JS regular expression character matching
Regular expression character matching
These are some notes compiled after reading "JavaScript Regular Expressions Mini Book".
Regular expression is a matching pattern, which can match characters and positions.
The following mainly introduces the situation of matching characters. I am also learning the situation of matching positions.
Two types of fuzzy matching:
1. Horizontal fuzzy matching: The length of a regular matchable string is not fixed. The way this is done is by using quantifiers. For example, {m,n} means that the character appears continuously at least m times and at most n times.
For example, /ab{2,5}c/ means matching a string like this: the first character is "a", followed by 2 to 5 characters "b", and finally the character "c" .
For example: (You can try it manually and think about the results you will get)
var regex = /ab{2,5}c/g;
var string = "abc abbc abbbc abbbbc abbbbbc abbbbbbc";
console.log( string.match(regex) );g is a modifier, which means global matching, that is, finding matching conditions in string in order all strings.
2. Vertical fuzzy matching: A regular matchable string is specific to a certain character. It does not need to be a certain character, and it can have many possibilities. The way it is implemented is to use the character group
such as /a[123]b/ to match such a string: the first character is a, and the second character can be '1', '2', ' Any one of 3', but only one.
Quantifier (repetition)
1. Common abbreviation form:
(1) {m,} means at least m times
(2) {m} means
appears m times (3)? Equivalent to {0,1} means
appears or does not appear (4) Equivalent to {1,} means at least 1 appears Times
(5)* is equivalent to {0,} which means it can appear any number of times, it can not appear or it can be several times
2. Greedy matching and lazy matching
(1) Greedy matching: /\d{2,5}/ means that the number appears 2-5 times in a row and will match as many as possible
var regex = /\d{2,5}/g;
var string = "123 1234 12345 123456";
console.log( string.match(regex) );
// => ["123", "1234", "12345", "12345"](2) Lazy matching: /\d{2,5} ?/ means that although 2-5 times are enough, when 2 is enough, no more attempts will be made.
var regex = /\d{2,5}?/g;
var string = "123 1234 12345 123456";
console.log( string.match(regex) );
// => ["12", "12", "34", "12", "34", "12", "34", "56"]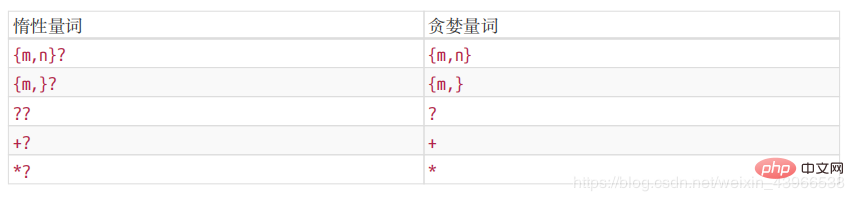
Character group
1. Range representation:
(1) Use the hyphen "-" to omit the abbreviation, such as [ 123456abcdefGHIJKLM] can be written as [1-6a-fG-M].
(2) Note: If there is a hyphen in the matched string, either put it at the beginning or end, or escape -.
2. Exclude character groups: For example, [^abc] means that a certain character can be anything, but it cannot be a, b, or c. The ^ caret represents negation, and there is also a corresponding range representation.
3. Common abbreviation form:
(1) \d means [0-9]. It is a single digit
(2) \D means [\^0-9]. Any character except numbers.
(3) \w means [0-9a-zA-Z_]. Numbers, uppercase and lowercase letters, and underscores. Also called the word character
(4) \W means [^0-9a-zA-Z_]. Non-word characters
(5) \s represents [ \t\v\n\r\f]. Represents whitespace characters, including spaces, horizontal tabs, vertical tabs, line feeds, carriage returns, and form feeds.
(6) \S means [^ \t\v\n\r\f]. Non-whitespace characters
(7) . means [^\n\r\u2028\u2029]. Wildcard character, representing almost any character. Exceptions include line feeds, carriage returns, line separators, and paragraph separators.
To match any character, use [\d\D], [\w\W], and [ Any one of ^].
Multi-selection branch
A mode can achieve horizontal and vertical fuzzy matching, and the multi-selection branch can support any one of multiple sub-modes.
Specific form: (p1|p2|p3) p1, p2, p3 are sub-patterns.
Please pay attention to the following issue.
var regex = /good|goodbye/g; var string = "goodbye"; console.log( string.match(regex) );
The result obtained in the above example is "good"
var regex = /goodbye|good/g; var string = "goodbye"; console.log( string.match(regex) );
The result obtained in this example is "goodbye"
We get the conclusion: the branch structure is also Lazy, that is, when the previous match is matched, the subsequent ones will not be tried again.
Recommended tutorial: "JS Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of JS regular expression character matching. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Face detection and recognition technology is already a relatively mature and widely used technology. Currently, the most widely used Internet application language is JS. Implementing face detection and recognition on the Web front-end has advantages and disadvantages compared to back-end face recognition. Advantages include reducing network interaction and real-time recognition, which greatly shortens user waiting time and improves user experience; disadvantages include: being limited by model size, the accuracy is also limited. How to use js to implement face detection on the web? In order to implement face recognition on the Web, you need to be familiar with related programming languages and technologies, such as JavaScript, HTML, CSS, WebRTC, etc. At the same time, you also need to master relevant computer vision and artificial intelligence technologies. It is worth noting that due to the design of the Web side
 PHP regular expression validation: number format detection
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:45 AM
PHP regular expression validation: number format detection
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:45 AM
PHP regular expression verification: Number format detection When writing PHP programs, it is often necessary to verify the data entered by the user. One of the common verifications is to check whether the data conforms to the specified number format. In PHP, you can use regular expressions to achieve this kind of validation. This article will introduce how to use PHP regular expressions to verify number formats and provide specific code examples. First, let’s look at common number format validation requirements: Integers: only contain numbers 0-9, can start with a plus or minus sign, and do not contain decimal points. floating point
 How to validate email address in Golang using regular expression?
May 31, 2024 pm 01:04 PM
How to validate email address in Golang using regular expression?
May 31, 2024 pm 01:04 PM
To validate email addresses in Golang using regular expressions, follow these steps: Use regexp.MustCompile to create a regular expression pattern that matches valid email address formats. Use the MatchString function to check whether a string matches a pattern. This pattern covers most valid email address formats, including: Local usernames can contain letters, numbers, and special characters: !.#$%&'*+/=?^_{|}~-`Domain names must contain at least One letter, followed by letters, numbers, or hyphens. The top-level domain (TLD) cannot be longer than 63 characters.
 How to match timestamps using regular expressions in Go?
Jun 02, 2024 am 09:00 AM
How to match timestamps using regular expressions in Go?
Jun 02, 2024 am 09:00 AM
In Go, you can use regular expressions to match timestamps: compile a regular expression string, such as the one used to match ISO8601 timestamps: ^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}(\.\d+)?(Z|[+-][0-9]{2}:[0-9]{2})$ . Use the regexp.MatchString function to check if a string matches a regular expression.
 PHP regular expressions: exact matching and exclusion of fuzzy inclusions
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
PHP regular expressions: exact matching and exclusion of fuzzy inclusions
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
PHP Regular Expressions: Exact Matching and Exclusion Fuzzy inclusion regular expressions are a powerful text matching tool that can help programmers perform efficient search, replacement and filtering when processing text. In PHP, regular expressions are also widely used in string processing and data matching. This article will focus on how to perform exact matching and exclude fuzzy inclusion operations in PHP, and will illustrate it with specific code examples. Exact match Exact match means matching only strings that meet the exact condition, not any variations or extra words.
 The relationship between js and vue
Mar 11, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
The relationship between js and vue
Mar 11, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
The relationship between js and vue: 1. JS as the cornerstone of Web development; 2. The rise of Vue.js as a front-end framework; 3. The complementary relationship between JS and Vue; 4. The practical application of JS and Vue.
 How to verify password using regular expression in Go?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:31 PM
How to verify password using regular expression in Go?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:31 PM
The method of using regular expressions to verify passwords in Go is as follows: Define a regular expression pattern that meets the minimum password requirements: at least 8 characters, including lowercase letters, uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Compile regular expression patterns using the MustCompile function from the regexp package. Use the MatchString method to test whether the input string matches a regular expression pattern.
 Chinese character filtering: PHP regular expression practice
Mar 24, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Chinese character filtering: PHP regular expression practice
Mar 24, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
PHP is a widely used programming language, especially popular in the field of web development. In the process of web development, we often encounter the need to filter and verify text input by users, among which character filtering is a very important operation. This article will introduce how to use regular expressions in PHP to implement Chinese character filtering, and give specific code examples. First of all, we need to clarify that the Unicode range of Chinese characters is from u4e00 to u9fa5, that is, all Chinese characters are in this range.




