

Statement: This article is based on Modern PHP and uses Laravel source code as an example to make it easier for everyone to study the underlying source code.
1. What is a namespace?
If you only need to know one of the modern PHP features, it should be naming space. Namespace was introduced in PHP5.3.0. Its function is to organize PHP code according to a virtual hierarchical structure. This hierarchical structure is similar to the directory structure of the file system in the operating system.
[Related recommendations: PHP Tutorial]
Namespace is the foundation of modern PHP component ecology. Modern PHP component framework codes are placed in their respective globals. in a unique vendor namespace to avoid conflict with common class names used by other vendors.
Let me take a look at how real PHP components use namespaces. The Http component in the Laravel framework is used to manage HTTP requests and responses. This component uses common class names, such as Request and Response. Many other PHP components also use such class names. Since other PHP codes also use the same class Name, how to use this component?
In fact, we can use it with confidence because the code of this component is placed in the only manufacturer namespace Illuminate.
Open the repository of this component in GitHub (https://github.com/laravel/framework/blob/master/src/Illuminate/Http/Response.php) and find Response.phpFile:
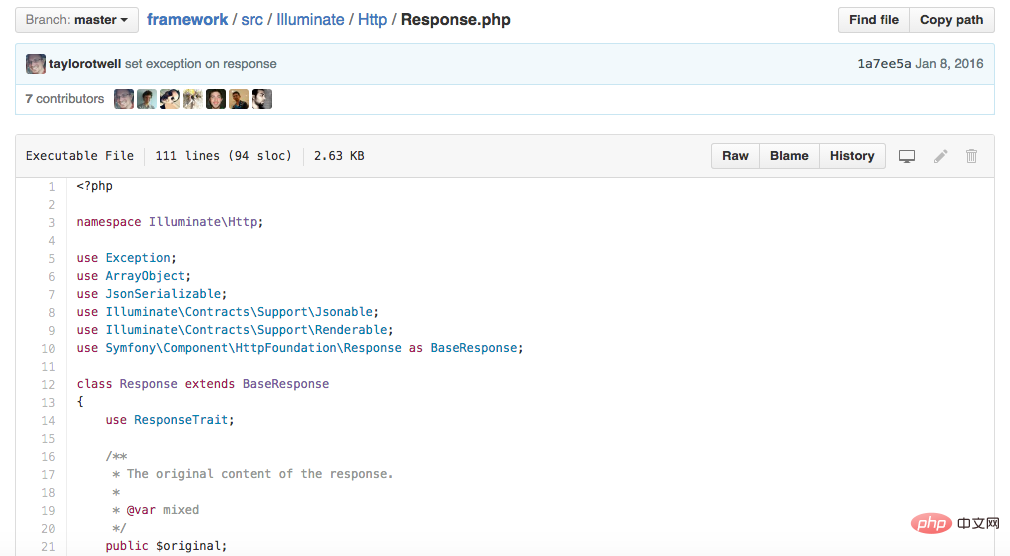
The 3rd line of code is as follows:
namespace Illuminate\Http;
This line is the PHP namespace declaration statement. The code declaring the namespace should always be placed The first line after the <?php tag. Through the declaration statement of this namespace, we can see that Response is located in the manufacturer namespace Illuminate (the top-level namespace). We also see that the Response class is in In the sub namespace Http, you can look at other files at the same level as the Response.php file and you will find that they all use the same namespace declaration statement.
The role of the namespace is to encapsulate and organize related PHP classes, just like placing related files in the same directory in the file system. The PHP namespace is different from the physical file system of the operating system. It is a virtual concept and does not necessarily have to be exactly the same as the directory structure in the file system. However, most PHP components are compatible with the widely used PSR-4 autoloading standard. The namespace will be placed in a subdirectory of the corresponding file system.
2. Why use namespaces
As mentioned earlier, our code may use the same class as other developers’ code Name, interface name, function or constant name. If the namespace is not used, the names will conflict, causing PHP execution errors. By using namespaces to place code in a unique manufacturer namespace, our code can use the same class name, interface name, function or constant name as other developers.
Of course, if you are developing a small personal project with only a few dependencies, class name conflicts may not be a problem, but if you work in a team and develop large projects that use many third-party dependencies, you must take it seriously. Naming conflict problem, because you cannot control the classes, interfaces, functions and constants introduced in the global namespace by the project dependencies, which is why namespaces are used.
3. Declare the namespace
Every PHP class, interface, function and constant is in the namespace. Declaring the namespace is very simple. , declared on the first line after the <?php tag, the declaration statement begins with namespace, followed by a space, then the name of the namespace, and finally ; end.
Namespace is often used to set the top-level vendor name. For example, we set the vendor name to LaravelAcademy:
<?php namespace LaravelAcademy;
All PHP classes declared after this namespace declaration statement, Interfaces, functions, and constants are all in the LaravelAcademy namespace and have some relationship with Laravel Academy. What if we want to organize the code used by the academy? The answer is to use subnamespaces.
The declaration method of sub-namespace is exactly the same as the previous example. The only difference is that we need to use the \ symbol to separate the namespace and sub-namespace, for example:
<?php namespace LaravelAcademy\ModernPHP;
All classes, interfaces, functions and constants after this namespace are located in LaravelAcademy\ModernPHP. Classes in the same namespace do not need to be declared in the same PHP file. You can specify a namespace or sub-namespace at the top of the PHP file. At this time, the code of this file is part of the namespace or sub-namespace. . Therefore we can write multiple classes belonging to the same namespace in different files.
注:厂商命名空间是最顶层的命名空间,也是最重要的命名空间,用于识别品牌或组织,必须具有全局唯一性。子命名空间相对而言没那么重要,但是可以用于组织项目的代码。
4、导入和别名
在命名空间出现之前,PHP开发者使用Zend风格的类名解决命名冲突问题,这是一种类的命名方案,因Zend框架而流行,这种命名方案在PHP类名中使用下划线的方式表示文件系统的目录分隔符。这种约定有两个作用:其一,确保类名是唯一的;其二,原生的自动加载器会把类名中的下划线替换成文件系统的目录分隔符,从而确定文件的路径。例如,Zend_Cloud_DocumentService_Adapter_WindowsAzure_Query类对应的文件是Zend/Cloud/DocumentService/Adapter/WindowsAzure/Query.php。可以看出,这种命名有个缺点:类名特别长。
现代的PHP命名空间也有这个问题,例如上述Response类完整的全名是Illuminate\Http\Response,幸好,我们可以通过导入以及创建别名的方式来改变这一状况。
导入的意思是指,在每个PHP文件中告诉PHP想使用哪个命名空间、类、接口、函数和常量,导入后就不用使用全名了:
<?php
use Illuminate\Http\Response;
$response = new Response(‘Oops’, 400);
$response->send();我们通过use关键字告诉PHP,我们想使用Illuminate\Http\Response类,我们只需要输入一次完全限定的类名,随后实例化Response的时候,无需使用完整的类名。
如果觉得这样的类名还是长,可以创建别名。创建别名指的是告诉PHP我要使用简单的名称引用导入的类、接口、函数或常量:
<?php
use Illuminate\Http\Response as Res;
$res = new Res(‘Oops’, 400);
$res->send();从PHP 5.6开始还可以导入函数和常量,不过要调整use关键字的句法,如果要导入函数,需要使用use func:
<?php
use func Namespace\functionName
functionName();如果想导入常量,可以使用use constant:
<?php
use constant Namespace\CONST_NAME;
echo CONST_NAME;当然也支持别名,创建方式和类一样。
5、实用技巧
多重导入
如果想要在PHP文件中导入多个类、接口、函数或常量,需要在PHP文件的顶部使用多个use语句,PHP支持用简短的语法把多个use语句写成一行:
<?php
use Illuminate\Http\Request,
Illuminate\Http\Response;但是为了可读性,建议不要这么写,还是一行写一个use语句比较好:
<?php
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Http\Response;一个文件使用多个命名空间
PHP允许在一个文件中定义多个命名空间:
<?php
namespace Foo {
//声明类、接口、函数、常量
}
namespace Bar {
//声明类、接口、函数、常量
}但这么做不好,违背了“一个文件一个类”的良好实践,因此不建议这么做。
全局命名空间
如果引用的类、接口、函数和常量没有指定命名空间,PHP假定引用的类、接口、函数和常量在当前的命名空间中。如果要使用其他命名空间的类、接口、函数或常量,需要使用完全限定的PHP类名(命名空间+类名)。
有些代码在全局命名空间中,没有命名空间,比如原生的Exception类就是这样。在命名空间中引用全局的代码时,需要在类、接口、函数或常量前加\符号:
<?php
namespace My\App;
class Foo {
public function doSomething() {
throw new \Exception();
}
}自动加载
命名空间还为PHP-FIG制定的PSR-4自动加载标准奠定了坚实的基础,大多数现代的PHP组件都使用了这种自动加载模式,使用依赖管理器Composer可以自动加载项目的依赖,后续我们还会详细介绍Composer和PHP-FIG,现在你只需要知道没有命名空间,就没有现代的PHP生态系统和基于组件的新型架构,由此可见命名空间的重要性。
相关学习推荐:PHP编程从入门到精通
The above is the detailed content of What is a namespace in PHP? Why use namespaces?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!