How many parts does an HTTP message consist of?
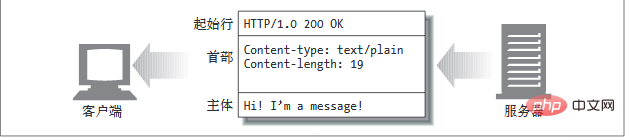
HTTP message consists of 3 parts, namely: 1. The starting line [start line] that describes the message; 2. The header [header] block containing attributes; 3. Optional, Contains the main body part of the data.

##HTTP message consists of 3 parts:
- Describes the message A start line,
- a header block containing attributes,
- , and optionally a body containing data (body) part.
Related learning recommendations:This is the format of the request message:
//是为服务器端提供一些额外的信息 <method> <request-URL> <version> <headers> <entity-body>
//为客户端提供一些额外的信息 <version> <status> <reason-phrase> <headers> <entity-body>
The following is a brief description of each part.
1. Method The action the client wants the server to perform on the resource. is a single word, such as GET, HEAD, or POST. Methods are detailed later in this chapter. 2. Request URL (request-URL) names the requested resource, or the complete URL of the URL path component. If you're talking to the server directly, there's usually no problem as long as the path component of the URL is an absolute path to the resource - the server can assume it's the host/port of the URL. Chapter 2 introduces the syntax of URL in detail. 3. Version Status code (status-code) These three digits describe what happened during the request. The first digit of each status code is used to describe the general category of status ("success", "error", etc.). A complete list of status codes and their meanings defined by the HTTP specification are provided later in this chapter. 4. Reason phrase A human-readable version of the numeric status code, including all text before the line termination sequence. Examples of reason phrases for all status codes defined by the HTTP specification are provided later in this chapter. Reason phrases only have meaning to humans, so, for example, although the meaning of the reason phrase in the response linesHTTP/1.0 200 NOT OK and HTTP/1.0 200 OK is different, both will is treated as a success indication.
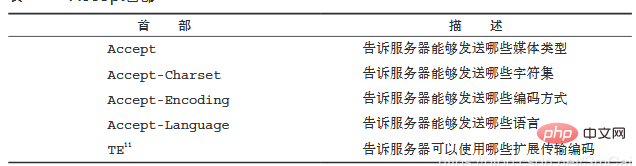 ## // Tell the server which media types it can send
## // Tell the server which media types it can send
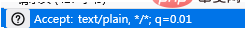 //Tell the server which encoding methods you can send
//Tell the server which encoding methods you can send
The above is the detailed content of How many parts does an HTTP message consist of?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What does http status code 520 mean?
Oct 13, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
What does http status code 520 mean?
Oct 13, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
HTTP status code 520 means that the server encountered an unknown error while processing the request and cannot provide more specific information. Used to indicate that an unknown error occurred when the server was processing the request, which may be caused by server configuration problems, network problems, or other unknown reasons. This is usually caused by server configuration issues, network issues, server overload, or coding errors. If you encounter a status code 520 error, it is best to contact the website administrator or technical support team for more information and assistance.
 What is http status code 403?
Oct 07, 2023 pm 02:04 PM
What is http status code 403?
Oct 07, 2023 pm 02:04 PM
HTTP status code 403 means that the server rejected the client's request. The solution to http status code 403 is: 1. Check the authentication credentials. If the server requires authentication, ensure that the correct credentials are provided; 2. Check the IP address restrictions. If the server has restricted the IP address, ensure that the client's IP address is restricted. Whitelisted or not blacklisted; 3. Check the file permission settings. If the 403 status code is related to the permission settings of the file or directory, ensure that the client has sufficient permissions to access these files or directories, etc.
 Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand common application scenarios of web page redirection and understand the HTTP 301 status code
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:41 PM
Understand the meaning of HTTP 301 status code: common application scenarios of web page redirection. With the rapid development of the Internet, people's requirements for web page interaction are becoming higher and higher. In the field of web design, web page redirection is a common and important technology, implemented through the HTTP 301 status code. This article will explore the meaning of HTTP 301 status code and common application scenarios in web page redirection. HTTP301 status code refers to permanent redirect (PermanentRedirect). When the server receives the client's
 How to use Nginx Proxy Manager to implement automatic jump from HTTP to HTTPS
Sep 26, 2023 am 11:19 AM
How to use Nginx Proxy Manager to implement automatic jump from HTTP to HTTPS
Sep 26, 2023 am 11:19 AM
How to use NginxProxyManager to implement automatic jump from HTTP to HTTPS. With the development of the Internet, more and more websites are beginning to use the HTTPS protocol to encrypt data transmission to improve data security and user privacy protection. Since the HTTPS protocol requires the support of an SSL certificate, certain technical support is required when deploying the HTTPS protocol. Nginx is a powerful and commonly used HTTP server and reverse proxy server, and NginxProxy
 Send POST request with form data using http.PostForm function
Jul 25, 2023 pm 10:51 PM
Send POST request with form data using http.PostForm function
Jul 25, 2023 pm 10:51 PM
Use the http.PostForm function to send a POST request with form data. In the http package of the Go language, you can use the http.PostForm function to send a POST request with form data. The prototype of the http.PostForm function is as follows: funcPostForm(urlstring,dataurl.Values)(resp*http.Response,errerror)where, u
 Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files
Sep 12, 2023 pm 01:15 PM
Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files
Sep 12, 2023 pm 01:15 PM
Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files With the development of the Internet, the file download function has become one of the basic needs of many websites and applications. For scenarios where multiple files need to be downloaded at the same time, the traditional synchronous download method is often inefficient and time-consuming. For this reason, using PHP to download multiple files asynchronously over HTTP has become an increasingly common solution. This article will analyze in detail how to use PHP asynchronous HTTP through an actual development case.
 Common network communication and security problems and solutions in C#
Oct 09, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
Common network communication and security problems and solutions in C#
Oct 09, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
Common network communication and security problems and solutions in C# In today's Internet era, network communication has become an indispensable part of software development. In C#, we usually encounter some network communication problems, such as data transmission security, network connection stability, etc. This article will discuss in detail common network communication and security issues in C# and provide corresponding solutions and code examples. 1. Network communication problems Network connection interruption: During the network communication process, the network connection may be interrupted, which may cause
 http request 415 error solution
Nov 14, 2023 am 10:49 AM
http request 415 error solution
Nov 14, 2023 am 10:49 AM
Solution: 1. Check the Content-Type in the request header; 2. Check the data format in the request body; 3. Use the appropriate encoding format; 4. Use the appropriate request method; 5. Check the server-side support.



