JS sorting algorithm - front-end

Introduction
There is a saying:
Lei Feng knocked down Leifeng Pagoda, Java implements JavaScript.
At that time, JavaScript (originally known as LiveScript), which wanted to gain popularity by embracing Java and even changed its name, has now become brilliant. The emergence of node JS allows JavaScript to be used both on the front and back ends. Although Java still dominates the field of enterprise-level software development (C/C masters, don’t hit me...), in the world of the Web, JavaScript is unparalleled and takes the top spot.
However, in the field of traditional computer algorithms and data structures, the default language of most professional textbooks and books is Java or C/C. This has caused some trouble for me, who recently wanted to supplement the knowledge of algorithms and data structures, because I wanted to find an algorithm book with JavaScript as the default language. When I learned that there was a book in O’REILLY’s animal book series called “JavaScript Description of Data Structures and Algorithms”, I excitedly spent two days reading this book from cover to cover. It is a good introductory algorithm book for front-end developers. However, it has a big flaw, that is, there are many obvious small errors in it, which are so obvious that even a half-way programmer like me can see it at a glance. figure it out. Another problem is that many important algorithms and data structure knowledge are not mentioned in this book. These problems are simply intolerable to me as a late-stage obsessive-compulsive disorder patient. So, whenever I disagreed, I decided to look for information and summarize the algorithm myself. So, I will summarize it from the most basic knowledge point in the algorithm field-sorting algorithm.
I believe that there must be some bugs or errors or irregular grammar in the following code that I cannot find myself, so I hope you can point out the errors, because only by constantly correcting them can I Only by doing this can I make long-term progress.
Summary and comparison of the top ten classic algorithm sorting
One picture summary:
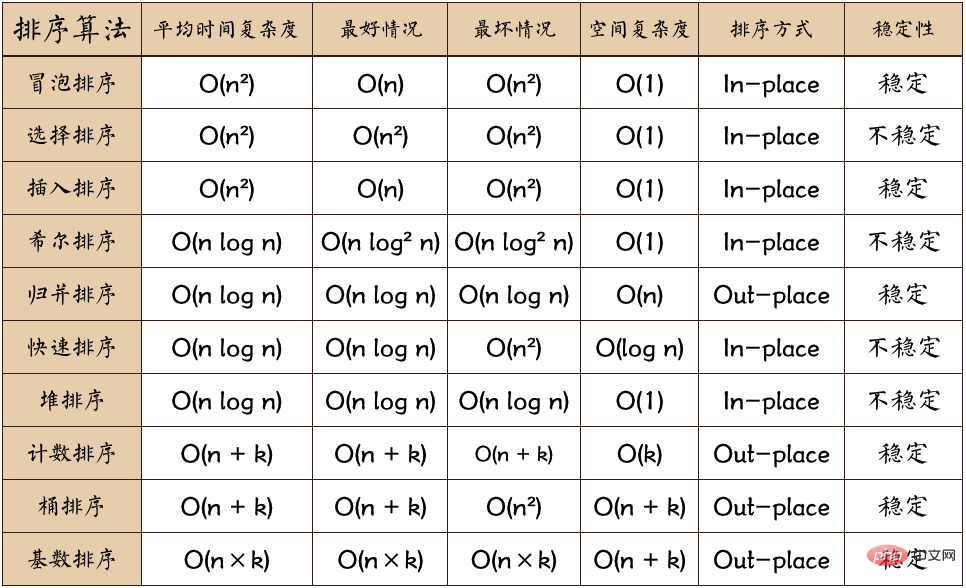
Overview of mainstream sorting algorithms
Explanation of terms:
n: Data scale
k: The number of “buckets”
In-place : Occupies constant memory, does not occupy additional memory
Out-place: Occupies additional memory
Stability: The order of 2 equal key values after sorting is the same as before sorting The order is the same
Bubble Sort
Instructions for Bubble Sort:
As the simplest sort One of the algorithms, bubble sort, gives me the same feeling as when Abandon appears in a word book. It is at the first place on the first page every time, so it is the most familiar. . . There is another optimization algorithm for bubble sorting, which is to set a flag. When the elements are not exchanged during a sequence traversal, it proves that the sequence is in order. But this improvement doesn't do much to improve performance. . .
When is the fastest (Best Cases):
When the input data is already in positive sequence (it is already in positive sequence, what is the use of bubble sorting? .)
When is the slowest (Worst Cases):
When the input data is in reverse order (just write a for loop to output the data in reverse order, why should you risk it? What about bubble sort, am I free...)
Bubble sort animation demonstration:
Bubble Sort animation demonstration algorithm Visual source: http://visualgo.net/
Bubble sorting JavaScript code implementation:
function bubbleSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length;
for (var i = 0; i arr[j+1]) { //相邻元素两两对比
var temp = arr[j+1]; //元素交换
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}Selection Sort
Selection sorting instructions:
One of the most stable sorting algorithms, because no matter what data is entered, the time complexity is O(n²). . . So when using it, the smaller the data size, the better. The only advantage may be that it does not occupy additional memory space.
Selection Sort animation demonstration:
Selection Sort animation demonstration Algorithm visualization source: http://visualgo.net/
选择排序JavaScript代码实现:
function selectionSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length;
var minIndex, temp;
for (var i = 0; i插入排序(Insertion Sort)
插入排序须知:
插入排序的代码实现虽然没有冒泡排序和选择排序那么简单粗暴,但它的原理应该是最容易理解的了,因为只要打过扑克牌的人都应该能够秒懂。当然,如果你说你打扑克牌摸牌的时候从来不按牌的大小整理牌,那估计这辈子你对插入排序的算法都不会产生任何兴趣了。。。
插入排序和冒泡排序一样,也有一种优化算法,叫做拆半插入。对于这种算法,得了懒癌的我就套用教科书上的一句经典的话吧:感兴趣的同学可以在课后自行研究。。。
插入排序动图演示:
Insertion Sort 动图演示 算法可视化来源:http://visualgo.net/
插入排序JavaScript代码实现:
function insertionSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length;
var preIndex, current;
for (var i = 1; i = 0 && arr[preIndex] > current) {
arr[preIndex+1] = arr[preIndex];
preIndex--;
}
arr[preIndex+1] = current;
}
return arr;
}希尔排序(Shell Sort)
希尔排序须知:
希尔排序是插入排序的一种更高效率的实现。它与插入排序的不同之处在于,它会优先比较距离较远的元素。希尔排序的核心在于间隔序列的设定。既可以提前设定好间隔序列,也可以动态的定义间隔序列。动态定义间隔序列的算法是《算法(第4版》的合著者Robert Sedgewick提出的。在这里,我就使用了这种方法。
希尔排序JavaScript代码实现:
function shellSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length,
temp,
gap = 1;
while(gap 0; gap = Math.floor(gap/3)) {
for (var i = gap; i = 0 && arr[j] > temp; j-=gap) {
arr[j+gap] = arr[j];
}
arr[j+gap] = temp;
}
}
return arr;
}归并排序(Merge Sort)
归并排序须知:
作为一种典型的分而治之思想的算法应用,归并排序的实现由两种方法:
- 自上而下的递归(所有递归的方法都可以用迭代重写,所以就有了第2种方法)
- 自下而上的迭代
在《数据结构与算法JavaScript描述》中,作者给出了自下而上的迭代方法。但是对于递归法,作者却认为:
However, it is not possible to do so in JavaScript, as the recursion goes too deep
for the language to handle.
然而,在 JavaScript 中这种方式不太可行,因为这个算法的递归深度对它来讲太深了。
说实话,我不太理解这句话。意思是JavaScript编译器内存太小,递归太深容易造成内存溢出吗?还望有大神能够指教。
和选择排序一样,归并排序的性能不受输入数据的影响,但表现比选择排序好的多,因为始终都是O(n log n)的时间复杂度。代价是需要额外的内存空间。
归并排序动图演示:
Merge Sort 动图演示 算法可视化来源:http://visualgo.net/
归并排序JavaScript代码实现:
function mergeSort(arr) { //采用自上而下的递归方法
var len = arr.length;
if(len =>快速排序(Quick Sort)
快速排序须知:
又是一种分而治之思想在排序算法上的典型应用。本质上来看,快速排序应该算是在冒泡排序基础上的递归分治法。
快速排序的名字起的是简单粗暴,因为一听到这个名字你就知道它存在的意义,就是快,而且效率高! 它是处理大数据最快的排序算法之一了。虽然Worst Case的时间复杂度达到了O(n²),但是人家就是优秀,在大多数情况下都比平均时间复杂度为O(n log n) 的排序算法表现要更好,可是这是为什么呢,我也不知道。。。好在我的强迫症又犯了,查了N多资料终于在《算法艺术与信息学竞赛》上找到了满意的答案:
快速排序的最坏运行情况是O(n²),比如说顺序数列的快排。但它的平摊期望时间是O(n log n) ,且O(n log n)记号中隐含的常数因子很小,比复杂度稳定等于O(n log n)的归并排序要小很多。所以,对绝大多数顺序性较弱的随机数列而言,快速排序总是优于归并排序。
快速排序动图演示:
Quick Sort 动图演示 算法可视化来源:http://visualgo.net/
快速排序JavaScript代码实现:
function quickSort(arr, left, right) {
var len = arr.length,
partitionIndex,
left = typeof left != 'number' ? 0 : left,
right = typeof right != 'number' ? len - 1 : right;
if (left =>堆排序(Heap Sort)
堆排序须知:
堆排序可以说是一种利用堆的概念来排序的选择排序。分为两种方法:
- 大顶堆:每个节点的值都大于或等于其子节点的值,在堆排序算法中用于升序排列
- 小顶堆:每个节点的值都小于或等于其子节点的值,在堆排序算法中用于降序排列
堆排序动图演示:
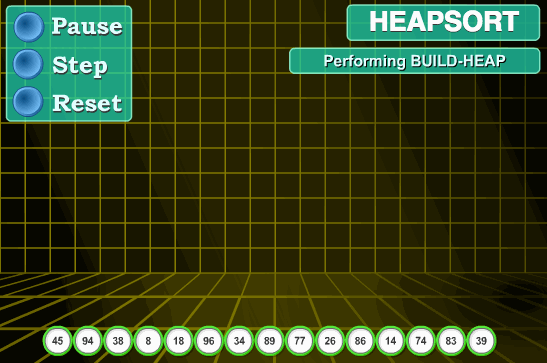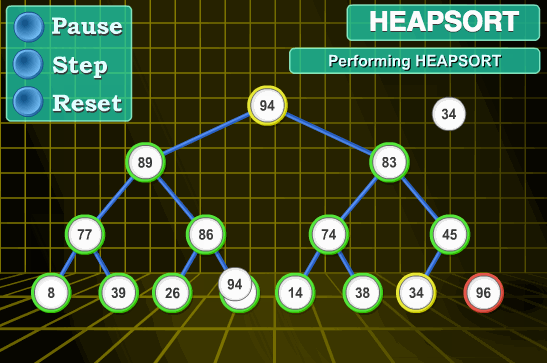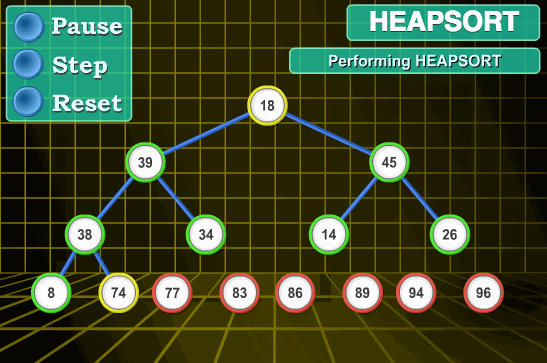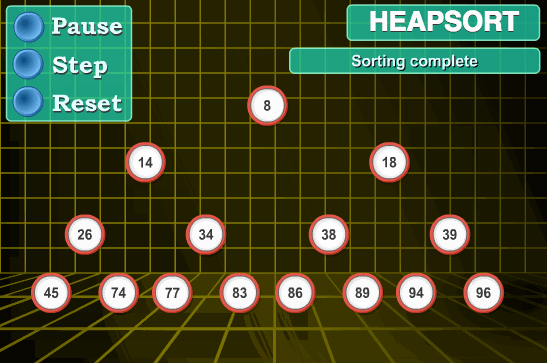
Heap Sort 动图演示 算法可视化来源:http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~courses/coe428/sorting/heapsort.html
堆排序JavaScript代码实现:
var len; //因为声明的多个函数都需要数据长度,所以把len设置成为全局变量
function buildMaxHeap(arr) { //建立大顶堆
len = arr.length;
for (var i = Math.floor(len/2); i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, i);
}
}
function heapify(arr, i) { //堆调整
var left = 2 * i + 1,
right = 2 * i + 2,
largest = i;
if (left arr[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
if (right arr[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
if (largest != i) {
swap(arr, i, largest);
heapify(arr, largest);
}
}
function swap(arr, i, j) {
var temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
function heapSort(arr) {
buildMaxHeap(arr);
for (var i = arr.length-1; i > 0; i--) {
swap(arr, 0, i);
len--;
heapify(arr, 0);
}
return arr;
}计数排序(Counting Sort)
计数排序须知:
计数排序的核心在于将输入的数据值转化为键存储在额外开辟的数组空间中。
作为一种线性时间复杂度的排序,计数排序要求输入的数据必须是有确定范围的整数。
计数排序动图演示:
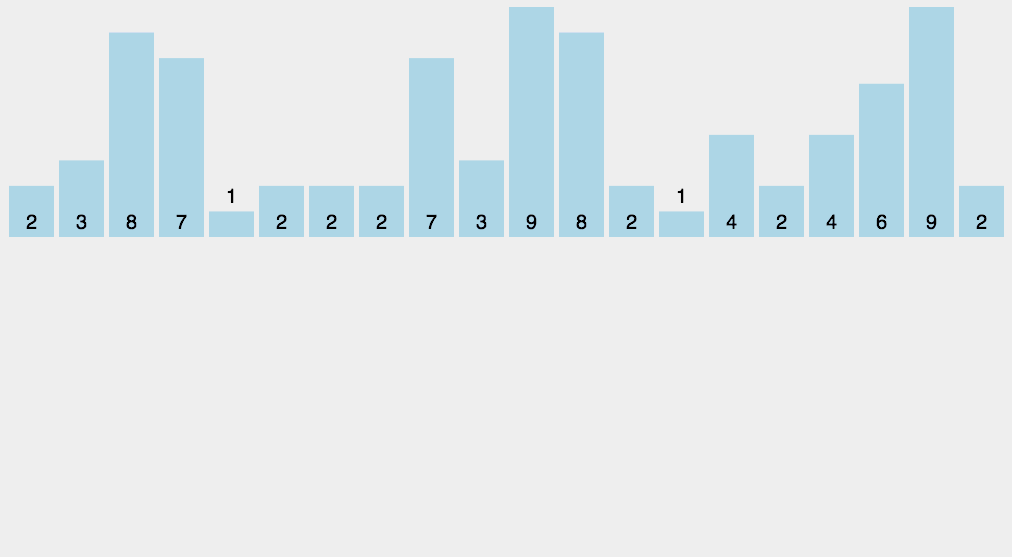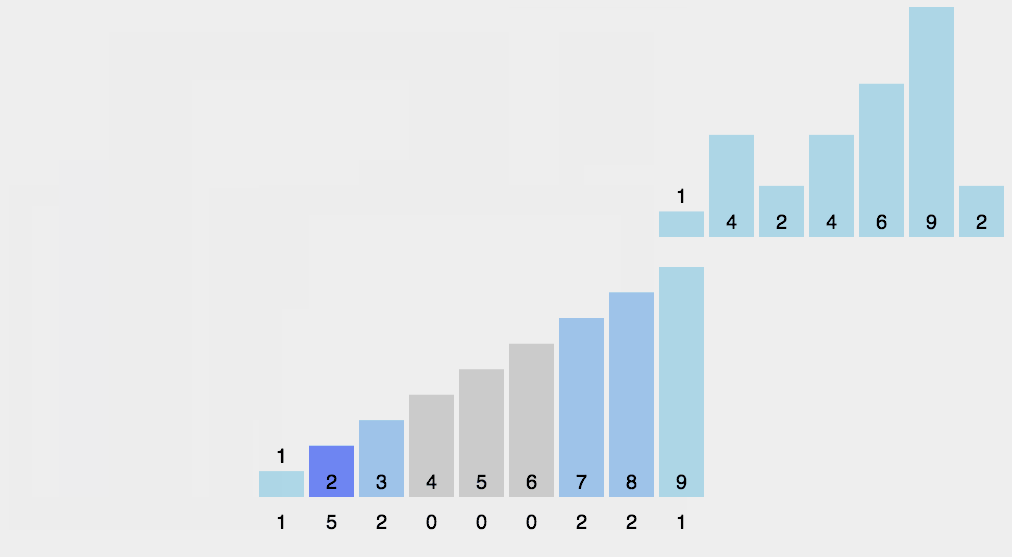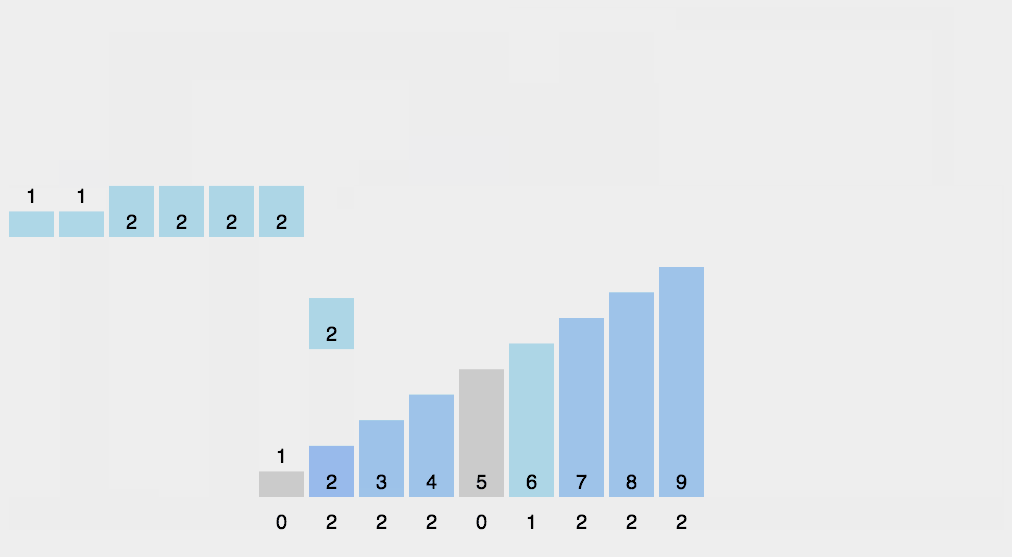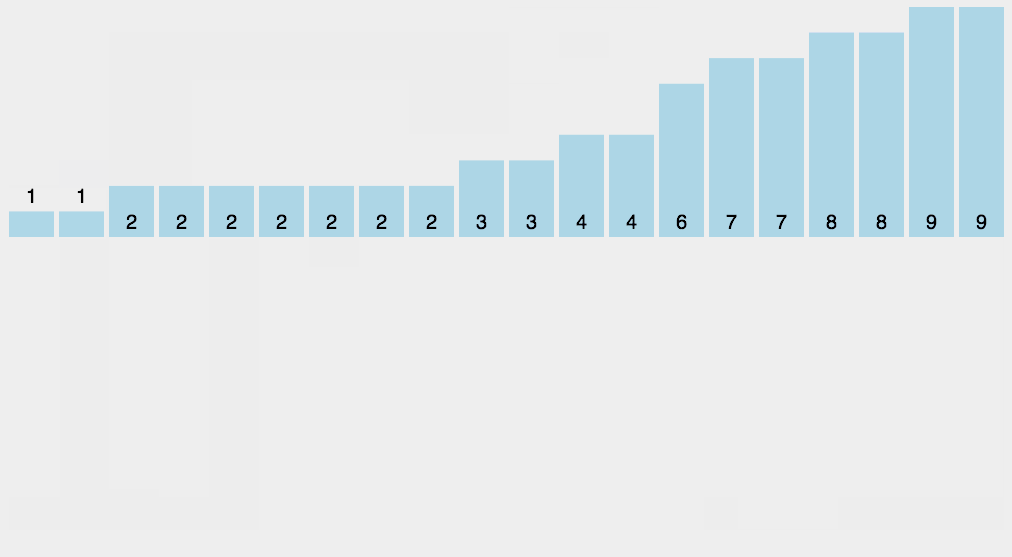
Counting Sort 动图演示 算法可视化来源:http://visualgo.net/
计数排序JavaScript代码实现:
function countingSort(arr, maxValue) {
var bucket = new Array(maxValue+1),
sortedIndex = 0;
arrLen = arr.length,
bucketLen = maxValue + 1;
for (var i = 0; i 0) {
arr[sortedIndex++] = j;
bucket[j]--;
}
}
return arr;
}桶排序(Bucket Sort)
桶排序须知:
桶排序是计数排序的升级版。它利用了函数的映射关系,高效与否的关键就在于这个映射函数的确定。
为了使桶排序更加高效,我们需要做到这两点:
- 在额外空间充足的情况下,尽量增大桶的数量
- 使用的映射函数能够将输入的N个数据均匀的分配到K个桶中
同时,对于桶中元素的排序,选择何种比较排序算法对于性能的影响至关重要。
什么时候最快(Best Cases):
当输入的数据可以均匀的分配到每一个桶中
什么时候最慢(Worst Cases):
当输入的数据被分配到了同一个桶中
桶排序JavaScript代码实现:
function bucketSort(arr, bucketSize) {
if (arr.length === 0) {
return arr;
}
var i;
var minValue = arr[0];
var maxValue = arr[0];
for (i = 1; i maxValue) {
maxValue = arr[i]; //输入数据的最大值
}
}
//桶的初始化
var DEFAULT_BUCKET_SIZE = 5; //设置桶的默认数量为5
bucketSize = bucketSize || DEFAULT_BUCKET_SIZE;
var bucketCount = Math.floor((maxValue - minValue) / bucketSize) + 1;
var buckets = new Array(bucketCount);
for (i = 0; i基数排序(Radix Sort)
基数排序须知:
基数排序有两种方法:
- MSD 从高位开始进行排序
- LSD 从低位开始进行排序
基数排序 vs 计数排序 vs 桶排序
这三种排序算法都利用了桶的概念,但对桶的使用方法上有明显差异:
基数排序:根据键值的每位数字来分配桶
计数排序:每个桶只存储单一键值
桶排序:每个桶存储一定范围的数值
LSD基数排序动图演示:

Radix Sort 动图演示 算法可视化来源:http://visualgo.net/
基数排序JavaScript代码实现:
//LSD Radix Sort
var counter = [];
function radixSort(arr, maxDigit) {
var mod = 10;
var dev = 1;
for (var i = 0; i写在最后
排序算法实在是博大精深,还有hin多hin多我没有总结到或者我自己还没弄明白的算法,仅仅是总结这十种排序算法都把我写哭了。。。
因此,以后如果我掌握了更多的排序姿势,我一定还会回来的!
推荐教程:《javascript基础教程》
The above is the detailed content of JS sorting algorithm - front-end. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
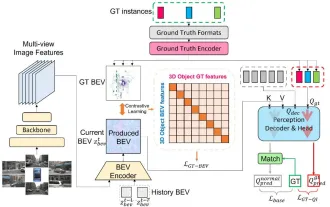 CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: At present, in the entire autonomous driving system, the perception module plays a vital role. The autonomous vehicle driving on the road can only obtain accurate perception results through the perception module. The downstream regulation and control module in the autonomous driving system makes timely and correct judgments and behavioral decisions. Currently, cars with autonomous driving functions are usually equipped with a variety of data information sensors including surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, and millimeter-wave radar sensors to collect information in different modalities to achieve accurate perception tasks. The BEV perception algorithm based on pure vision is favored by the industry because of its low hardware cost and easy deployment, and its output results can be easily applied to various downstream tasks.
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
The bottom layer of the C++sort function uses merge sort, its complexity is O(nlogn), and provides different sorting algorithm choices, including quick sort, heap sort and stable sort.
 Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and law enforcement opens up new possibilities for crime prevention and detection. The predictive capabilities of artificial intelligence are widely used in systems such as CrimeGPT (Crime Prediction Technology) to predict criminal activities. This article explores the potential of artificial intelligence in crime prediction, its current applications, the challenges it faces, and the possible ethical implications of the technology. Artificial Intelligence and Crime Prediction: The Basics CrimeGPT uses machine learning algorithms to analyze large data sets, identifying patterns that can predict where and when crimes are likely to occur. These data sets include historical crime statistics, demographic information, economic indicators, weather patterns, and more. By identifying trends that human analysts might miss, artificial intelligence can empower law enforcement agencies
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
1. Background of the Construction of 58 Portraits Platform First of all, I would like to share with you the background of the construction of the 58 Portrait Platform. 1. The traditional thinking of the traditional profiling platform is no longer enough. Building a user profiling platform relies on data warehouse modeling capabilities to integrate data from multiple business lines to build accurate user portraits; it also requires data mining to understand user behavior, interests and needs, and provide algorithms. side capabilities; finally, it also needs to have data platform capabilities to efficiently store, query and share user profile data and provide profile services. The main difference between a self-built business profiling platform and a middle-office profiling platform is that the self-built profiling platform serves a single business line and can be customized on demand; the mid-office platform serves multiple business lines, has complex modeling, and provides more general capabilities. 2.58 User portraits of the background of Zhongtai portrait construction
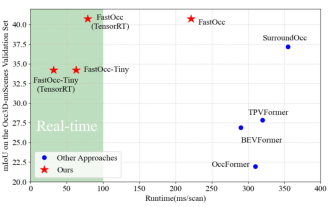 Add SOTA in real time and skyrocket! FastOcc: Faster inference and deployment-friendly Occ algorithm is here!
Mar 14, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
Add SOTA in real time and skyrocket! FastOcc: Faster inference and deployment-friendly Occ algorithm is here!
Mar 14, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
Written above & The author’s personal understanding is that in the autonomous driving system, the perception task is a crucial component of the entire autonomous driving system. The main goal of the perception task is to enable autonomous vehicles to understand and perceive surrounding environmental elements, such as vehicles driving on the road, pedestrians on the roadside, obstacles encountered during driving, traffic signs on the road, etc., thereby helping downstream modules Make correct and reasonable decisions and actions. A vehicle with self-driving capabilities is usually equipped with different types of information collection sensors, such as surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, millimeter-wave radar sensors, etc., to ensure that the self-driving vehicle can accurately perceive and understand surrounding environment elements. , enabling autonomous vehicles to make correct decisions during autonomous driving. Head




