Promise practice to implement WeChat applet interface encapsulation
I believe many developers have encountered the problem of callback hell. Since the APIs of WeChat mini programs are basically asynchronous operations based on callback functions, if you do not use other frameworks or encapsulated APIs, especially if you use a lot of wx.request(), you will basically encounter the problem of callback hell very quickly. Maintenance It was very painful.
For example
Suppose you are developing a social applet at this time. One of the functions is that after logging in, users of the applet can view nearby people.
Assuming the following implementation idea is used, we obtain the user's current location through wx.getLocation(), and then request the backend data through wx.request(). But before that, you need to log in. Refer to the login method recommended by the previous official document. First call wx.login() to get the code, and then use wx.request() to request the developer server. If the custom login status is successfully returned (usually access_token or other Token form), and then use the custom login state to request business data.
For the convenience of reading, I posted the login process in the official document ⬇️
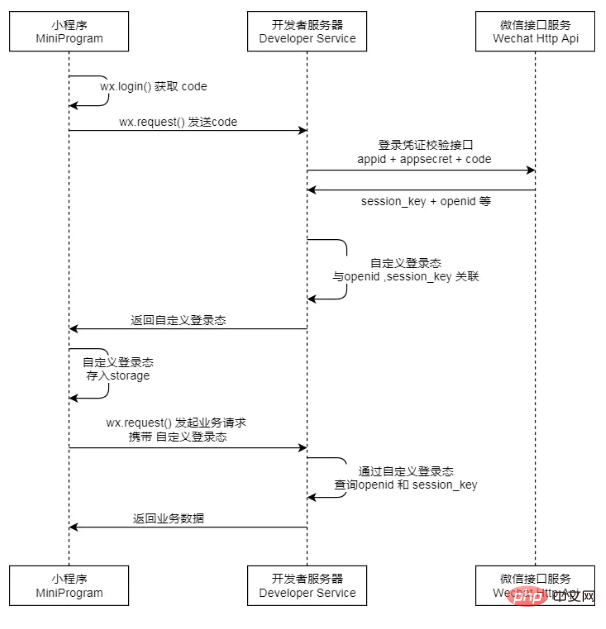
After the idea is determined, start trying coding (it is not recommended to read the following code )
/* 以下为Page对象的方法 */
getNearby: function() {
// 判断是否已认证,可采用wx.checkSession()方案
if (isAuth) {
// TODO: 获取业务数据
return
}
// wx.login获取code
wx.login({
success(res) {
if (res.code) {
// 获取自定义登录态
wx.request({
url,
method,
headers,
data,
success(res) {
// 请求成功
if (res.statuCode === 200) {
// 读取响应体中的自定义登录态
let token = res.data.token
// 保存自定义登录态
wx.setStorageSync("assess_token", token)
// 获取位置信息
wx.getLocation({
success(res) {
let { latitude, longitude } = res
// 请求业务数据
wx.request({
url,
method,
header,
data: { latitude, longitude },
success(res) {
// 请求成功
if (res.statuCode === 200) {
let data = res.data
// 数据渲染到V层
this.setData({ list: data })
}
// 请求失败
else if (res.statuCode === 400) {
// TODO
}
// 其他错误情况状态码处理
// TODO
},
fail(err) {
// 调用失败处理
}
})
},
fail(err) {
// 调用失败处理
}
})
}
// 请求失败
else if (res.statuCode == 400) {
// TODO
}
// 其他错误情况的状态码处理
},
fail(err) {
// 调用失败处理
}
})
}
else {
// TODO
// 登录失败
}
},
fail(err) {
// wx.login()调用失败处理
// TODO: ...
}
})
}Callback Hell appears. Qigong wave codes, let alone others, will make you feel sick even if you look at them.
One day Yingming’s product manager stood up and said that we can add some XXXXX. You may have to find a place to nest other WeChat interfaces or add a few more if else branches. By then Just find a place to cry.
Solution
In a sense, today's stormy front-end ecosystem relies on the emergence of Node and ES6.
After ES6, there are many solutions for asynchronous. One is to use generator/yield, but the generator function is actually more troublesome to use. The other is to use Promise, which is relatively simple. ES7 can also use async/await, but essentially async/await is also based on Promise. Promise is introduced below.
Promise
Promise Creation
Creating a Promise is very simple. Promise itself is a constructor. Created via new. The parameter of the constructor is a callback function, and the callback function has two parameters: resolve and reject (no manual maintenance required). resolve and reject are used to change state. I’ll talk about the status later.
// Promise实例的创建
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// TODO
})Promise has a disadvantage, it will be executed immediately once created. So it is usually wrapped with a function.
let getPromise = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// TODO
})
}Promise status
Promise instances have three states, pending, resolved and rejected, PromiseAfter the instance is created, it will be in the pending state. The resolve and reject in the callback function are used to change the Promise instance state. When resolve is called, the Promise instance will change from pending to resolved status, indicating success. When reject is called, the Promise instance will change from pending to rejected status, indicating failure.
let getPromise = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// TODO
// 处理结果
if (result) {
resolve(successObject)
}
else {
reject(error)
}
})
}Commonly used methods
The most commonly used methods are then() and catch(). Through then# The passing utility of ##() can solve the problem of callback hell.
then() can receive two parameters, both of which are callback functions. The first callback function is used to handle the resolved state, and the parameter is Promise The success object passed by the instance call resolve. The second callback function is used to handle the rejected status, and the parameter is the error object passed by calling the Promise instance and calling reject.
then()We generally only use it to handle the resolved situation, that is, only pass the first callback function. For rejected situations, catch() is used to handle them uniformly.
let getPromise = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// TODO
// 处理结果
if (result) {
resolve(successObject)
}
else {
reject(error)
}
})
}
getPromise()
.then(res => {
console.log(res)
// TODO
})
.catch(err => {
//TODO
})then() method can continue to return a Promise object, by return a new Promise, Can be passed down continuously.
getPromise()
.then(res => { //第一层Promise
console.log(res)
// TODO
return getPromise()
)
.then(res => { // 第二层Promise
console.log(res)
// TODO
})
.catch(err => {
// TODO
})Promise.all(), Promise.race(). Used when you need to wait for multiple Promise results. Both methods receive an array of objects consisting of Promise. When using Promise.all(), the state is resolved only when all Promise objects are resolved Promise.all(). When Promise.race() only needs one Promise object to be resolved, its status will be resolved.
Encapsulating Mini Program Interface
After learning the basics of Promise, by encapsulating asynchronous operations and using Promise chains, you can solve the callback hell problem. Because wx.request() is used more frequently, we encapsulate wx.request() first.
/* 可以将公用的方法挂在app.js中 */
request: function(method, url, header, data) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
wx.request({
method,
url,
header,
data,
success(res) {
resolve(res)
},
fail(err) {
reject(err)
}
})
})
}基本框架就这样,我们可以进一步修改,比如请求url的基础路径,添加一些公用的header,针对状态码做一些全局处理等。
request: function(method, url, header = {}, data = {}) {
// 启动时可将storage中的令牌挂到app.js
let token = app.assess_token
if (token) {
header["Authorization"] = token
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
wx.request({
method,
url: "https://api.domain.com/v1" + url,
header,
data,
success(res) {
// 请求成功
if (res.statusCode === 200) {
resolve(res)
}
// 请求成功无响应体
else if (res.statusCode === 204) {
/*
可做一些成功提示,
如调用wx.showToast()、wx.showModal()或自定义弹出层等
*/
resolve(res)
}
// 未认证
else if (res.statusCode === 401) {
/* 可做一些错误提示,或者直接跳转至登录页面等 */
reject(res)
}
else if (res.statusCode == 400) {
/* 可做一些错误提示*/
reject(res)
}
else if (res.statuCode === 403) {
/* 无权限错误提示*/
reject(res)
}
// ...其他状态码处理
},
fail(err) {
/* 可做一些全局错误提示,如网络错误等 */
reject(err)
}
})
})
}封装之后,举个例子,发送请求就可以修改为
/* 方法体中 */
let app = getApp()
app.request("POST", "/auth", {}, { username, password })
.then(res => { // 第一层请求
// TODO 成功处理
return app.request("GET", "/goods", {}, {})
})
.then(res => { // 第二层请求
// TODO 成功处理
// 渲染视图
})
.catch(err => {
// TODO 错误处理
})封装一下其他的微信接口
/* 可以将公用的方法挂在app.js中 */
wxLogin: function() {
return new Promise((resovle, reject) => {
wx.login({
success(res) {
if (res.code) {
resovle(res)
}
else {
reject({ message: "登录失败" })
}
},
fail(err) {
reject(err)
}
})
})
}
getLocation: function() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
wx.getLocation({
success(res) {
resolve(res)
},
fail(err) {
reject(err)
}
})
})
}对于最初的例子,可以就修改为
/* Page对象的方法 */
getNearby: function() {
// 判断是否已认证,可采用wx.checkSession()方案
if (isAuth) {
// TODO: 获取业务数据
return
}
app.wxLogin()
.then(res => {
// 将code发送给开发者服务器,获取自定义登录态
return app.request("POST", "/auth", {}, { code, res.code })
})
.then(res => {
// 保存自定义登录态
setStorage("access_token", res.data.access_token)
// TODO: 其他登录成功操作...
return app.getLocation()
})
.then(({ latitude, longitude }) => {
let url = "/nearby?latitude=" + latitude + "&longitude=" + longitude
return app.request("GET", url)
})
.then(res => {
// TODO: 数据处理
let data = res.data
// 渲染视图层
this.setData({ data })
})
.catch(err => {
// TODO 错误处理
})
}之后若有需添加新的请求或者其他异步操作,直接在Promise链上操作就行了。
推荐教程:《微信小程序》
The above is the detailed content of Promise practice to implement WeChat applet interface encapsulation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
In daily life, we often encounter problems between promises and fulfillment. Whether in a personal relationship or a business transaction, delivering on promises is key to building trust. However, the pros and cons of commitment are often controversial. This article will explore the pros and cons of commitments and give some advice on how to keep your word. The promised benefits are obvious. First, commitment builds trust. When a person keeps his word, he makes others believe that he is a trustworthy person. Trust is the bond established between people, which can make people more
 What should I do if I encounter Uncaught (in promise) TypeError in a Vue application?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 06:39 PM
What should I do if I encounter Uncaught (in promise) TypeError in a Vue application?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 06:39 PM
Vue is a popular front-end framework, and you often encounter various errors and problems when developing applications. Among them, Uncaught(inpromise)TypeError is a common error type. In this article, we will discuss its causes and solutions. What is Uncaught(inpromise)TypeError? Uncaught(inpromise)TypeError error usually appears in
 Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Detailed explanation of Promise.resolve() requires specific code examples. Promise is a mechanism in JavaScript for handling asynchronous operations. In actual development, it is often necessary to handle some asynchronous tasks that need to be executed in sequence, and the Promise.resolve() method is used to return a Promise object that has been fulfilled. Promise.resolve() is a static method of the Promise class, which accepts a
 Example analysis of the principle and use of ES6 Promise
Aug 09, 2022 pm 03:49 PM
Example analysis of the principle and use of ES6 Promise
Aug 09, 2022 pm 03:49 PM
Use Promise objects to change ordinary functions to return Promise to solve the problem of callback hell. Understand the success and failure calling logic of Promise and make adjustments flexibly. Understand the core knowledge, use it first, and slowly integrate and absorb the knowledge.
 What are promise objects?
Nov 01, 2023 am 10:05 AM
What are promise objects?
Nov 01, 2023 am 10:05 AM
The promise object states are: 1. pending: initial state, neither success nor failure state; 2. fulfilled: means the operation was successfully completed; 3. rejected: means the operation failed. Once a Promise object is completed, it will change from the pending state to the fulfilled or rejected state, and cannot change again. Promise objects are widely used in JavaScript to handle asynchronous operations such as AJAX requests and timed operations.
 Which browsers support Promise?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
Which browsers support Promise?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
Browser compatibility: Which browsers support Promises? As the complexity of web applications continues to increase, developers are eager to solve the problem of asynchronous programming in JavaScript. In the past, developers often used callback functions to handle asynchronous operations, but this resulted in code that was complex and difficult to maintain. To solve this problem, ECMAScript6 introduced Promise, which provides a more intuitive and flexible way to handle asynchronous operations. Promise is a method used to handle exceptions
 What are the advantages of PHP functions returning Promise objects?
Apr 19, 2024 pm 05:03 PM
What are the advantages of PHP functions returning Promise objects?
Apr 19, 2024 pm 05:03 PM
Advantages: asynchronous and non-blocking, does not block the main thread; improves code readability and maintainability; built-in error handling mechanism.
 One article will help you master Promise easily
Feb 10, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
One article will help you master Promise easily
Feb 10, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
In front-end js learning, the most uncomfortable thing for everyone is the problem of asynchronousness. To solve problems such as asynchronous and callback hell, you must learn promises. For most front-end programmers, promises are simply a nightmare. This article starts from the easy-to-understand Angle is used as the entry point to help everyone easily master promises.




