Detailed explanation of session expiration time in laravel
The following tutorial column from Laravel will introduce you to the session expiration time in laravel. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!

In the process of project development, the front-end and back-end separation need to use session to save the user’s login information
This involves the validity period of the session
Session is divided into session validity period in php and session validity period in laravel
Their default validity period is
View session.gc_maxlifetime in php.ini
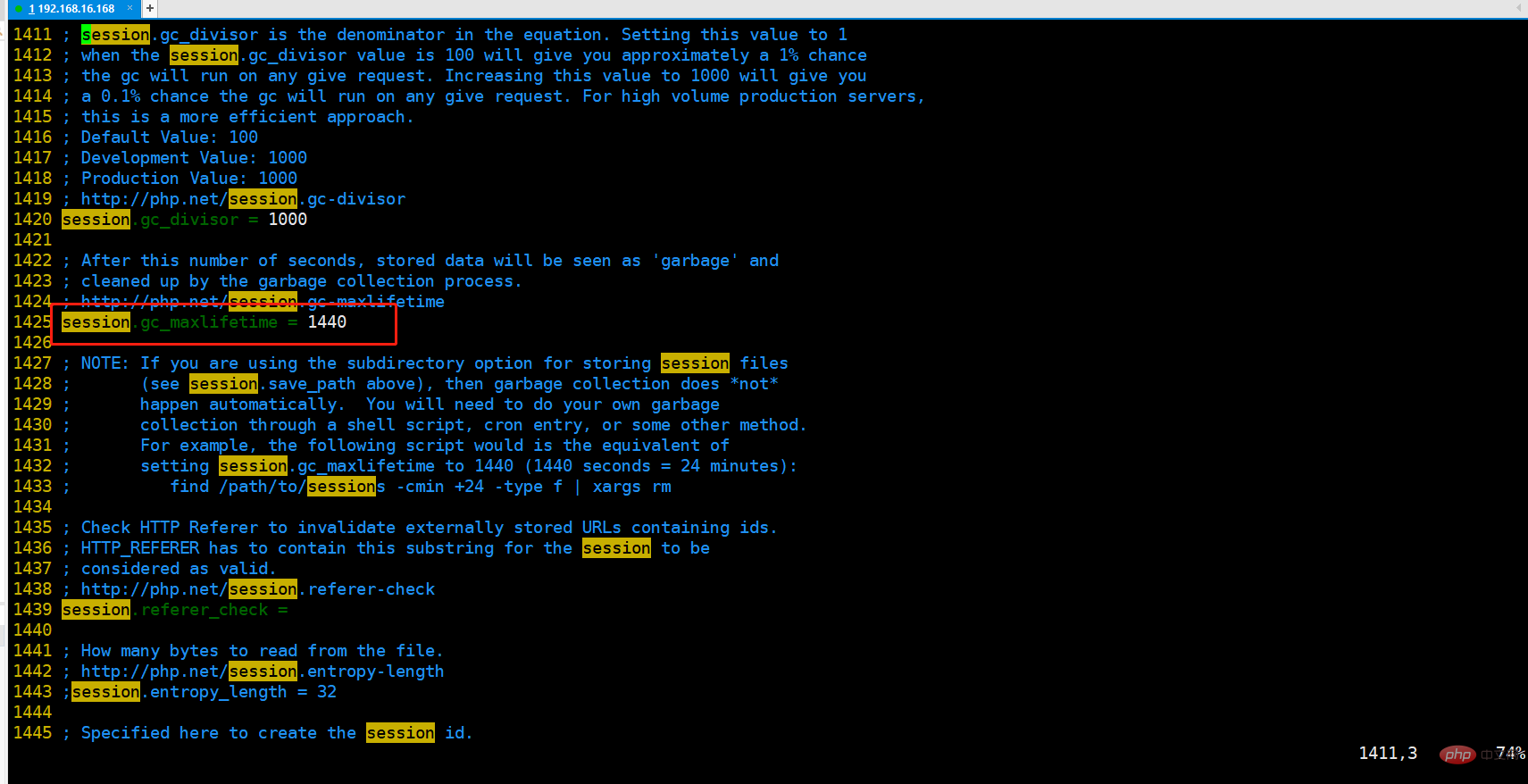
The default is 1440 seconds, which is almost 24 minutes
And laravel's session validity period is in config/session.php
'lifetime' => 120, 'expire_on_close' => false,
If 'expire_on_close' is set to If false, 'lifetime' is valid. If 'expire_on_close' is set to true, 'lifetime' is invalid.
About the specific use of laravel's session
Learning source: https://www.chenyudong .com/archives/laravel-session-use.html
Official document address: http://laravelacademy.org/post/7954.html
Use Laravel to develop applications and convert the original Copy the code. The previous code session used $_SESSION. I thought it would run well after transplanting it because it did not rely on other components. As a result, this
Undefined variable appeared: _SESSION
Laravel's session configuration file is configured in app/config/session.php. When using it, you can take a look at the option settings and comments available in the session configuration file.
Laravel uses file by default to implement session. She does not use PHP's native $_SESSION (php's native session depends on the location of php.ini), so it ignores PHP-related session functions, such as session_start(), $_SESSION. During the running process, Laravel will write session information in the app/storage/session/ directory, so this directory needs to have write permission, otherwise the session will not be written successfully.
In addition to using the default file as the session implementation, Laravel also supports cookie, Memcached, Redis and database The back-end driver serves as the implementation of session. When necessary, you need to implement a session implementation yourself, such as in the interaction between WeChat public accounts and users. The session cannot be used directly, because the WeChat server makes the request every time, and the user cannot be identified by the source of the request.
Laravel's session brief API
Session's API is relatively simple. You can probably know what it means by looking at the Chinese documentation. But there are a few that are not easy to understand.
//session的永久保存(在不过期范围内) Session::put('key', 'value'); //等同于PHP的原生session $_SESSION['key'] = 'value'; //get操作 $value = Session::get('key', 'default'); //去除操作并删除,类似pop概念 $value = Session::pull('key', 'default'); //检测是否存在key Session::has('users'); //删除key Session::forget('key');
As long as the session does not expire, this correspondence is basically saved permanently and will exist for the next http request. Different from the following flash concept.
The concept of flash in laravel's session
But Laravel came up with the concept of flash flash, which confused me all of a sudden. This flash is valid for two requests (this time and the next request are valid), regardless of how many times this request is performed.
//保存key,value Session::flash('key', 'value'); //取值方法还是一样的 Session::get('key'); //刷新快闪数据时间,保持到下次请求 Session::keep(array('username', 'email'));
The concept of this flash is different from the concept of put above.
- put: As long as the session does not expire, this correspondence is basically saved permanently and will exist for the next request.
- flash: The saved value can be used in this request and the next http request, but it will not exist the next time.
That is to say, the next request will be destroyed when it is used up. It will not make the session value become larger and larger, and some temporary data can be saved.
Usage scenarios for this situation include:
- The user requests a page, an error message appears, and is redirected to a new page, which needs to display the previous data. (Although it can be passed through url parameters, there may be XSS vulnerabilities if not handled properly).
- The user visited a page, and the filter found that it did not have permission. It saved the current page URL and redirected to the login page. If the login was successful, the value was taken out and redirected to the original page. (You may need to refresh the saved flash data here)
Session landing time
I naively thought that Session::put# was used ##The function can save this variable. So my code is written like this:
class LoginController {
public function login(){
Session::put('key','value');
print_r( Session::all() ); //取出来看看是否put成功
exit; //习惯性的调试都exit,不执行后续代码
//return Redirect::to(/); 框架在return后还会有后续的代码执行的
}
}app/storage/session directory, no file is generated. Something feels wrong.
Session::save(), so I also used it and found that the session file was successfully generated. So I felt that Laravel does not use PHP's native session, so it should do something after the controller to write the session to the file, instead of writing every put operation, which will cause IO operations Too frequent will affect performance.
bootstrap/compiled.php
class Middleware implements HttpKernelInterface
{
...
public function handle(Request $request, $type = HttpKernelInterface::MASTER_REQUEST, $catch = true)
{
$this->checkRequestForArraySessions($request);
if ($this->sessionConfigured()) {
$session = $this->startSession($request); // 启动session
$request->setSession($session);
}
$response = $this->app->handle($request, $type, $catch); // 调用controller的method
if ($this->sessionConfigured()) {
$this->closeSession($session); //关闭session
$this->addCookieToResponse($response, $session);
}
return $response;
}
...
protected function closeSession(SessionInterface $session)
{
$session->save(); // 保存session
$this->collectGarbage($session);
}
}小提示:如果不知道函数调用情况,可以在controller中throw new Exception();,然后在/config/app.php的debug更改为debug=>true。可以看到函数的调用关系。
可以看见,在调用完controller之后,调用了session->save()的方法,来主动的保存session。这样session才能落地保存起来,如果在controller或者view里面写了exit;,那么session是不会被保存的,除非主动的写Session::save()才能手工的保存起来。因此在debug调试的时候千万要注意啊。
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of session expiration time in laravel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Comparison of the latest versions of Laravel and CodeIgniter
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Comparison of the latest versions of Laravel and CodeIgniter
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
The latest versions of Laravel 9 and CodeIgniter 4 provide updated features and improvements. Laravel9 adopts MVC architecture and provides functions such as database migration, authentication and template engine. CodeIgniter4 uses HMVC architecture to provide routing, ORM and caching. In terms of performance, Laravel9's service provider-based design pattern and CodeIgniter4's lightweight framework give it excellent performance. In practical applications, Laravel9 is suitable for complex projects that require flexibility and powerful functions, while CodeIgniter4 is suitable for rapid development and small applications.
 How do the data processing capabilities in Laravel and CodeIgniter compare?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 01:34 PM
How do the data processing capabilities in Laravel and CodeIgniter compare?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 01:34 PM
Compare the data processing capabilities of Laravel and CodeIgniter: ORM: Laravel uses EloquentORM, which provides class-object relational mapping, while CodeIgniter uses ActiveRecord to represent the database model as a subclass of PHP classes. Query builder: Laravel has a flexible chained query API, while CodeIgniter’s query builder is simpler and array-based. Data validation: Laravel provides a Validator class that supports custom validation rules, while CodeIgniter has less built-in validation functions and requires manual coding of custom rules. Practical case: User registration example shows Lar
 Laravel - Artisan Commands
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Artisan Commands
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Artisan Commands - Laravel 5.7 comes with new way of treating and testing new commands. It includes a new feature of testing artisan commands and the demonstration is mentioned below ?
 Which one is more beginner-friendly, Laravel or CodeIgniter?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:50 PM
Which one is more beginner-friendly, Laravel or CodeIgniter?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:50 PM
For beginners, CodeIgniter has a gentler learning curve and fewer features, but covers basic needs. Laravel offers a wider feature set but has a slightly steeper learning curve. In terms of performance, both Laravel and CodeIgniter perform well. Laravel has more extensive documentation and active community support, while CodeIgniter is simpler, lightweight, and has strong security features. In the practical case of building a blogging application, Laravel's EloquentORM simplifies data manipulation, while CodeIgniter requires more manual configuration.
 Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Which framework is better for large projects?
Jun 04, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Which framework is better for large projects?
Jun 04, 2024 am 09:09 AM
When choosing a framework for large projects, Laravel and CodeIgniter each have their own advantages. Laravel is designed for enterprise-level applications, offering modular design, dependency injection, and a powerful feature set. CodeIgniter is a lightweight framework more suitable for small to medium-sized projects, emphasizing speed and ease of use. For large projects with complex requirements and a large number of users, Laravel's power and scalability are more suitable. For simple projects or situations with limited resources, CodeIgniter's lightweight and rapid development capabilities are more ideal.
 Questions and Answers on PHP Enterprise Application Microservice Architecture Design
May 07, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Questions and Answers on PHP Enterprise Application Microservice Architecture Design
May 07, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Microservice architecture uses PHP frameworks (such as Symfony and Laravel) to implement microservices and follows RESTful principles and standard data formats to design APIs. Microservices communicate via message queues, HTTP requests, or gRPC, and use tools such as Prometheus and ELKStack for monitoring and troubleshooting.
 Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Which framework is better for small projects?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
Laravel vs CodeIgniter: Which framework is better for small projects?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:29 PM
For small projects, Laravel is suitable for larger projects that require strong functionality and security. CodeIgniter is suitable for very small projects that require lightweight and ease of use.
 Which is the better template engine, Laravel or CodeIgniter?
Jun 03, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Which is the better template engine, Laravel or CodeIgniter?
Jun 03, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Comparing Laravel's Blade and CodeIgniter's Twig template engine, choose based on project needs and personal preferences: Blade is based on MVC syntax, which encourages good code organization and template inheritance. Twig is a third-party library that provides flexible syntax, powerful filters, extended support, and security sandboxing.




