
Basic Linux operations include: 1. [passwd] is to set a password; 2. [su] is to switch users; 3. [who] is to view online users; 4. [whoami] is to view the current user User; 5. [hostname] displays the host name, etc.

The basic operations of Linux are:
1. Overview
1. Common operating systems
Server operating systems: linux, unix, windows server
Stand-alone operating systems: windows (dos, ucdos, win95, win98, win2000, XP, Vista, Win7, Win8)
Mac, Linux (Ubuntu)
mobile operating system Android, iOS, Windows Phone
# 2, Linux operating system introduction introduction
Linux is a free and open source UNIX-like operating system. It has openness, multi-user, multi-tasking, rich network functions, reliable system security, and good portability. Good user interface (command interface, graphical interface, etc.), excellent speed performance and other advantages. Now it is mainly used for:
2. Linux system environment
By default, there are 6 command interaction channels and a graphical interface interaction channel. The graphical interface channel is entered by default:1. Graphical interface interaction mode
2. Command interaction mode
shen@ubuntu:~$
shen: Username
ubuntu: Host name
~ : Path, if the current If the path is exactly the root directory where the user stores data, it will display ~
$: Type of user $ represents ordinary user # represents super User
3. Commonly used commands
(press tab to create automatic completion)1. Log out, Shut down and restart
shutdown -rTime (permission issues are similar to the above)
2. System command
sudo apt-get update
Update system
whoami : View the current user, such as
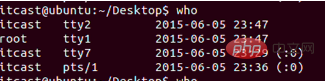
Which window tty2 represents (ctrl alt f2), pts/1 represents the terminal opened in the graphical interface.
hostname: Display host name
##uname: Display system information
a : Display complete system information
top: Display information on the current time-consuming process (part), every 3 Refresh once every second, similar to Windows Task Manager (cltr c interrupt)
ps : Display a snapshot of the current process (all)
df :Disk usage (disk free)
ifconfig :View or Configure the network card information, such as ipconfig of windows
ping Test the connection with the target host
netstat in this machine (cmd): Network connection details
clear : Clear the screen (windows: cls)
man: Help command
kill: kill process (kill pid)
useradd : Add user
hadoop:x:1000:1000:UbuntuA,,,:/home/hadoop:/bin/bash
hadoop:Username
x: Password: Already encrypted, the password is stored in /etc/shadow
1000: Account id, userId
1000: Group id, group id
UbuntuA,,,: Account description
/ home/hadoop: The default location where the account stores files ~
/bin/bash: The user’s shell script parsing method, sh, bash, rbash
/home/lijing directory (create the "lijing" file under home )
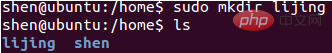
useradd command

passwd to set the password
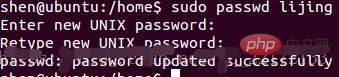
suSwitch user
Related learning recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of What are the basic operations of Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!