Understanding and learning about Proxy objects
1. What exactly is the Proxy object?
What exactly is the Proxy object? Proxy means proxy. The function of the proxy object is to create a proxy object through Proxy, and then operate the proxy object to allow you to customize some behaviors of the specified object.
Proxy(target,handler); The Proxy constructor receives two objects. The first parameter is the object to be processed, and the second parameter is the collection of methods to be customized (that is, an object). .
Very abstract? In fact, it is very similar to Object.defineProperty in js (that is, the accessor property, which is used to implement the bottom layer of vue2.x).
Object.defineProperty defines accessor properties, which can control the reading and writing behavior of a certain property. It can also be done in Proxy, and Proxy is more flexible and powerful. It can do many things with accessor properties. Things that can’t be accomplished.
For example, listen for attribute deletion events (delete obj.prop;), in events ('id' in obj;), apply calls, etc.
Let’s first take a look at what the proxy object contains.
var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {};
// 此处,我们先不对targetObj的行为进行干预,所以传个空对象进去即可。
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
console.log(proxy);Look at what the printed proxy is, as shown below.
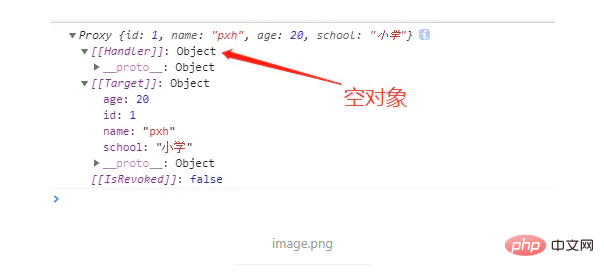
As you can see, the proxy object contains the Handler attribute, Target attribute and IsRevoked. Their values are the handler we passed in, targetObj and false respectively.
This isRevoked indicates whether it is revocable. Use the Proxy.revocable() method to generate a revocable proxy object. For details, you can go to MDN to view the documentation.
2. Operate the original object through the Proxy object
Above we created a proxy object, now we try to operate the original object by operating the proxy object, operating the proxy object is the same as operating the native object That’s it. (Actually, the proxy object is mapped internally.)
var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {};
// 此处,我们先不对targetObj的行为进行干预,所以传个空对象进去即可。
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
/**
* 1、读取及修改属性,可以看到原来的对象的属性也被修改了
*/
console.log(proxy.age); // 20
console.log(targetObj.age); // 20
proxy.age = 22;
console.log(proxy.age); // 22
console.log(targetObj.age); // 22
/**
* 2、删除proxy对象的属性,影响原来的对象的属性
*/
console.log(proxy.school); // 小学
console.log(targetObj.school); // 小学
delete proxy.age;
console.log(proxy.school); // undefined
console.log(targetObj.school); // undefined3. Set method and get method
Okay, now we can start to interfere with the behavior of the original object. Specifically, we implement the following methods Achieve the purpose of intervening in the target's behavior.
handler.apply
handler.construct Intervene in the new behavior of the constructor
- ##handler. defineProperty Intervenes in the object’s data attribute or accessor attribute definition
- handler.deleteProperty Intervenes in the object’s property deletion behavior
- handler.get Intervenes in the object’s Attribute reading behavior
- handler.getOwnProperty Intervening the characteristic value of the object's attribute ##handler.has Intervening in the object's in behavior (prop in obj )
- handler.isExtensible
- handler.ownKeys
- ##handler.set Set the behavior
...
- First intervene in the get behavior (attribute reading behavior)
var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {
// 定义get方法,get方法可以接收2个参数,分别是原来的对象及属性
get : function(target,prop){
console.log(`${prop}属性正在被查看`);
console.log(targetObj == target); // true
return target[prop];
}
};
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
console.log(proxy.id);
/**
* 可以看到,打印顺序为:
* id属性正在被查看
* true
* 1
*/ var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {
// 定义get方法,get方法可以接收2个参数,分别是原来的对象及属性
get : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id'){
return undefined;
}
return target[prop];
},
// 定义set方法,set方法比get多1个参数,那就是该属性修改时的值
set : function(target,prop,value){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许修改${prop}属性`)
}else{
target[prop] = value;
}
}
};
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
/**
* 修改属性,分别打印
* 不允许修改id属性
* 不允许修改name属性
* 不允许修改age属性
*/
proxy.id = 2;
proxy.name = 'pxh222';
proxy.age = 23;
proxy.school = '中学'; // 这个无打印
/**
* 读取属性,可以看到分别打印
* undefined
* pxh
* 20
* 中学 // 这个没有拦截,因此可以修改
*/
console.log(proxy.id);
console.log(proxy.name);
console.log(proxy.age);
console.log(proxy.school); var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {
// 在handler中定义get方法,get方法可以接收2个参数,分别是原来的对象及属性
get : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id'){
return undefined;
}
return target[prop];
},
// set方法比get多1个参数,那就是该属性修改时的值
set : function(target,prop,value){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许修改${prop}属性`)
}else{
target[prop] = value;
}
},
/**
* 这个方法要求返回个boolean值,表示是否删除成功
* 如果返回的值不是boolean值,则会进行类型转换成boolean值再返回
*/
deleteProperty : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许删除${prop}属性`);
return false;
}else{
delete target[prop];
return true;
}
}
};
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
/**
* 尝试删除id属性,可以看到打印顺序为:
* 不允许删除id属性
* false
*/
console.log(delete proxy.id);
/**
* 删除school属性,可以看到打印
* true
* undefined
*/
console.log(delete proxy.school);
console.log(proxy.school);Copy after login
5. Intervene in prop in obj behavior (determine whether the object has a certain attribute) Above we are not allowed to obtain the id value of the object, nor can we modify or delete it. Now we put it Hide it. var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {
// 在handler中定义get方法,get方法可以接收2个参数,分别是原来的对象及属性
get : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id'){
return undefined;
}
return target[prop];
},
// set方法比get多1个参数,那就是该属性修改时的值
set : function(target,prop,value){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许修改${prop}属性`)
}else{
target[prop] = value;
}
},
/**
* 这个方法要求返回个boolean值,表示是否删除成功
* 如果返回的值不是boolean值,则会进行类型转换成boolean值再返回
*/
deleteProperty : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许删除${prop}属性`);
return false;
}else{
delete target[prop];
return true;
}
}
};
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
/**
* 尝试删除id属性,可以看到打印顺序为:
* 不允许删除id属性
* false
*/
console.log(delete proxy.id);
/**
* 删除school属性,可以看到打印
* true
* undefined
*/
console.log(delete proxy.school);
console.log(proxy.school); var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {
// 在handler中定义get方法,get方法可以接收2个参数,分别是原来的对象及属性
get : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id'){
return undefined;
}
return target[prop];
},
// set方法比get多1个参数,那就是该属性修改时的值
set : function(target,prop,value){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许修改${prop}属性`)
}else{
target[prop] = value;
}
},
/**
* 这个方法要求返回个boolean值,表示是否删除成功
* 如果返回的值不是boolean值,则会进行类型转换成boolean值再返回
*/
deleteProperty : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许删除${prop}属性`);
return false;
}else{
delete target[prop];
return true;
}
},
/**
* 通过has 方法来控制,返回值也是个boolean,表示对象是否拥有某个属性
* 如果返回的值不是boolean值,则会进行类型转换成boolean值再返回
*/
has : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id'){
return false
}else{
return prop in target;
}
}
};
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
console.log('id' in proxy); // false
console.log('name' in proxy); // trueCopy after login
6. SummarySimilarly, proxy can also intervene in many objects’ behaviors, so I won’t introduce them one by one here. If you are interested, please click on the MDN document Recommended tutorial: " var targetObj = {
id : 1,
name : 'pxh',
age : 20,
school : '小学'
}
var handler = {
// 在handler中定义get方法,get方法可以接收2个参数,分别是原来的对象及属性
get : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id'){
return undefined;
}
return target[prop];
},
// set方法比get多1个参数,那就是该属性修改时的值
set : function(target,prop,value){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许修改${prop}属性`)
}else{
target[prop] = value;
}
},
/**
* 这个方法要求返回个boolean值,表示是否删除成功
* 如果返回的值不是boolean值,则会进行类型转换成boolean值再返回
*/
deleteProperty : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id' || prop == 'name' || prop == 'age'){
console.log(`不允许删除${prop}属性`);
return false;
}else{
delete target[prop];
return true;
}
},
/**
* 通过has 方法来控制,返回值也是个boolean,表示对象是否拥有某个属性
* 如果返回的值不是boolean值,则会进行类型转换成boolean值再返回
*/
has : function(target,prop){
if(prop == 'id'){
return false
}else{
return prop in target;
}
}
};
var proxy = new Proxy(targetObj,handler);
console.log('id' in proxy); // false
console.log('name' in proxy); // trueWeChat Mini Program
"The above is the detailed content of Understanding and learning about Proxy objects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 Nginx Proxy Manager configuration analysis and optimization
Sep 26, 2023 am 09:24 AM
Nginx Proxy Manager configuration analysis and optimization
Sep 26, 2023 am 09:24 AM
Overview of NginxProxyManager configuration analysis and optimization: NginxProxyManager is a reverse proxy management tool based on Nginx, which can help us easily configure and manage reverse proxy servers. In the process of using NginxProxyManager, we can improve the performance and security of the server by parsing and optimizing its configuration. Configuration analysis: Configuration file location and structure: NginxProxyManag
 How to configure and use proxy protocol in nginx
May 18, 2023 am 08:47 AM
How to configure and use proxy protocol in nginx
May 18, 2023 am 08:47 AM
When proxyprotocol is used in nginx, we know that nginx is a web server and proxy server. It generally works behind proxyserver or load balancing software (Haproxy, Amazon Elastic LoadBalancer (ELB)). The client first requests proxyserver or LSB load balancing software, and then to nginx Perform real web access. Because it has gone through multiple layers of software, some client information such as IP address, port number, etc. may be hidden, which is detrimental to our problem analysis and data statistics. Because for nginx, We want to be able to get real clients
 Deployment strategy of containers and microservices under Nginx Proxy Manager
Sep 27, 2023 pm 01:06 PM
Deployment strategy of containers and microservices under Nginx Proxy Manager
Sep 27, 2023 pm 01:06 PM
The deployment strategy of containers and microservices under NginxProxyManager requires specific code examples. Summary: With the popularity of microservice architecture, containerization technology has become an important part of modern software development. In the microservice architecture, NginxProxyManager plays a very important role, used to manage and proxy the traffic of microservices. This article will introduce how to use NginxProxyManager to deploy and manage containerized microservices, and provide relevant code examples.
 How to use Nginx Proxy Manager to achieve load balancing of multiple servers
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:42 PM
How to use Nginx Proxy Manager to achieve load balancing of multiple servers
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:42 PM
How to use NginxProxyManager to achieve load balancing of multiple servers. NginxProxyManager is a proxy server management tool developed based on Nginx. It provides a simple and easy-to-use Web interface that can easily configure and manage Nginx proxy servers. In practical applications, we often need to distribute requests to multiple servers to achieve load balancing and improve system performance and availability. This article will introduce how to use NginxProx
 Nginx Proxy Manager Tutorial: Quick Start Guide
Sep 27, 2023 pm 05:39 PM
Nginx Proxy Manager Tutorial: Quick Start Guide
Sep 27, 2023 pm 05:39 PM
NginxProxyManager Tutorial: Quick Start Guide, Specific Code Examples Needed Introduction: With the development of network technology, proxy servers have become a part of our daily use of the Internet. NginxProxyManager is a proxy server management platform based on Nginx, which can help us quickly establish and manage proxy servers. This article will introduce you to the quick start guide of NginxProxyManager, as well as some specific code examples. one
 Log analysis and monitoring of Nginx Proxy Manager
Sep 26, 2023 am 09:21 AM
Log analysis and monitoring of Nginx Proxy Manager
Sep 26, 2023 am 09:21 AM
Log analysis and monitoring of NginxProxyManager requires specific code examples. Introduction: NginxProxyManager is a proxy server management tool based on Nginx. It provides a simple and effective method to manage and monitor proxy servers. In actual operation, we often need to analyze and monitor the logs of NginxProxyManager in order to discover potential problems or optimize performance in time. This article will introduce how to use some commonly used
 Nginx Proxy Manager implements cache acceleration of HTTP requests
Sep 26, 2023 am 10:53 AM
Nginx Proxy Manager implements cache acceleration of HTTP requests
Sep 26, 2023 am 10:53 AM
NginxProxyManager is a tool for managing Nginx proxy servers. By using it, you can achieve cache acceleration of HTTP requests. The following will introduce in detail how to use NginxProxyManager to implement cache acceleration and provide specific code examples. 1. Install and configure NginxProxyManager Install NginxProxyManager: $npminstall-g@nginx
 Nginx Proxy Manager Principles and Practice: The Key to Optimizing Website Performance
Sep 26, 2023 am 11:06 AM
Nginx Proxy Manager Principles and Practice: The Key to Optimizing Website Performance
Sep 26, 2023 am 11:06 AM
NginxProxyManager Principle and Practice: The key to optimizing website performance, specific code examples are required Introduction: In today's Internet era, website performance is crucial to user experience and search engine optimization. In order to improve the performance of the website, an effective method is to use Nginx as a reverse proxy server to manage and distribute traffic. This article will introduce the principles and practices of NginxProxyManager and show how to optimize the website through NginxProxyManager




