What is recursion?

#What is recursion?
#The programming technique in which a program calls itself is called recursion.
Recursion as an algorithm is widely used in programming languages. A process or function has a method of directly or indirectly calling itself in its definition or description. It usually transforms a large and complex problem into a smaller problem similar to the original problem to solve. The recursive strategy only A small number of programs are needed to describe the multiple repeated calculations required in the problem-solving process, which greatly reduces the amount of program code. The power of recursion lies in defining infinite collections of objects with finite statements.
Generally speaking, recursion requires boundary conditions, a recursive forward section and a recursive return section. When the boundary conditions are not met, the recursion advances; when the boundary conditions are met, the recursion returns.
Example of nested function calling process
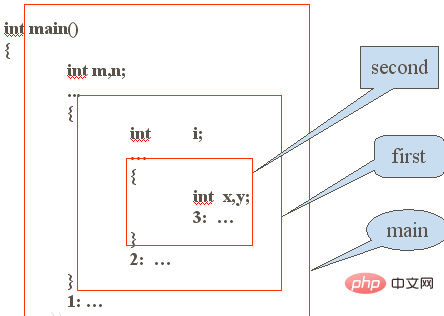
Conditions required to constitute recursion:
1 . The sub-problem must be the same thing as the original problem, and simpler;
2. It cannot call itself unlimitedly, there must be an exit, and it can be simplified to non-recursive situation processing .
In mathematics and computer science, recursion refers to a class of objects or methods defined by one (or more) simple base cases, and stipulates that all other cases can be reduced to their base cases Condition.
In mathematics and computer science, recursion refers to a class of objects or methods defined by one (or more) simple base cases, with the stipulation that all other cases can be reduced to their base cases.
For example, the following is the recursive definition of someone's ancestor: someone's parents are his ancestors (base case).
The parents of someone’s ancestor are also someone’s ancestors (recursive step). Fibonacci Sequence, also known as the golden section sequence, refers to such a sequence: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21.... I [1]
The Fibonacci sequence is a typical case of recursion: the recursive relationship is when the entity establishes a relationship with itself.
Fib(0) = 1 [base case] Fib(1) = 1 [base case] For all integers n > 1: Fib(n) = (Fib(n-1) Fib(n -2)) [Recursive definition] Although many mathematical functions can be expressed recursively, in practical applications, the high overhead of recursive definition is often prohibitive. For example:
Factorial (1) = 1 [Basic case] For all integers n > 1: Factorial (n) = (n * Factorial (n-1)) [Recursive definition] An easy to understand The mental model is that recursive definitions define objects in terms of "previously defined" objects of the same type. For example: How can you move 100 boxes? Answer: You first move a box and note where it is moved, and then move on to the smaller problem: How can you move 99 boxes? Eventually, your problem becomes how to move a box, and you already know how to do it.
Such a definition is very common in mathematics. For example, the formal definition of natural numbers in set theory is: 1 is a natural number, and every natural number has a successor, which is also a natural number.
Droste Effect
The Droste effect is a visual form of recursion. Among the objects the woman is holding is a small picture of herself holding the same object, and then there is an even smaller picture of her holding the same object, and so on.
For another example, if we place a burning candle between two opposite mirrors, we will see a candle in one of the mirrors, and there is a mirror behind the candle, and there is another candle in the mirror. Candles...this is also a manifestation of recursion.
For more related knowledge, please visit PHP Chinese website! !
The above is the detailed content of What is recursion?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Is there a limit to recursion depth?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Is there a limit to recursion depth?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:30 AM
The recursion depth of C++ functions is limited, and exceeding this limit will result in a stack overflow error. The limit value varies between systems and compilers, but is usually between 1,000 and 10,000. Solutions include: 1. Tail recursion optimization; 2. Tail call; 3. Iterative implementation.
 Do C++ lambda expressions support recursion?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Do C++ lambda expressions support recursion?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Yes, C++ Lambda expressions can support recursion by using std::function: Use std::function to capture a reference to a Lambda expression. With a captured reference, a Lambda expression can call itself recursively.
 Count the number of occurrences of a substring recursively in Java
Sep 17, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Count the number of occurrences of a substring recursively in Java
Sep 17, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Given two strings str_1 and str_2. The goal is to count the number of occurrences of substring str2 in string str1 using a recursive procedure. A recursive function is a function that calls itself within its definition. If str1 is "Iknowthatyouknowthatiknow" and str2 is "know" the number of occurrences is -3. Let us understand through examples. For example, input str1="TPisTPareTPamTP", str2="TP"; output Countofoccurrencesofasubstringrecursi
 Recursive program to find minimum and maximum elements of array in C++
Aug 31, 2023 pm 07:37 PM
Recursive program to find minimum and maximum elements of array in C++
Aug 31, 2023 pm 07:37 PM
We take the integer array Arr[] as input. The goal is to find the largest and smallest elements in an array using a recursive method. Since we are using recursion, we will iterate through the entire array until we reach length = 1 and then return A[0], which forms the base case. Otherwise, the current element is compared to the current minimum or maximum value and its value is updated recursively for subsequent elements. Let’s look at various input and output scenarios for this −Input −Arr={12,67,99,76,32}; Output −Maximum value in the array: 99 Explanation &mi
 Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Comparative analysis of recursive and non-recursive algorithms?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Recursive implementation of C++ functions: Comparative analysis of recursive and non-recursive algorithms?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
The recursive algorithm solves structured problems through function self-calling. The advantage is that it is simple and easy to understand, but the disadvantage is that it is less efficient and may cause stack overflow. The non-recursive algorithm avoids recursion by explicitly managing the stack data structure. The advantage is that it is more efficient and avoids the stack. Overflow, the disadvantage is that the code may be more complex. The choice of recursive or non-recursive depends on the problem and the specific constraints of the implementation.
 How to solve Python's maximum recursion depth error?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:48 PM
How to solve Python's maximum recursion depth error?
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:48 PM
Python is a programming language that is easy to learn and use. However, when using Python to write recursive functions, you may encounter errors in which the recursion depth is too large. This problem needs to be solved. This article will show you how to solve Python's maximum recursion depth error. 1. Understand recursion depth. Recursion depth refers to the number of layers of nested recursive functions. By default in Python, the limit of recursion depth is 1000. If the number of recursion levels exceeds this limit, the system will report an error. This error is often called the "maximum recursion depth error"
 Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: application of recursion in string processing
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Detailed explanation of C++ function recursion: application of recursion in string processing
Apr 30, 2024 am 10:30 AM
A recursive function is a technique that calls itself repeatedly to solve a problem in string processing. It requires a termination condition to prevent infinite recursion. Recursion is widely used in operations such as string reversal and palindrome checking.
 A beginner's guide to C++ recursion: Building foundations and developing intuition
May 01, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
A beginner's guide to C++ recursion: Building foundations and developing intuition
May 01, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Recursion is a powerful technique that allows a function to call itself to solve a problem. In C++, a recursive function consists of two key elements: the base case (which determines when the recursion stops) and the recursive call (which breaks the problem into smaller sub-problems ). By understanding the basics and practicing practical examples such as factorial calculations, Fibonacci sequences, and binary tree traversals, you can build your recursive intuition and use it in your code with confidence.





