

How to improve the performance of Web pages, many developers start from many aspects, such as JavaScript, image optimization, server configuration, file compression or adjusting CSS. It's clear that HTML has reached a bottleneck, even though it is the core language necessary for developing Web interfaces. The load of HTML pages is also getting heavier and heavier. Most pages require an average of 40K of space. For example, some large websites contain thousands of HTML elements, and the page size will be larger.
How to effectively reduce the complexity of HTML code and the number of page elements. This article mainly solves this problem. It introduces how to write concise and clear HTML code from many aspects, which can make the page load faster. , and can run well on a variety of devices.
The following principles need to be followed during the design and development process:
Structural separation: Use HTML to add structure, not style content;
Keep it tidy: Add code validation tools to your workflow; use tools or style wizards to maintain code structure and format
Learn a new language: Get element structure and semantic markup.
Ensure accessibility: Use ARIA attributes and Fallback attributes, etc.
Test: Make the website run well on multiple devices and can be used emulators and performance tools.
##The relationship between HTML, CSS and JavaScript
HTML is used to adjust the page structure and The content's markup language. HTML cannot be used to modify style content, nor can you enter text content in the header tag, making the code lengthy and complex. Instead, it is more appropriate to use CSS to modify layout elements and appearance. The default appearance of HTML elements is defined by the browser's default style sheet. For example, in Chrome, the h1 tag element will be rendered into a 32px Times bold font. Three general design rules:The document structure can also be optimized, as follows:
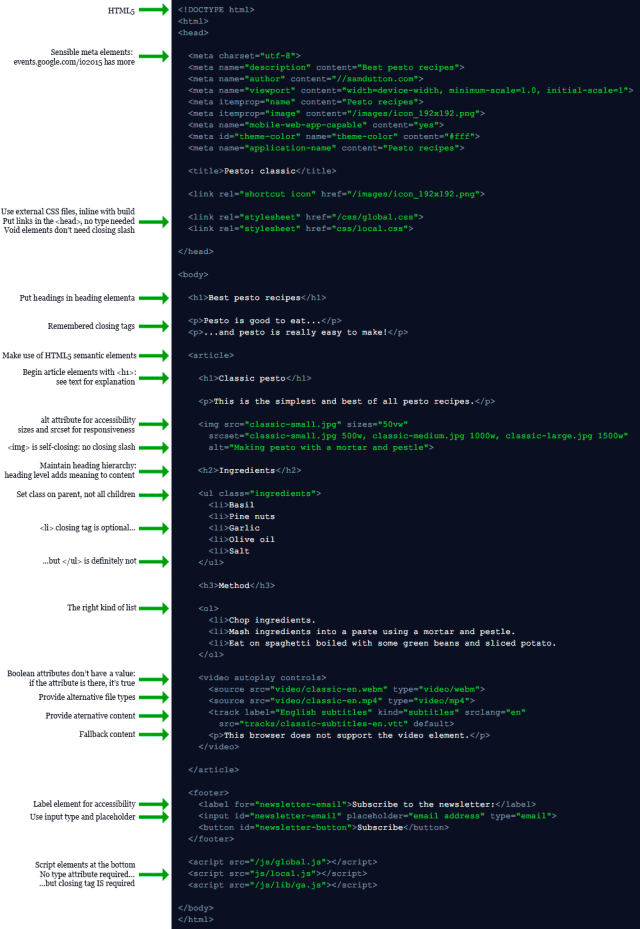
Use the HTML5 document type, the following is an empty file:<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Recipes: pesto</title> </head> <body> <h1>Pesto</h1> <p>Pesto is good!</p> </body> </html>
<head> <title>My pesto recipe</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/css/global.css"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/local.css"> </head>
<body> ... <script src="/js/global.js"> <script src="js/local.js"> </body>
<head> ... <script src="js/local.js"> </head> <body onload="init()"> ... <button onclick="handleFoo()">Foo</button> ... </body>
index.html:
<head> ... </head> <body> ... <button id="foo">Foo</button> ... <script src="js/local.js"> </body>
init();
var fooButton =
document.querySelector('#foo');
fooButton.onclick = handleFoo();Verification
One way to optimize a web page is that the browser can Handle illegal HTML code. Legal HTML code is easy to debug, takes up less memory, consumes less resources, is easy to parse, renders and runs faster. Illegal HTML code makes it extremely difficult to implement responsive design. When using templates, legal HTML code is extremely important. It often happens that templates run well alone but report various errors when integrated with other modules. Therefore, the quality of HTML code must be ensured. , you can take the following measures:Code format
Format consistency makes HTML code easy to read, understand, optimize, and debug.Semantic tags
Semantic refers to things related to meaning. HTML can see semantics from the content of the page: the naming of elements and attributes expresses the role of the content to a certain extent. and function. HTML5 introduces new semantic elements such as