

1. The difference between String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder
(Related tutorial recommendations: java interview questions)
The value of String is immutable, which results in a new String object being generated every time an operation is performed on String.
Objects of the StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes can be modified multiple times without generating new unused objects
The speed is: StringBuilder > StringBuffer > String
The biggest difference between the StringBuilder class and StringBuffer is that StringBuilder's methods are not thread-safe.
Look at the picture:
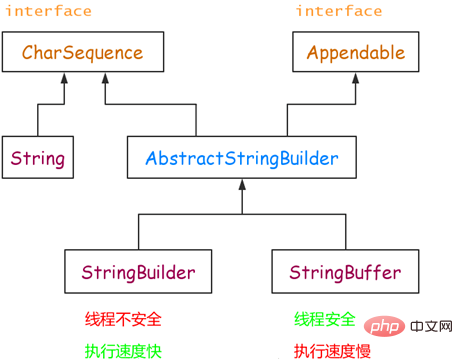
(Recommended tutorial: java entry program)
2. All All classes inherit from the object class. What are the direct subclasses of the object class that you have used? What are the commonly used methods of the object class?
Boolean
Character
Class
ClassLoader
Compiler
Enum
String
System
Thread
Common methods of Object class
toString ();
3. What are generics, how are they used, and what are their benefits?
is a special type that defers the work of type clarification until when the object is created or the method is called. Parameterized type, pass the type as a parameter. It is a design pattern that supports polymorphism very well, such as various containers. Benefits: Advances runtime problems to the compilation period, avoiding forced type conversion.4. Why should serialversionUID be used for Java object serialization?
1. Why serialize objects?java video tutorial)
5. Advantages and disadvantages of reflection
1. AdvantagesReflection improves the flexibility and scalability of Java programs, reduces coupling, and improves adaptive capabilities. It allows programs to create and control objects of any class without raising the hard-coded target class. Reflection is not available in some other commonly used languages, such as C, C, Fortran or Pascal. Java reflection technology has a wide range of applications, such as software testing, JavaBean, etc. Many popular open source frameworks such as Struts, Hibernate, and Spring use this technology in their implementation. 2. Disadvantages (1) Performance OverheadReflection includes some dynamic types, so the JVM cannot optimize these codes. Therefore, reflective operations are much less efficient than those non-reflective operations. We should avoid using reflection in frequently executed code or in programs with high performance requirements. (2) Security RestrictionsUsing reflection technology requires that the program must run in an environment without security restrictions. This is a problem if a program must run in a security-restricted environment, such as an applet. . (3) Exposure of InternalsSince reflection allows code to perform some operations that are not allowed under normal circumstances (such as accessing private properties and methods), using reflection may cause leading to unexpected side effects. The code has functional errors that reduce portability. Reflective code breaks abstraction, so when the platform changes, the behavior of the code may also change.The above is the detailed content of Collection of classic Java interview questions (3). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!