Getting Started with Django Framework 1.0
Development tools: PyCharm community version or professional version CMD command line
The difference between the community version and the professional version is that the professional version can directly create Django projects , while the Community Edition needs to be created manually. Since we are all just getting started, it is better for us to create it manually, which will help us become familiar with Django commands and related operations.
Create a new Django minimal program
Create a new Web framework project
We use the command line interface to enter the directory where we want to create the project, and then enter the following command:
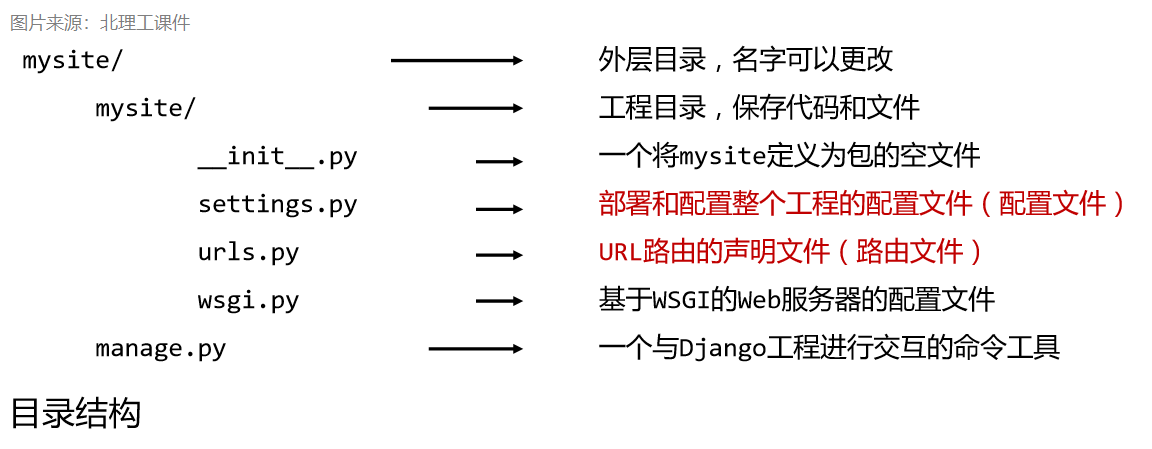
django-admin startproject mysite
The django-admin here is a tool for managing django. When we install django, dependencies will be installed by default. mysite is the project name and can be modified according to your own needs. After creation, we will get the following directory structure:
Modify the project and add Function
We need to add specific application here, and add related functions by configuring routing mapping.
What is the relationship between project and app?
The project corresponds to a website, which is a collection of configurations and applications. Applications correspond to specific functions, which are specific Function carrier Separation of configuration and function is a manifestation of high modularity
[Modify project] Create a specific application (app)
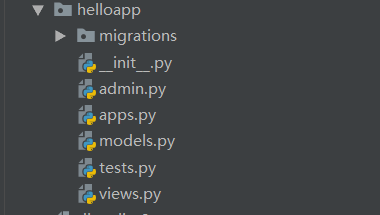
Command: python manage.py startapp helloapp
After the command execution is completed, A new directory helloapp will be created under the root directory
【Modify Project】Modify the application's
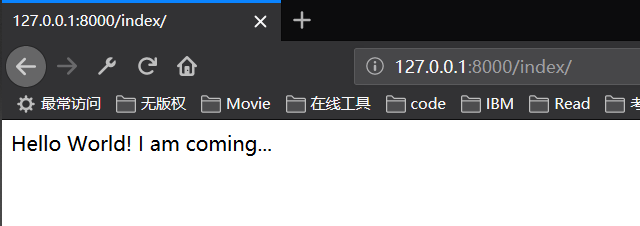
views.py<code class="hljs"><span class="hljs-comment"># Create your views here.</span><br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> django.http <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> HttpResponse<br/><br/><span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-keyword">def</span> <span class="hljs-title">hello</span><span class="hljs-params">(request)</span>:</span><br/><span class="hljs-keyword">return</span> HttpResponse(<span class="hljs-string">"Hello World! I am coming..."</span>)<br/></code>
Copy after login【Modify the project】Modify the URL routing
in conjunction with the project name The path relationship between the URL and the processing function is specified in the
urls.pyfile in the corresponding directory.<code class="hljs"><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> django.contrib <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> admin<br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> django.urls <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> include, path<br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> helloapp <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> views <span class="hljs-comment"># from the subapp import related views</span><br/><br/>urlpatterns = [ <span class="hljs-comment"># config the routes like vue's vue-router</span><br/> path(<span class="hljs-string">'admin/'</span>, admin.site.urls),<br/> path(<span class="hljs-string">'index/'</span>, views.hello),<br/>]<br/></code>
Copy after loginWe first need to introduce the views file under the corresponding app, and then configure the routing correspondence
[Modification Project] Modify URL routing
path('index/', views.hello)The first parameter here represents the url address, and what we have here will respond to
domain name/index/Access to this path; The second parameter indicates specifying a certain processing function, for example, here we have formulatedviews.hello.
Visit the page
##Run the project
python manage.py runserver
What I have to saydjango-admin andmanage.py
django-admin
##django-admindjango-admin is a global management tool for the Django framework:
- Create and manage Django projects
- Create and manage Django projects Database
- Control debugging or log information
- Run and maintain Django projects
- We can also Use the
command to view more features
manage.py
python manage.pyFunction is similar to
, but the scope only applies to the current project. We can also view more functions through the
command.
Improvement of minimal program
Requirement: Return an HTML page instead of a stringIdea: Create a template (T), respond to specific requests, and return the template pageCreate a new hello2app applicationCreate a new hello2app and access it through index2
`python manage.py startapp hello2app`
使用
templateTest.html为返回页面,修改views.py
```python
# hello2app/views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
def hello(request):
return render(request, "PYC01-HTMLJSDemo.html")
```
这里,`render()` 是一个打包函数,第一个参数是 request, 第二个参数是要返回的模板页面。在hello2app应用中,新增
urls.py文件(本地路由文件)<code class="hljs"><span class="hljs-comment"># hello2app/urls.py</span><br/><br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> django.urls <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> path<br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> . <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> views <span class="hljs-comment"># . 代表当前 app</span><br/>urlpatterns = [ <span class="hljs-comment"># urlpatterns 变量名成是固定的</span><br/> path(<span class="hljs-string">''</span>, views.hello)<br/>]<br/></code>
Copy after login在全局路由文件中增加对本应用路由文件的引用
<code class="hljs"><span class="hljs-comment"># mysite/urls.py</span><br/><br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> django.contrib <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> admin<br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> django.urls <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> include, path<br/><span class="hljs-comment"># include()函数,用于引入其他路由文件</span><br/><span class="hljs-keyword">from</span> helloapp <span class="hljs-keyword">import</span> views<br/>urlpatterns = [<br/> path(<span class="hljs-string">'index2/'</span>, include(<span class="hljs-string">'hello2app.urls'</span>)),<br/> <span class="hljs-comment"># 将hello2app的局部路由增加到全局路由中</span><br/> path(<span class="hljs-string">'index/'</span>, views.hello),<br/> path(<span class="hljs-string">'admin/'</span>, admin.site.urls),<br/>]<br/></code>
Copy after login设置模板路径,让Django框架找到模板所在目录
我们由于返回了模板文件,所以我们需要对
mysite/settings.py进行修改配置一下路径,至此,也就完成了一个最小的Django项目了!<code class="hljs">TEMPLATES = [<br/>{<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'BACKEND'</span>: <span class="hljs-string">'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates'</span>,<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'DIRS'</span>: [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, <span class="hljs-string">'hello2app/templates'</span>)], <span class="hljs-comment"># 指定templates所在路径</span><br/> <span class="hljs-string">'APP_DIRS'</span>: <span class="hljs-literal">True</span>,<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'OPTIONS'</span>: {<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'context_processors'</span>: [<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'django.template.context_processors.debug'</span>,<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'django.template.context_processors.request'</span>,<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth'</span>,<br/> <span class="hljs-string">'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages'</span>,<br/> ],<br/> },<br/> },<br/>]<br/></code>Copy after login
The above is the detailed content of Getting Started with Django Framework 1.0. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 37
37
 110
110
 How to check django version
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
How to check django version
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
Steps to check the Django version: 1. Open a terminal or command prompt window; 2. Make sure Django has been installed. If Django is not installed, you can use the package management tool to install it and enter the pip install django command; 3. After the installation is complete , you can use python -m django --version to check the Django version.
 Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django and Flask are both leaders in Python Web frameworks, and they both have their own advantages and applicable scenarios. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of these two frameworks and provide specific code examples. Development Introduction Django is a full-featured Web framework, its main purpose is to quickly develop complex Web applications. Django provides many built-in functions, such as ORM (Object Relational Mapping), forms, authentication, management backend, etc. These features allow Django to handle large
 Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django is a complete development framework that covers all aspects of the web development life cycle. Currently, this framework is one of the most popular web frameworks worldwide. If you plan to use Django to build your own web applications, then you need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of the Django framework. Here's everything you need to know, including specific code examples. Django advantages: 1. Rapid development-Djang can quickly develop web applications. It provides a rich library and internal
 What is the difference between django versions?
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
What is the difference between django versions?
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
The differences are: 1. Django 1.x series: This is an early version of Django, including versions 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8 and 1.9. These versions mainly provide basic web development functions; 2. Django 2.x series: This is the mid-term version of Django, including 2.0, 2.1, 2.2 and other versions; 3. Django 3.x series: This is the latest version series of Django. Including versions 3.0, 3, etc.
 How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations, specific code examples required Introduction: Django is a powerful Python Web framework that is continuously updated and upgraded to provide better performance and more features. However, for developers using older versions of Django, upgrading Django may face some challenges. This article will introduce the steps and precautions on how to upgrade the Django version, and provide specific code examples. 1. Back up project files before upgrading Djan
 How to check django version
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
How to check django version
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
How to check the django version: 1. To check through the command line, enter the "python -m django --version" command in the terminal or command line window; 2. To check in the Python interactive environment, enter "import django print(django. get_version())" code; 3. Check the settings file of the Django project and find a list named INSTALLED_APPS, which contains installed application information.
 Is django front-end or back-end?
Nov 21, 2023 pm 02:36 PM
Is django front-end or back-end?
Nov 21, 2023 pm 02:36 PM
django is the backend. Details: Although Django is primarily a backend framework, it is closely related to front-end development. Through features such as Django's template engine, static file management, and RESTful API, front-end developers can collaborate with back-end developers to build powerful, scalable web applications.
 Django, Flask, and FastAPI: Which framework is right for beginners?
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:06 PM
Django, Flask, and FastAPI: Which framework is right for beginners?
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:06 PM
Django, Flask, and FastAPI: Which framework is right for beginners? Introduction: In the field of web application development, there are many excellent Python frameworks to choose from. This article will focus on the three most popular frameworks, Django, Flask and FastAPI. We will evaluate their features and discuss which framework is best for beginners to use. At the same time, we will also provide some specific code examples to help beginners better understand these frameworks. 1. Django: Django