 Database
Database
 Redis
Redis
 One article to understand the five major data types and application scenarios of Redis
One article to understand the five major data types and application scenarios of Redis
One article to understand the five major data types and application scenarios of Redis
1.string type
Add/modify data: set key value
Get data: get key
Delete data: del key
Add/modify multiple data: mset key value key1 value1
mget key key1
append key value
1-2 String type increase and decrease operations
Set the value to increase the value in the specified range: incr key defaults to increment by 1 each time | incrby key value each time a new value is added
Set the data to decrease the specified range: decr key | decrby key value is the same as adding new one
Application scenario
Control the primary key of the database table id, provides a primary key generation strategy for the database table to ensure the consistency of the primary key of the data table.
Set expiration time: setex key seconds value
Application scenarios
Realize time-limited voting function: for example, a WeChat vote can be cast once an hour
Realize hot information: for example, e-commerce Popular products in the industry, popular news on news websites
Weibo big V homepage For high-frequency visits, the number of fans, followers, and Weibo needs to be updated from time to time. This is high-frequency information. We can use the string type of redis to solve it. 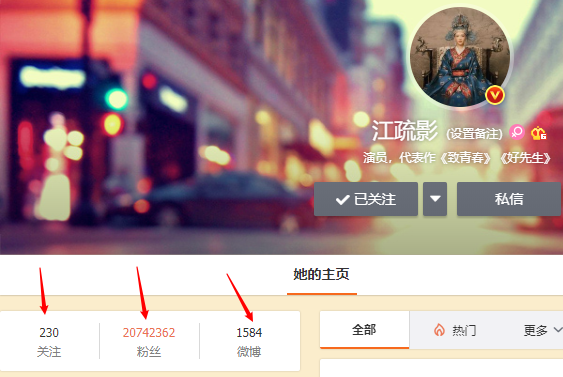
Set user information for big V in redis, using the user's primary key and attributes as key values. The following is the implementation case. 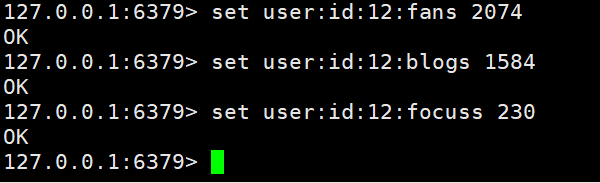
Here we need to briefly talk about the key naming rules: table name primary key primary key value field: field value. Naming according to such rules can manage our key values very well.
We can also use another way to achieve it, which is to directly follow the key with a structure, for example 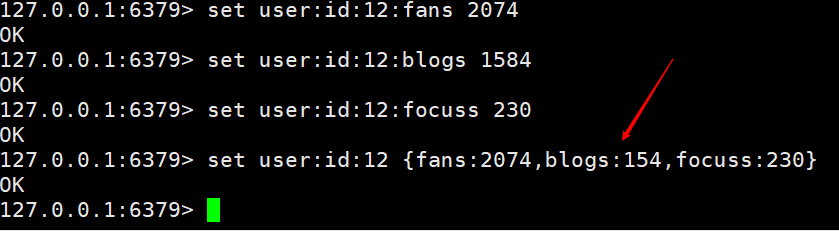
Both of the above methods can be achieved. Yes, it's just that the first one can easily manage any value, while the second one has to be changed once every time. Depending on the business scenario, it can be refreshed regularly.
Add/modify data: hset key field value
Get data: hget key field | hgetall key
Delete data: hdel key field field1
Add/modify multiple data: hmset key field value field1 value1
hmget key field field1
hlen key
hexists key field
2-2 Extended operations for hash type data
Get all the field values in the hash table: hkeys key
Get all the field values in the hash table: hvals key
Set the value of the specified field to increase the value of the specified range: hincrby key field increment | hincrbyfloat key field increment
This picture comes from the Internet and is not homemade. It just simulates the shopping cart scene.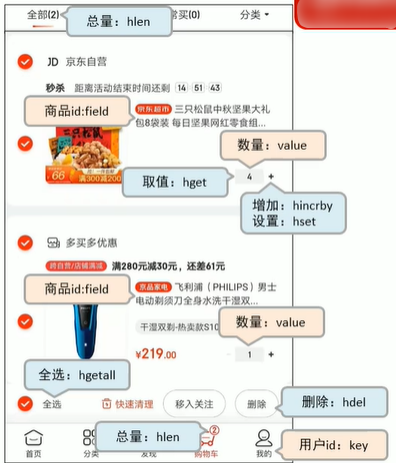
In the above picture, we can see the information in the shopping cart. Next, we use redis to process this. Shopping cart implementation.
Here is an implementation of adding a shopping cart and getting a shopping cart. The keys are named table name primary key primary key value 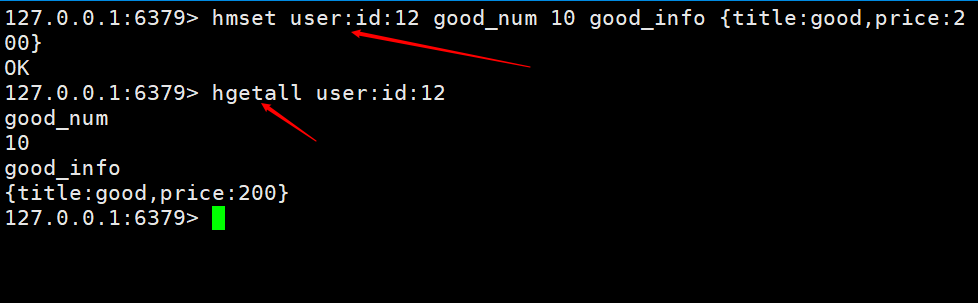
In the above picture, we will One problem is that there will be a lot of duplication in product information storage, so we also need to hash the products individually. As shown in the figure below, only the product id
is provided here. One is to set multiple fields, and the other is to store it directly as json. If the information does not change frequently, you can use json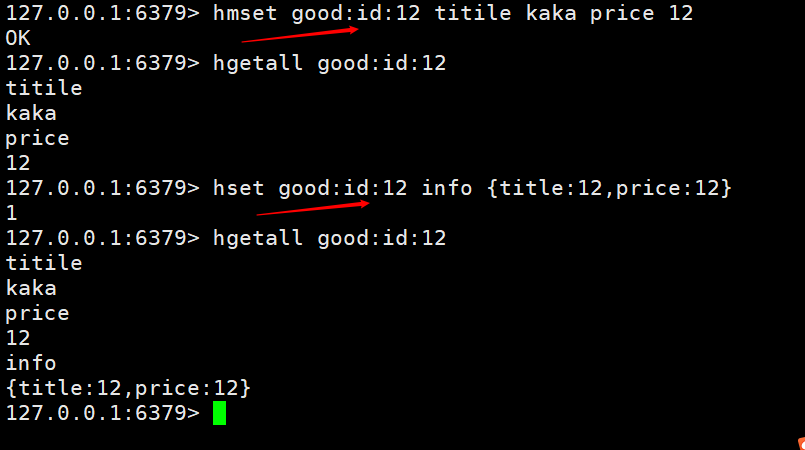
to provide you with a methodhsetnx key field value. If it exists, it will not be added, if not, it will be added. This function is used to avoid overwriting and useless operations when different users add the same product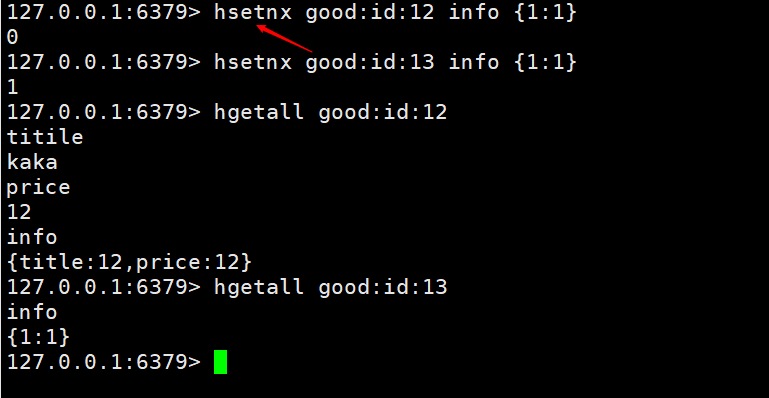
Data storage requirements: store multiple data, and distinguish the order of the storage space of the data
Required data structure: one storage space saves multiple data, and the entry sequence can be reflected through the data
list type: save multiple data, the bottom layer uses a doubly linked list storage structure to implement
Add/modify data: lpush key value value1 | rpush key value value1
Get data: lrange key start end | lindex key index | llen key
Delete data: rpop key | lpop key
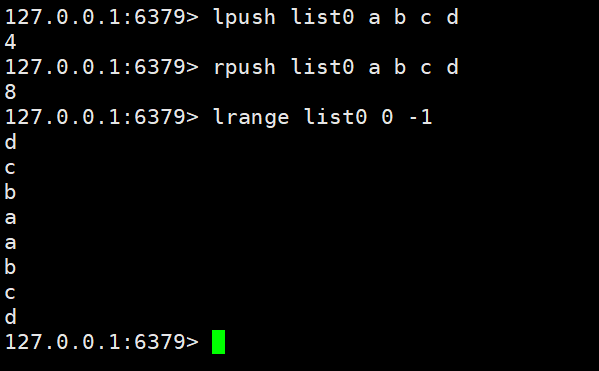
##3-2 Extended operations for list type data
Get and remove data within the specified time: blpop key1 key2 timeout | brpop key1 key2 timeout
Write a simple case for this function , easy to understand
After the terminal command on the left is executed, it will wait for 30 seconds to return the deleted data
When the add command on the right is executed The left side will directly return the deleted data
Above we know the basic operations of the list. Executing lpop key or rpop key can delete from the do or from the right, but now there is a scenario where the circle of friends likes business and then cancels the data from the middle. The case is as shown below
We first add a b c d
to list5 and then remove c
After checking, only a b d is left 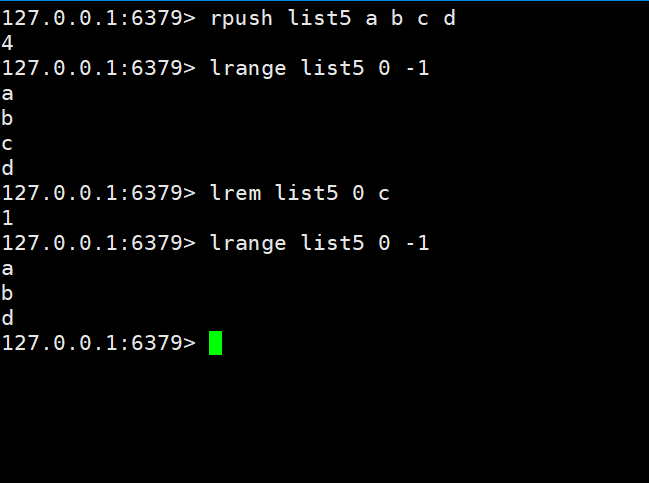
New storage requirements: store a large amount of data and provide higher efficiency for query convenience
Required storage structure: able to save a large amount of data , efficient internal storage mechanism, easy to query
set type: exactly the same as hash storage structure, only stores keys, not values (nil), and values are not allowed to be repeated
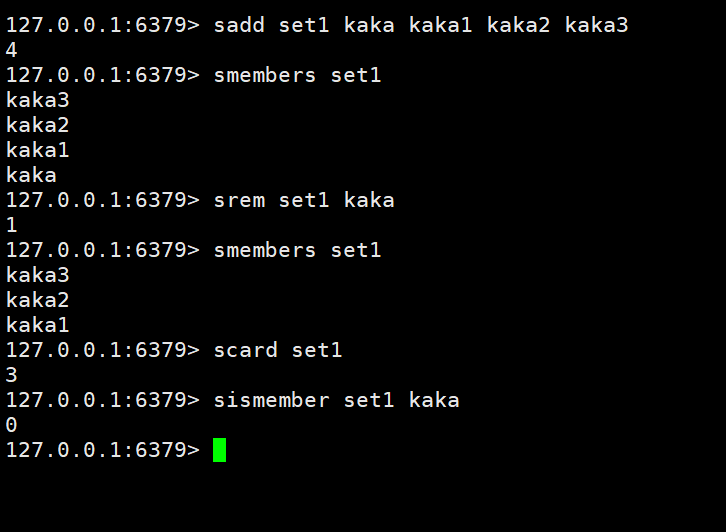
Add/modify data:sadd key member member1
Get data: smembers key
Delete data: srem key member1
Get the total amount of collection data: scard key
Judge whether the collection contains the specified data: sismember key member
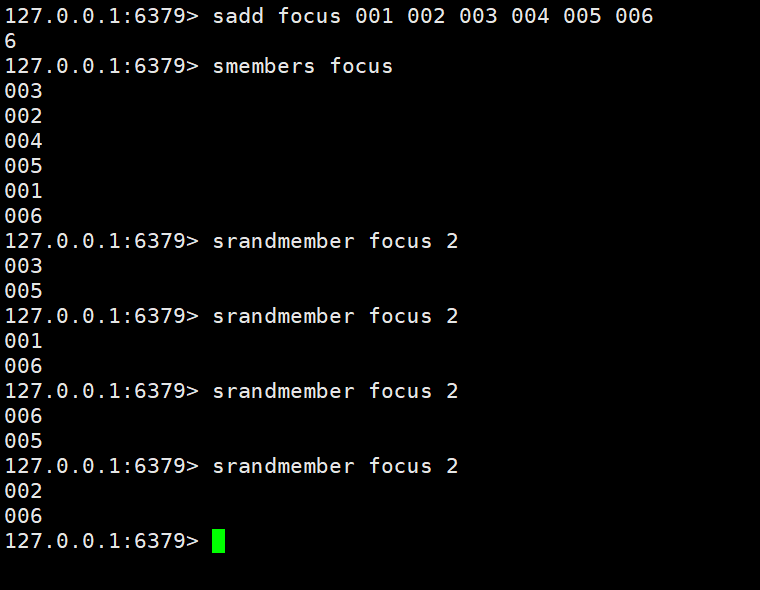
Randomly obtain the specified number of data in the set: srandmember key count
Randomly obtain a certain data in the collection and remove the new data set from the collection: spop key
Randomly push hot information, hot news, hot-selling travel, application app recommendations, follow recommendations, etc.
Since Kaka has been writing discuz recently, this case is used to achieve attention recommendation.
Case 1: Store corresponding users in the set according to a certain recommendation mechanism, and then randomly obtain 2 users who need to be recommended each time
Case 2: Store the corresponding users in the set according to a certain recommendation mechanism, and then the users recommended every day based on the date cannot be repeated

The intersection, union, and Difference set
sinter key key1 sunion key key1 sdiff key key1
The intersection, union and difference set of two sets are stored in the specified set
sinterstore destination key1 key2 sunionstore destination key1 key2 sdiffstore destination key1 key2
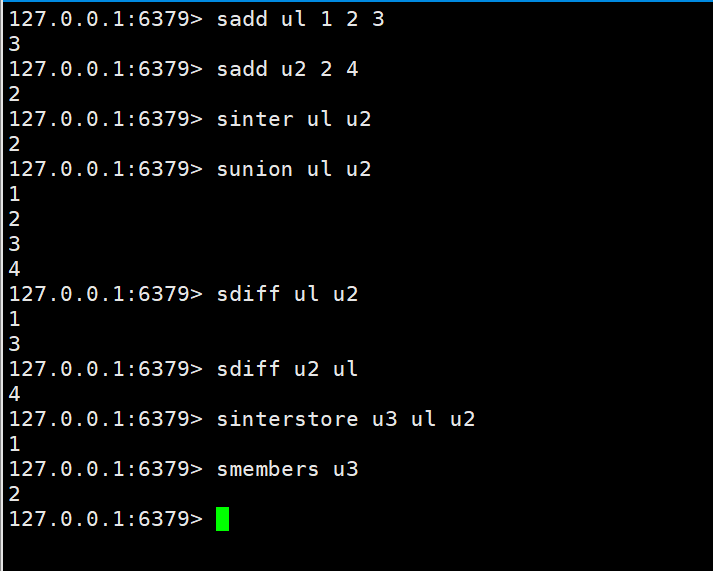
案例:我们需要挖掘一个信息的共同好友。例如微信公众号的共同关注好友数量、QQ添加新好友的推荐机制、深度挖掘用户直接的联系
就根据上述案例,我们可以使用差集来实现qq的有可能认识的好友。
PV直接使用string类型的incr统计即可
UV和IP都是独立不重复的,使用set来操作。
在上边我们知道set有一个特性就是不能重复,我们就可以根据这一点来轻松实现这个功能。然后使用scard key 来统计数量。
As for UV as an independent visitor, you can use local cookies to achieve it. In the same way, pass the cookie to redis for recording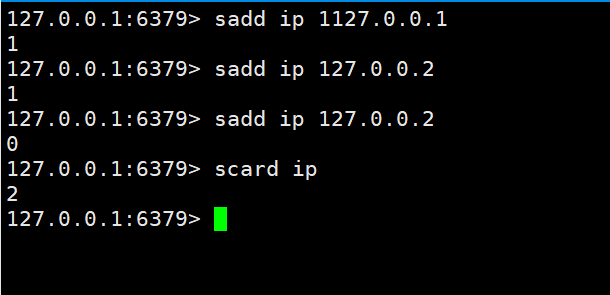
None of the previous four types supports sorting. The sorted_set type we will look at below supports both storage of big data and Sorting function
Add data:zadd key score member
Get data:zrange key start stop | zrevrange key start stop
Delete data: zrem key member
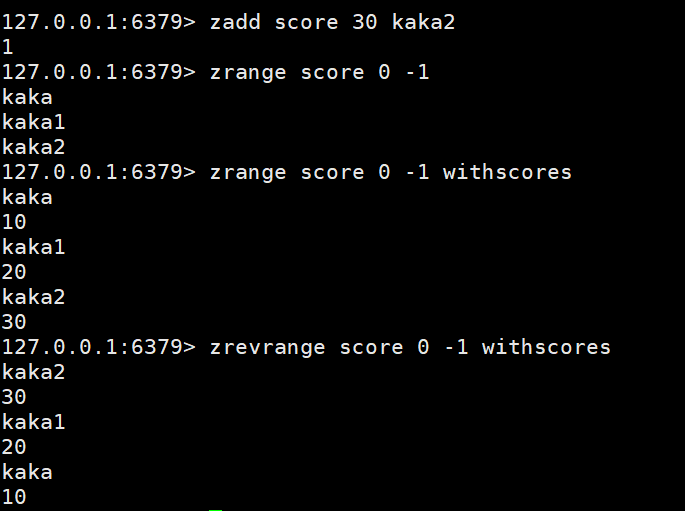
Get data based on conditions: zrangebyscore key min max limit | zrevrangescore key max min
Conditional deletion of data: zremrangebyrank key start stop | zremrangebyscore key min max
Get the total amount of collection data: zcard key | zcount key min max
Set intersection and operation: zinterstore destination numkeys key | zunionstore destination numkeys key(This command will not be demonstrated, you can check the document yourself. It is similar to set, except that it will The sums of all intersections are added up. Then there is numkeys. This parameter is the total number of keys required for calculation. How many keys are needed later)
Get the index corresponding to the data:zrank key member | zrevrank key member
socre value acquisition and modification: zscore key member | zincrby key increment member
The above is a brief introduction and specific application of the redis data type. In the following article, actual combat will be carried out based on specific needs.
The above is the detailed content of One article to understand the five major data types and application scenarios of Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Redis, as a message middleware, supports production-consumption models, can persist messages and ensure reliable delivery. Using Redis as the message middleware enables low latency, reliable and scalable messaging.



