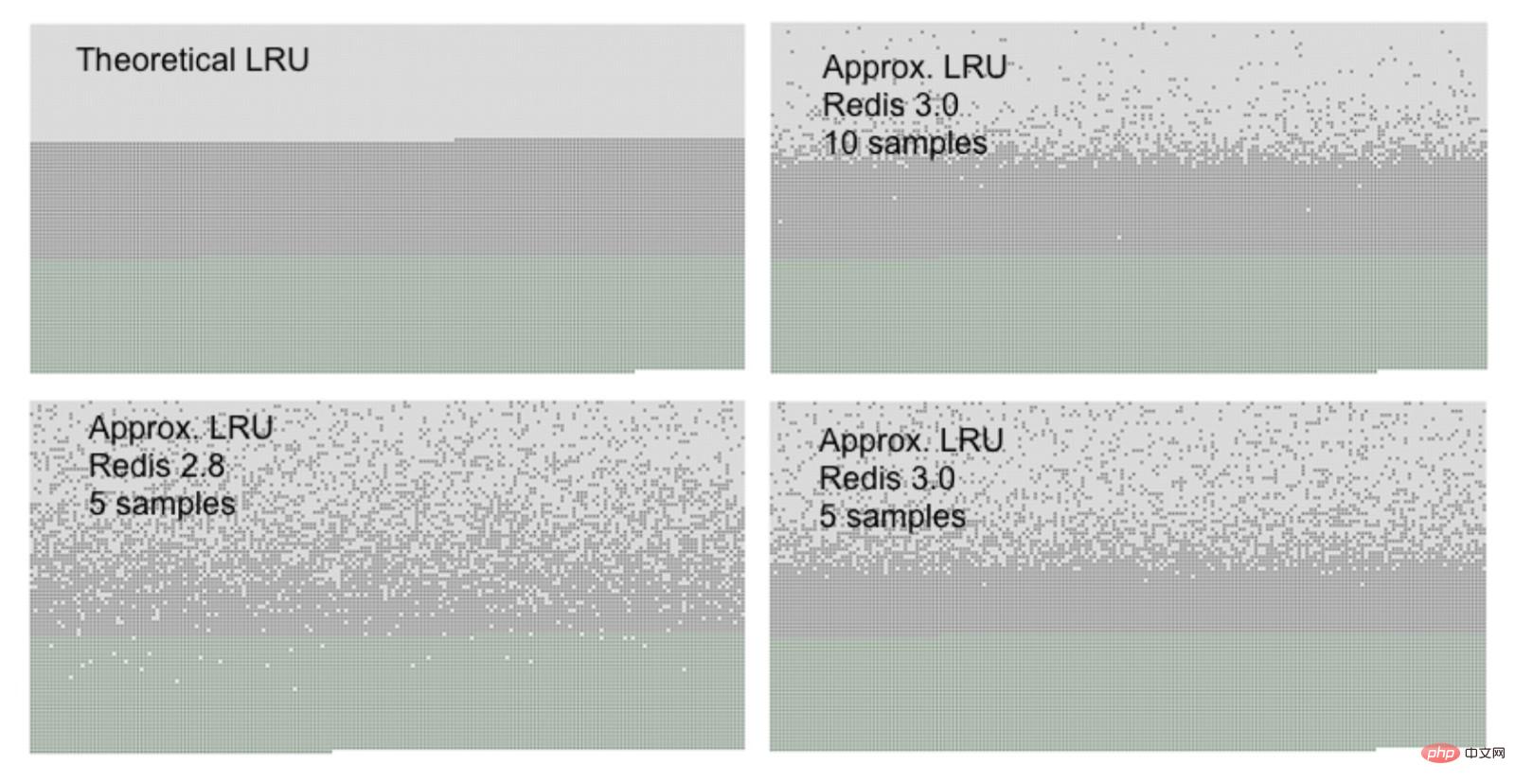
The reason why Redis does not use the real LRU implementation is to save memory usage. Although not a true LRU implementation, they are almost equivalent in application. The following figure is a comparison between the approximate LRU implementation of Redis and the theoretical LRU implementation:

测试开始首先在Redis中导入一定数目的key,然后从第一个key依次访问到最后一个key,因此根据LRU算法第一个被访问的key应该最新被置换,之后再增加50%数目的key,导致50%的老的key被替换出去。
在上图中你可以看到三种类型的点,组成三种不同的区域:
淡灰色的是被置换出去的key
灰色的是没有被置换出去的key
绿色的是新增加的key
理论LRU实现就像我们期待的那样,最旧的50%数目的key被置换出去,Redis的LRU将一定比例的旧key置换出去。
可以看到在样本数为5的情况下,Redis3.0要比Redis2.8做的好很多,Redis2.8中有很多应该被置换出去的数据没有置换出去。在样本数为10的情况下,Redis3.0很接近真正的LRU实现。
LRU是一个预测未来我们会访问哪些数据的模型,如果我们访问数据的形式接近我们预想——幂律,那么近似LRU算法实现将能处理的很好。
在模拟测试中我们可以发现,在幂律访问模式下,理论LRU和Redis近似LRU的差距很小或者就不存在差距。
如果你将maxmemory-samples设置为10,那么Redis将会增加额外的CPU开销以保证接近真正的LRU性能,可以通过检查命中率来查看有什么不同。
通过CONFIG SET maxmemory-samples
2、LRU的实现
<?php
/**
* LRU是最近最少使用页面置换算法(Least Recently Used),也就是首先淘汰最长时间未被使用的页面
*/
class LRU_Cache
{
private $array_lru = array();
private $max_size = 0;
function __construct($size)
{
// 缓存最大存储
$this->max_size = $size;
}
public function set_value($key, $value)
{
// 如果存在,则向队尾移动,先删除,后追加
// array_key_exists() 函数检查某个数组中是否存在指定的键名,如果键名存在则返回true,如果键名不存在则返回false。
if (array_key_exists($key, $this->array_lru)) {
// unset() 销毁指定的变量。
unset($this->array_lru[$key]);
}
// 长度检查,超长则删除首元素
if (count($this->array_lru) > $this->max_size) {
// array_shift() 函数删除数组中第一个元素,并返回被删除元素的值。
array_shift($this->array_lru);
}
// 队尾追加元素
$this->array_lru[$key] = $value;
}
public function get_value($key)
{
$ret_value = false;
if (array_key_exists($key, $this->array_lru)) {
$ret_value = $this->array_lru[$key];
// 移动到队尾
unset($this->array_lru[$key]);
$this->array_lru[$key] = $ret_value;
}
return $ret_value;
}
public function vardump_cache()
{
echo "<br>";
var_dump($this->array_lru);
}
}
$cache = new LRU_Cache(5); // 指定了最大空间 6
$cache->set_value("01", "01");
$cache->set_value("02", "02");
$cache->set_value("03", "03");
$cache->set_value("04", "04");
$cache->set_value("05", "05");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";
$cache->set_value("06", "06");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";
$cache->set_value("03", "03");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";
$cache->set_value("07", "07");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";
$cache->set_value("01", "01");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";
$cache->get_value("04");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";
$cache->get_value("05");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";
$cache->get_value("10");
$cache->vardump_cache();
echo "<br>";更多redis知识请关注redis入门教程栏目。
The above is the detailed content of How to set up LRU algorithm in redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




