 Database
Database
 Redis
Redis
 Detailed explanation of why Redis is single-threaded, highly concurrency and fast
Detailed explanation of why Redis is single-threaded, highly concurrency and fast
Detailed explanation of why Redis is single-threaded, highly concurrency and fast

The reasons for high concurrency and speed of Redis
1.redis is based on memory, and the memory read and write speed is very fast;
2.redis It is single-threaded, which saves a lot of time in context switching threads;
3.redis uses multiplexing technology and can handle concurrent connections. The internal implementation of non-blocking IO uses epoll, using a simple event framework implemented by epoll itself. Read, write, close, and connect in epoll are all converted into events, and then use the multiplexing feature of epoll to never waste any time on io.
The following focuses on the reasons why single-threaded design and IO multiplexing core design are fast.
Why Redis is single-threaded
1. Official answer
Because Redis is a memory-based operation , CPU is not the bottleneck of Redis. The bottleneck of Redis is most likely the size of machine memory or network bandwidth. Since single-threading is easy to implement and the CPU will not become a bottleneck, it is logical to adopt a single-threaded solution.
2. Performance indicators
Regarding the performance of redis, the official website also has it. An ordinary notebook can easily handle hundreds of thousands of requests per second.
3. Detailed reasons
1) There is no need for the performance consumption of various locks
The data structure of Redis is not all simple Key-Value , as well as complex structures such as list and hash. These structures may perform very fine-grained operations, such as adding an element after a long list, adding or deleting an object from the hash. These operations may require adding a lot of locks, resulting in a greatly increased synchronization overhead.
In short, in the case of a single thread, there is no need to consider various lock issues. There is no locking and releasing lock operations, and there is no performance consumption caused by possible deadlocks.
2) Single-threaded multi-process cluster solution
The power of single-thread is actually very powerful, and the efficiency of each core is also very high. Multi-threading can naturally have a higher performance limit than single-threading. , but in today's computing environment, even the upper limit of single-machine multi-threading often cannot meet the needs. What needs to be further explored is multi-server clustering solutions, in which multi-threading technology is still not available.
So single-threaded, multi-process cluster is a fashionable solution.
3) CPU consumption
Uses a single thread to avoid unnecessary context switching and competition conditions, and there is no CPU consumption due to switching caused by multi-process or multi-thread.
But what if the CPU becomes the bottleneck of Redis, or you don’t want other CPU cores of the server to be idle?
You can consider starting several more Redis processes. Redis is a key-value database, not a relational database, and there are no constraints between data. As long as the client distinguishes which keys are placed in which Redis process, it will be fine.
Advantages and disadvantages of Redis single thread
1. Advantages of single process and single thread
The code is clearer and the processing logic is simpler. There is no need to consider various lock issues, they do not exist There is no performance consumption due to possible deadlocks in locking and releasing lock operations. There is no CPU consumption due to switching caused by multiple processes or multi-threads
2. The disadvantages of single process and single thread
Unable to Give full play to multi-core CPU performance, but it can be improved by opening multiple Redis instances on a single machine;
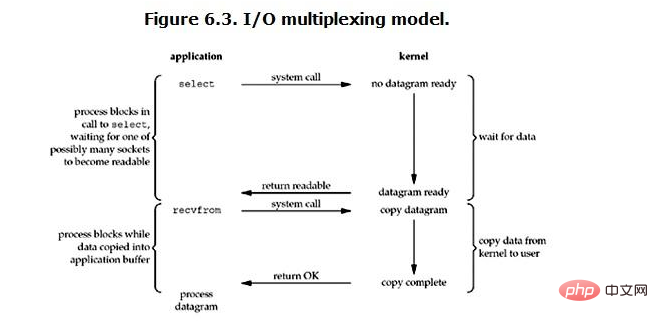
IO multiplexing technology
redis uses network IO multiplexing technology to ensure that multiple connections time, high throughput of the system.
Multi-channel - refers to multiple socket connections, and multiplexing - refers to reusing one thread. There are three main multiplexing technologies: select, poll, and epoll. epoll is the latest and best multiplexing technology available.
Here "multiple" refers to multiple network connections, and "reuse" refers to reusing the same thread. The use of multi-channel
I/O multiplexing technology allows a single thread to efficiently handle multiple connection requests (minimizing the time consumption of network IO), and Redis operates data in memory very quickly (in-memory The operation will not become the performance bottleneck here). The above two points mainly contribute to the high throughput of Redis.
 1. Redis is a pure memory database, generally They are all simple access operations. The thread takes up a lot of time. The time spent is mainly concentrated on IO, so the reading speed is fast.
1. Redis is a pure memory database, generally They are all simple access operations. The thread takes up a lot of time. The time spent is mainly concentrated on IO, so the reading speed is fast.
2. Let’s talk about IO again. Redis uses non-blocking IO and IO multiplexing. It uses a single thread to poll the descriptor and converts the opening, closing, reading and writing of the database into events. , reducing context switching and competition when switching threads.
3. Redis adopts a single-threaded model, which ensures the atomicity of each operation and reduces thread context switching and competition.
4. In addition, the data structure also helps a lot. Redis uses hash structure throughout the process, which has fast reading speed. There are also some special data structures that optimize data storage, such as compressed tables and short data. Compressed storage, another example, skip tables, uses ordered data structures to speed up reading.
5. Another point is that Redis uses its own event separator, which is relatively efficient. It uses a non-blocking execution method internally and has a relatively large throughput capacity.
Related references:Redis Tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of why Redis is single-threaded, highly concurrency and fast. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.



