 WeChat Applet
WeChat Applet
 Mini Program Development
Mini Program Development
 The use of wepy-redux and storage of global variables in small programs
The use of wepy-redux and storage of global variables in small programs
The use of wepy-redux and storage of global variables in small programs
Wepy recommends using wepy-redux to store global variables
Use
1. Initialize store
// app.wpy
import { setStore } from 'wepy-redux'
import configStore from './store'
const store = configStore()
setStore(store) //setStore是将store注入到所有页面中// store文件夹下的index.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import promiseMiddleware from 'redux-promise'
import rootReducer from './reducers'
export default function configStore () {
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(promiseMiddleware)) //生成一个 store 对象
return store
}applyMiddleware The function of the function is to enhance and transform the store.dispatch method
Here is to use redux-promise to solve the asynchronous problem
2.page to get the store
import { getStore } from 'wepy-redux'
const store = getStore()
// dispatch
store.dispatch({type: 'xx', payload: data}) //xx是reducer名字 payload就是携带的数据
store.dispatch(getAllHoomInfo(store.getState().base)) //xx是action名字
//获取state
const state = store.getState()3. Connection component
@connect({
data:(state) => state.base.data //注意这里是base下的state 所有要加上base.
})File introduction
redux file
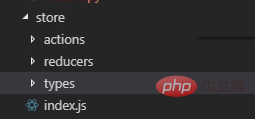
type
Types is the name of the function that triggers the action. It just stores the function name.
Create type.js according to the module
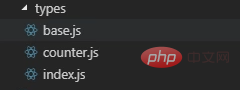
//base.js export const GETALLHOMEINFO = 'GETALLHOMEINFO'
After writing the function name, export it in index.js
export * from './counter' export * from './base'
reducers
Follow As the application becomes more complex, the reducer function needs to be split. Each piece after the split is independently responsible for managing a part of the state.
At this time, the reducers of multiple modules are combined into a final reducer through combineReducers Function,
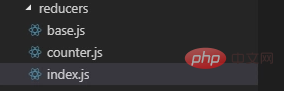
import { combineReducers } from 'redux'
import base from './base'
import counter from './counter'
export default combineReducers({
base,
counter
}) module uses handleActions to process the reducer, and writes multiple related reducers together
handleActions There are two parameters: the first is multiple reducers, and the second is the initial state
GETALLHOMEINFO reducer assigns the value returned by the asynchronous action to data
//base.js
import { handleActions } from 'redux-actions'
import { GETALLHOMEINFO } from '../types/base'
const initialState = {
data: {}
}
export default handleActions({
[GETALLHOMEINFO] (state, action) {
return {
...state,
data: action.payload
}
}
}, initialState)actions
actions is the processing of data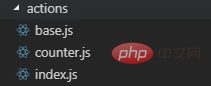
Exported in index.js
export * from './counter' export * from './base'
createAction is used to create Action
import { GETALLHOMEINFO } from '../types/base'
import { createAction } from 'redux-actions'
import { Http, Apis } from '../../libs/interface'
export const getAllHoomInfo = createAction(GETALLHOMEINFO, (base) => {
return new Promise(async resolve => {
let data = await Http.get({
url: Apis.ls_url + Apis.allHomeInfo,
data: {}
})
resolve(data)**//返回到reduer的action.payload**
})
})Usage
<script>
import wepy from 'wepy'
import { connect } from 'wepy-redux'
import { getAllHoomInfo } from '../store/actions/base.js'// 引入action方法
import { getStore } from 'wepy-redux'
const store = getStore()
@connect({
data:(state) => state.base.data
})
export default class Index extends wepy.page {
data = {
}
computed = {
}
onLoad() {
store.dispatch(getAllHoomInfo(store.getState().base))
}
}
</script>Recommended tutorial: "WeChat Mini Program"
The above is the detailed content of The use of wepy-redux and storage of global variables in small programs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Develop WeChat applet using Python
Jun 17, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
Develop WeChat applet using Python
Jun 17, 2023 pm 06:34 PM
With the popularity of mobile Internet technology and smartphones, WeChat has become an indispensable application in people's lives. WeChat mini programs allow people to directly use mini programs to solve some simple needs without downloading and installing applications. This article will introduce how to use Python to develop WeChat applet. 1. Preparation Before using Python to develop WeChat applet, you need to install the relevant Python library. It is recommended to use the two libraries wxpy and itchat here. wxpy is a WeChat machine
 Can small programs use react?
Dec 29, 2022 am 11:06 AM
Can small programs use react?
Dec 29, 2022 am 11:06 AM
Mini programs can use react. How to use it: 1. Implement a renderer based on "react-reconciler" and generate a DSL; 2. Create a mini program component to parse and render DSL; 3. Install npm and execute the developer Build npm in the tool; 4. Introduce the package into your own page, and then use the API to complete the development.
 Implement card flipping effects in WeChat mini programs
Nov 21, 2023 am 10:55 AM
Implement card flipping effects in WeChat mini programs
Nov 21, 2023 am 10:55 AM
Implementing card flipping effects in WeChat mini programs In WeChat mini programs, implementing card flipping effects is a common animation effect that can improve user experience and the attractiveness of interface interactions. The following will introduce in detail how to implement the special effect of card flipping in the WeChat applet and provide relevant code examples. First, you need to define two card elements in the page layout file of the mini program, one for displaying the front content and one for displaying the back content. The specific sample code is as follows: <!--index.wxml-->&l
 Alipay launched the 'Chinese Character Picking-Rare Characters' mini program to collect and supplement the rare character library
Oct 31, 2023 pm 09:25 PM
Alipay launched the 'Chinese Character Picking-Rare Characters' mini program to collect and supplement the rare character library
Oct 31, 2023 pm 09:25 PM
According to news from this site on October 31, on May 27 this year, Ant Group announced the launch of the "Chinese Character Picking Project", and recently ushered in new progress: Alipay launched the "Chinese Character Picking-Uncommon Characters" mini program to collect collections from the society Rare characters supplement the rare character library and provide different input experiences for rare characters to help improve the rare character input method in Alipay. Currently, users can enter the "Uncommon Characters" applet by searching for keywords such as "Chinese character pick-up" and "rare characters". In the mini program, users can submit pictures of rare characters that have not been recognized and entered by the system. After confirmation, Alipay engineers will make additional entries into the font library. This website noticed that users can also experience the latest word-splitting input method in the mini program. This input method is designed for rare words with unclear pronunciation. User dismantling
 How uniapp achieves rapid conversion between mini programs and H5
Oct 20, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
How uniapp achieves rapid conversion between mini programs and H5
Oct 20, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
How uniapp can achieve rapid conversion between mini programs and H5 requires specific code examples. In recent years, with the development of the mobile Internet and the popularity of smartphones, mini programs and H5 have become indispensable application forms. As a cross-platform development framework, uniapp can quickly realize the conversion between small programs and H5 based on a set of codes, greatly improving development efficiency. This article will introduce how uniapp can achieve rapid conversion between mini programs and H5, and give specific code examples. 1. Introduction to uniapp unia
 Tutorial on writing a simple chat program in Python
May 08, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Tutorial on writing a simple chat program in Python
May 08, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Implementation idea: Establishing the server side of thread, so as to process the various functions of the chat room. The establishment of the x02 client is much simpler than the server. The function of the client is only to send and receive messages, and to enter specific characters according to specific rules. To achieve the use of different functions, therefore, on the client side, you only need to use two threads, one is dedicated to receiving messages, and the other is dedicated to sending messages. As for why not use one, that is because, only
 How to operate mini program registration
Sep 13, 2023 pm 04:36 PM
How to operate mini program registration
Sep 13, 2023 pm 04:36 PM
Mini program registration operation steps: 1. Prepare copies of personal ID cards, corporate business licenses, legal person ID cards and other filing materials; 2. Log in to the mini program management background; 3. Enter the mini program settings page; 4. Select " "Basic Settings"; 5. Fill in the filing information; 6. Upload the filing materials; 7. Submit the filing application; 8. Wait for the review results. If the filing is not passed, make modifications based on the reasons and resubmit the filing application; 9. The follow-up operations for the filing are Can.
 How to get membership in WeChat mini program
May 07, 2024 am 10:24 AM
How to get membership in WeChat mini program
May 07, 2024 am 10:24 AM
1. Open the WeChat mini program and enter the corresponding mini program page. 2. Find the member-related entrance on the mini program page. Usually the member entrance is in the bottom navigation bar or personal center. 3. Click the membership portal to enter the membership application page. 4. On the membership application page, fill in relevant information, such as mobile phone number, name, etc. After completing the information, submit the application. 5. The mini program will review the membership application. After passing the review, the user can become a member of the WeChat mini program. 6. As a member, users will enjoy more membership rights, such as points, coupons, member-exclusive activities, etc.



