 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP7
PHP7
 Let's talk about the understanding and comparison of new features of php7
Let's talk about the understanding and comparison of new features of php7
Let's talk about the understanding and comparison of new features of php7

null coalescing operator (??)
?? Syntax: If the variable exists and the value is not NULL, it will return its own value, otherwise it will return it The second operand.
//php7以前 if判断if(empty($_GET['param'])) {
$param = 1;
}else{
$param = $_GET['param'];
}//php7以前 三元运算符$param = empty($_GET['param']) ? 1 : $_GET['param'];//PHP7 null合并运算符$param = $_GET['param'] ?? 1;//1define() defines a constant array
//php7以前define("CONTENT", "hello world");echo CONTENT;//hello world//PHP7define('ANIMALS', [ 'dog', 'cat', 'bird']);echo ANIMALS[2];//bird//PHP7 类外也可使用const来定义常量const CONSTANT = 'Hello World';
echo CONSTANT;//Hello WorldCombined comparison operator (<=>)
Combined comparison operator is used to compare two An expression. When a is less than, equal to or greater than b, it returns -1, 0 or 1 respectively. The principle of comparison is to follow the general comparison rules of PHP.
//整数echo 1 <=> 1; // 0echo 1 <=> 2; // -1echo 2 <=> 1; // 1//浮点数echo 1.5 <=> 1.5; // 0echo 1.5 <=> 2.5; // -1echo 2.5 <=> 1.5; // 1 //字符串echo "a" <=> "a"; // 0echo "a" <=> "b"; // -1echo "b" <=> "a"; // 1
Variable type declaration
Two modes: mandatory (default) and strict mode. The following type parameters can be used: string, int, float, bool
//... 操作符: 表示这是一个可变参数. php5.6及以上的版本可使用: 函数定义的时候变量前使用.function intSum(int ...$ints){ return array_sum($ints);
}
var_dump(intSum(2,'3.5'));//5//严格模式//模式声明:declare(strict_types=1); 默认情况值为0,值为1代表为严格校验的模式 declare(strict_types=1);function add(int $a,int $b){ return $a+$b;
}
var_dump(add(2,'3.5')); //Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Argument 2 passed to add() must be of the type integerReturn value type declaration
Add support for return type declaration .Similar to parameter type declaration. (For usage, add: type name after the function definition)
1 //有效的返回类型2 declare(strict_types = 1);3 function getInt(int $value): int {4 return $value;5 }6 print(getInt(6));//61 //无效返回类型2 declare(strict_types = 1);3 function getNoInt(int $value): int {4 return $value+'2.5';5 }6 print(getNoInt(6));//Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: Return value of getNoInt() must be of the type integerAnonymous class
Allows new class {} to create an anonymous object.
<?php//php7以前 接口实现interface User{ public function getDiscount();
}class VipUser implements User{ //折扣系数
private $discount = 0.6; public function getDiscount() { return $this->discount;
}
}class Goods{ private $price = 200; private $objectVipUser; //User接口VipUser类实现
public function getUserData(User $User){ $this->objectVipUser = $User;
$discount = $this->objectVipUser->getDiscount(); echo "商品价格:".$this->price*$discount;
}
}
$display = new Goods();//常规实例化接口实现对象$display->getUserData(new VipUser);//商品价格:120<?php//php7 创建一个匿名的对象interface User{ public function getDiscount();
}class Goods{ private $price = 200; private $objectVipUser; public function getUserData($User){ $this->objectVipUser = $User;
$discount = $this->objectVipUser->getDiscount(); echo "商品价格:".$this->price*$discount;
}
}
$display = new Goods();//new匿名对象实现user接口$display->getUserData(new class implements User{ private $discount = 0.6; public function getDiscount() { return $this->discount;
}
});//商品价格:120Closure::call()
The Closure::call() method was added as a short way to temporarily bind an object scope to a closure and call it. Compared to PHP5's bindTo .Its performance is much faster.
<?php//php7以前class A { private $attribute = 'hello world';
}
$getClosure = function(){ return $this->attribute;
};
$getAttribute = $getClosure->bindTo(new A, 'A');//中间层闭包echo $getAttribute();//hello world<?php//PHP7class A { private $attribute = 'hello world';
}
$getClosure = function(){ return $this->attribute;
};echo $getClosure->call(new A);//hello worldunserialize()
unserialize() function: filtering feature can prevent illegal data from being injected into the code, providing safer deserialization Data
<?php class A{
public $name = 'admin_a';
}
class B{
public $name = 'admin_b';
}
$objA = new A();
$objB = new B();
$serializedObjA = serialize($objA);
$serializedObjB = serialize($objB);
//默认行为是接收所有类; 第二个参数可以忽略$dataA = unserialize($serializedObjA , ["allowed_classes" => true]);
var_dump($dataA);//object(A)#3 (1) { ["name"]=> string(7) "admin_a" }//如果allowed_classes设置为false,unserialize会将所有对象转换为__PHP_Incomplete_Class对象 $dataA = unserialize($serializedObjA , ["allowed_classes" => false]);
var_dump($dataA);//object(__PHP_Incomplete_Class)#4 (2) { ["__PHP_Incomplete_Class_Name"]=> string(1) "A" ["name"]=> string(7) "admin_a" }//转换所有对象到 __PHP_Incomplete_Class对象,除了对象"B"$dataB = unserialize($serializedObjB , ["allowed_classes" => ["B"]]);
var_dump($dataB);//object(B)#3 (1) { ["name"]=> string(7) "admin_b" }IntlChar
IntlChar: Provides access to some utility methods that can be used to access Unicode character information. NOTE: The Intl extension must be installed to use!
1 var_dump(IntlChar::CODEPOINT_MAX);//int(1114111) 2 echo '<br>';3 var_dump(IntlChar::charName('+'));//string(9) "PLUS SIGN" 4 echo '<br>';5 var_dump(IntlChar::ispunct('?'));//bool(true)
CSPRNG
The CSPRNG function provides a simple mechanism to generate cryptographic random numbers.
random_bytes() - Cryptographically protected pseudo-random string.
random_int() - Cryptographically protected pseudo-random integers.
1 $bytes = random_bytes(8); 2 echo(bin2hex($bytes));//随机2073a110a2e3c4973 echo '<br>';4 echo(random_int(1, 999));//随机7865 echo '<br>';6 print(random_int(-999, -1));//随机-357
use statement
You can use a single use statement to import classes, functions, and constants from the same namespace, instead of using multiple use statements.
//PHP7之前use some\namespace\ClassA;use some\namespace\ClassB;use some\namespace\ClassC as C;use function some\namespace\fn_a;use function some\namespace\fn_b;use function some\namespace\fn_c;use const some\namespace\ConstA;use const some\namespace\ConstB;use const some\namespace\ConstC;// PHP7之后use some\namespace\{ClassA, ClassB, ClassC as C};use function some\namespace\{fn_a, fn_b, fn_c};use const some\namespace\{ConstA, ConstB, ConstC};intp
The newly added intp() function receives two parameters and the return value is the value of the first parameter divided by the second parameter and rounded.
1 echo intp(8,4);//22 echo intp(10,4);//23 echo intp(5,10);//0
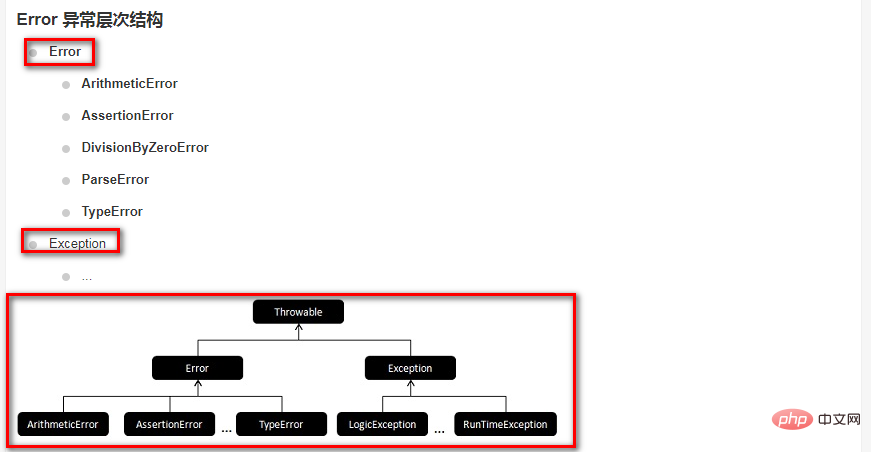
PHP7 Error Handling
PHP7 has changed the way most errors are reported. Unlike the traditional error reporting mechanism of PHP5, most errors are now thrown as Error exceptions.
This An Error exception can be caught by a try/catch block like a normal exception. If there is no matching try/catch block, the exception handling function (registered by set_exception_handler()) is called for processing.
If the exception handling function has not been registered, It is handled in the traditional way: it is reported as a fatal error (Fatal Error).
The Error class is not extended from the Exception class, so code such as catch (Exception $e) { ... } cannot be caught. to Error. You can use code like catch (Error $e) { ... },
or catch Error by registering an exception handling function (set_exception_handler()).
<?php//php7以前 自定义异常处理class getException extends Exception{ public function errorMsg(){ return '错误的信息'.$this->getMessage().'<br>错误的代码'.$this->getCode();
}
}try {
$num =10; if($num > 1) { throw new getException($num,404);
}
} catch (getException $e) { echo $e->errorMsg();
}Recommended tutorial: "PHP Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the understanding and comparison of new features of php7. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52

