Share several practical SQL statements in MySQL

When writing SQL, you often use some SQL statement writing skills to greatly simplify program logic. Reducing the number of interactions between the program and the database is beneficial to the high availability of the database. It also makes your SQL skills stand out to your colleagues.
Practical SQL
1. Insert or replace
If we want to insert a new Record (INSERT), but if the record already exists, delete the original record first, and then insert the new record.
Scenario example: This table stores the latest transaction order information of each customer. It is required to ensure that single user data is not repeatedly entered, and the execution efficiency is the highest, with the least interaction with the database, and supports the high availability of the database.
At this time, you can use the "REPLACE INTO" statement, so that you don't have to query first and then decide whether to delete first and then insert.
The "REPLACE INTO" statement is based on a unique index or primary key to determine uniqueness (whether it exists).
The "REPLACE INTO" statement is based on a unique index or primary key to determine uniqueness (whether it exists).
The "REPLACE INTO" statement is based on a unique index or primary key to determine uniqueness (whether it exists).
Note: As shown in the following SQL, a unique index (Unique) needs to be established on the username field, and the transId setting can be incremented.
-- 20点充值 REPLACE INTO last_transaction (transId,username,amount,trans_time,remark) VALUES (null, 'chenhaha', 30, '2020-06-11 20:00:20', '会员充值'); -- 21点买皮肤 REPLACE INTO last_transaction (transId,username,amount,trans_time,remark) VALUES (null, 'chenhaha', 100, '2020-06-11 21:00:00', '购买盲僧至高之拳皮肤');
If the record of username='chenhaha' does not exist, the REPLACE statement will insert a new record (first recharge), otherwise, the current record of username='chenhaha' will be deleted, and then a new record will be inserted.
Do not give a specific value for id, otherwise it will affect SQL execution, unless the business has special needs.
2. Insert or update
If we want to insert a new record (INSERT), but if the record already exists, update the record, at this time, you can use "INSERT INTO ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE ..." statement:
Scenario example: This table stores the user's historical recharge amount. If the user recharges for the first time, a new piece of data will be added. If the user recharges If the historical recharge amount is accumulated, it is necessary to ensure that the data of a single user is not entered repeatedly.
You can use the "INSERT INTO ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE ..." statement at this time.
Note: Same as above, the "INSERT INTO ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE ..." statement is based on a unique index or primary key to determine uniqueness (whether it exists). As shown in the following SQL, a unique index (Unique) needs to be established on the username field, and the transId setting can be incremented.
-- 用户陈哈哈充值了30元买会员 INSERT INTO total_transaction (t_transId,username,total_amount,last_transTime,last_remark) VALUES (null, 'chenhaha', 30, '2020-06-11 20:00:20', '充会员') ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE total_amount=total_amount + 30, last_transTime='2020-06-11 20:00:20', last_remark ='充会员'; -- 用户陈哈哈充值了100元买瞎子至高之拳皮肤 INSERT INTO total_transaction (t_transId,username,total_amount,last_transTime,last_remark) VALUES (null, 'chenhaha', 100, '2020-06-11 20:00:20', '购买盲僧至高之拳皮肤') ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE total_amount=total_amount + 100, last_transTime='2020-06-11 21:00:00', last_remark ='购买盲僧至高之拳皮肤';
If the record with username='chenhaha' does not exist, the INSERT statement will insert a new record. Otherwise, the current record with username='chenhaha' will be updated, and the updated fields are specified by UPDATE.
3. Insert or ignore
If we want to insert a new record (INSERT), but if the record already exists, just ignore it and do nothing. When, you can use the INSERT IGNORE INTO... statement: There are many scenarios, so I won’t give them any examples.
Note: Same as above, the "INSERT IGNORE INTO..." statement is based on a unique index or primary key to determine uniqueness (whether it exists), and a unique index (Unique) needs to be established on the username field. The transId setting can be incremented by itself.
-- 用户首次添加 INSERT IGNORE INTO users_info (id, username, sex, age ,balance, create_time) VALUES (null, 'chenhaha', '男', 12, 0, '2020-06-11 20:00:20'); -- 二次添加,直接忽略 INSERT IGNORE INTO users_info (id, username, sex, age ,balance, create_time) VALUES (null, 'chenhaha', '男', 12, 0, '2020-06-11 21:00:20');
If the record with username='chenhaha' does not exist, the INSERT statement will insert a new record, otherwise, no operation will be performed.
4. If-else judgment statement in SQL
As we all know, if-else judgment is useful everywhere, in SQL statements, "CASE WHEN. .. THEN ... ELSE ... END" statements can be used in various types of add, delete, modify and query statements.
Give me a scenario: Women’s Day big reward, new users registered in 2020, all adult female accounts will receive a 10-yuan red envelope, and other users will receive a 5-yuan red envelope, which will be automatically recharged.
Example sentences are as follows:
-- 送红包语句
UPDATE users_info u
SET u.balance = CASE WHEN u.sex ='女' and u.age > 18 THEN u.balance + 10
ELSE u.balance + 5 end
WHERE u.create_time >= '2020-01-01'* Scenario 2: There is a student's college entrance examination score table, and the grades need to be listed. A score of 650 or above is a key university, 600-650 is a book, 500- A score of 600 means two books, a score of 400-500 means three books, and a college score below 400;
The original test data is as follows:
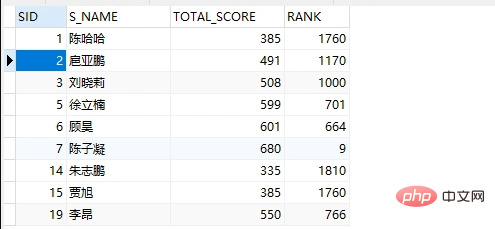
SELECT *,case when total_score >= 650 THEN '重点大学'
when total_score >= 600 and total_score <650 THEN '一本'
when total_score >= 500 and total_score <600 THEN '二本'
when total_score >= 400 and total_score <500 THEN '三本'
else '大专' end as status_student
from student_score;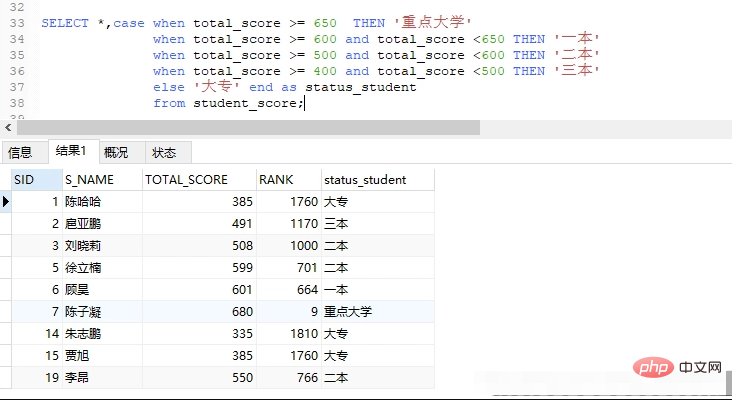
5. Specify data snapshot or backup
If you want to take a snapshot of a table, make a copy To transfer data from the current table to a new table, you can combine CREATE TABLE and SELECT:-- 对class_id=1(一班)的记录进行快照,并存储为新表students_of_class1: CREATE TABLE students_of_class1 SELECT * FROM student WHERE class_id=1;
6. Write the query result set
If the query result set needs to be written into the table, you can combine INSERT and SELECT to directly insert the result set of the SELECT statement to the specified table. For example, create a statistics table to record the average score of each class:CREATE TABLE statistics (
id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
class_id BIGINT NOT NULL,
average DOUBLE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);INSERT INTO statistics (class_id, average) SELECT class_id, AVG(score) FROM students GROUP BY class_id;
确保INSERT语句的列和SELECT语句的列能一一对应,就可以在statistics表中直接保存查询的结果:
SELECT * FROM statistics;
+----+----------+--------------+ | id | class_id | average | +----+----------+--------------+ | 1 | 1 | 475.5 | | 2 | 2 | 473.33333333 | | 3 | 3 | 488.66666666 | +----+----------+--------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
7.强制使用指定索引
在查询的时候,数据库系统会自动分析查询语句,并选择一个最合适的索引。但是很多时候,数据库系统的查询优化器并不一定总是能使用最优索引。如果我们知道如何选择索引,可以使用FORCE INDEX强制查询使用指定的索引。例如:
SELECT * FROM students FORCE INDEX (idx_class_id) WHERE class_id = 1 ORDER BY id DESC;
指定索引的前提是索引idx_class_id必须存在。
心得体会:
MySQL路漫漫,其修远兮。永远不要眼高手低,一起加油,希望本文能对你有所帮助。
推荐教程: 《mysql教程》
The above is the detailed content of Share several practical SQL statements in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.




