What is the physical unit of disk read and write operations?
The physical unit of disk read and write operations is: sector. The operating system performs read/write operations on the disk in units of sectors. A sector is the smallest physical unit in which a disk stores information.

Sector refers to the area divided on the disk. Each track on the disk is divided into several arc segments, and these arc segments are sectors of the disk. Sectors are the basic unit for hard disk reading and writing.
Each side of the disk is divided into many tracks, which are concentric circles on the surface. The closer to the center, the smaller the circles.
Each track is divided into equal parts in units of 512 bytes, called sectors. In the parameter list of some hard disks, you can see parameters describing the number of sectors for each track. It Usually marked with a range, such as 373~746, which means that the outermost track has 746 sectors, and the innermost track has 373 sectors. Therefore, it can be calculated that the capacity of the tracks is from 186.5KB to 373KB(190976B--381952B).
Disk drives read and write data to the disk in units of sectors.
On the disk, the DOS operating system allocates disk space to files in units of "clusters". The cluster of a hard disk is usually multiple sectors, which is related to the type of disk, DOS version and the size of the hard disk partition.
Each cluster can only be occupied by one file. Even if there are several bytes in this file, more than two files are never allowed to share a cluster, otherwise data confusion will occur.
This mechanism with clusters as the smallest allocation unit makes it relatively easy to manage data on the hard disk, but it also causes a waste of disk space, especially when there are a large number of small files. A large gigabit hard drive can waste hundreds of megabytes of disk space.
In order to search and manage sectors, sectors need to be numbered. The numbering of sectors starts from track 0, and the starting sector is sector 1, followed by sectors 2 and 3. ..., after the sector numbering of track 0 ends, the starting sectors of track 1 accumulate numbers until the last sector (n sector) of the last track.
For example, a hard disk has 1024 tracks, and each track is divided into 63 sectors. Then the sector number of track 0 is 1~63, and the starting sector number of track 1 is 64. The starting sector number of track 1 is 64. The last sector number is 64512.
There are some differences between hard disks and floppy disks in sector numbering. In one track of a floppy disk, the sector numbers are arranged once, that is, 1, 2, 3...n sectors. Due to the high speed of the hard disk, the magnetic head must transfer the data to the microcomputer after completing reading and writing data in a certain sector. This takes a while, but at this time the hard disk continues to rotate at high speed. When the data transmission is completed, the magnetic head reads and writes. At the second sector, the disk has rotated to another sector. Therefore, in early hard disks, sector numbers were jumped according to a certain interval coefficient.
For more related knowledge, please visit: PHP Chinese website!
The above is the detailed content of What is the physical unit of disk read and write operations?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Steps to configure RAID 1 on Windows 11
Sep 22, 2023 pm 03:05 PM
Steps to configure RAID 1 on Windows 11
Sep 22, 2023 pm 03:05 PM
Windows 11 has strict requirements, and after struggling to obtain that storage, losing your hard drive and data would be a shame. Well, we have good news that can help you buffer against hard drive failure. Using built-in Windows tools, you can copy all your data from one drive to another. This way, if one drive fails, you can mirror and rebuild the original data on the replacement drive. Can Windows 11 do RAID? With Windows Storage Spaces feature, you can perform RAID on Windows 11. This feature allows you to create multiple virtual disks using a hard drive connected directly to your computer without degrading performance. Benefits of Raid: Reduce the cost of disk
 Convert VirtualBox fixed disk to dynamic disk and vice versa
Mar 25, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Convert VirtualBox fixed disk to dynamic disk and vice versa
Mar 25, 2024 am 09:36 AM
When creating a virtual machine, you will be asked to select a disk type, you can select fixed disk or dynamic disk. What if you choose fixed disks and later realize you need dynamic disks, or vice versa? Good! You can convert one to the other. In this post, we will see how to convert VirtualBox fixed disk to dynamic disk and vice versa. A dynamic disk is a virtual hard disk that initially has a small size and grows in size as you store data in the virtual machine. Dynamic disks are very efficient at saving storage space because they only take up as much host storage space as needed. However, as disk capacity expands, your computer's performance may be slightly affected. Fixed disks and dynamic disks are commonly used in virtual machines
 How to RAID an external hard drive on Windows 11
Sep 16, 2023 pm 10:05 PM
How to RAID an external hard drive on Windows 11
Sep 16, 2023 pm 10:05 PM
RAID or Redundant Array of Independent Disks is a data storage technology in which multiple external drives are combined into one. It was widely used when large hard drives were expensive, but many people still prefer the RAID external drive method. There are several levels of RAID, each serving a specific purpose. Keep in mind that the average user doesn't have to delve into the complexity, a simple setup of RAID0 or RAID1 should work fine. Reasons to consider raiding an external drive: Improved PC performance Easy to configure, cheaper than existing alternatives Faster data reading and writing Efficient backup solution through mirroring How to RAID an external drive on Windows 11? Before RAID external hard drives, you need to pay attention to the following first things
 How to convert dynamic disk to basic disk on Windows 11
Sep 23, 2023 pm 11:33 PM
How to convert dynamic disk to basic disk on Windows 11
Sep 23, 2023 pm 11:33 PM
If you want to convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk in Windows 11, you should create a backup first as the process will erase all data in it. Why should you convert dynamic disk to basic disk in Windows 11? According to Microsoft, dynamic disks have been deprecated from Windows and their use is no longer recommended. Additionally, Windows Home Edition does not support dynamic disks, so you will not be able to access these logical drives. If you want to combine more disks into a larger volume, it is recommended to use Basic Disks or Storage Spaces. In this article, we will show you how to convert dynamic disk to basic disk on Windows 11 How to convert dynamic disk to basic disk in Windows 11? In the beginning
 Binary file reading and writing operations in PHP
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:09 AM
Binary file reading and writing operations in PHP
Jun 22, 2023 am 09:09 AM
PHP is a language widely used in web development. It provides many functions and methods for processing files. In PHP, we can use binary mode to read and write files. This method can improve the efficiency of file operations, especially when processing binary files. In this article, we will explore binary file reading and writing operations in PHP and how to use this method to process binary files. What is a binary file? Binary files refer to files represented by pure binary, and their contents may contain different encoded character sets.
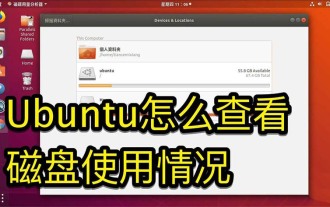 How to master disk usage in Ubuntu system
Jan 03, 2024 pm 11:13 PM
How to master disk usage in Ubuntu system
Jan 03, 2024 pm 11:13 PM
We want to check the hard disk usage in the system. How to check the Ubuntu system? Let's take a look at the tutorial on checking the hard disk usage in Ubuntu system. 1. On the system, click on the lower left corner of the desktop, as shown in the picture. 2. In the system, click Utilities, as shown in the figure. 3. Click Disk Usage, as shown in the picture. 4. Then you can see the disk usage, that is, the disk in the middle is your computer’s hard drive, as shown in the picture. The small print below the disk shows the usage. 5. Or click the disk on the utility program, as shown in the picture. 6. Then under the capacity, you can see the hard disk usage, as shown in the picture. The following is the text version to view disk usage: df-h The results are as follows: FilesystemSizeUsedAvailU
![How to increase disk size in VirtualBox [Guide]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/171064142025068.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) How to increase disk size in VirtualBox [Guide]
Mar 17, 2024 am 10:10 AM
How to increase disk size in VirtualBox [Guide]
Mar 17, 2024 am 10:10 AM
We often encounter situations where the predefined disk size has no room for more data? If you need more virtual machine hard disk space at a later stage, you must expand the virtual hard disk and partitions. In this post, we will see how to increase disk size in VirtualBox. Increasing the disk size in VirtualBox It is important to note that you may want to back up your virtual hard disk files before performing these operations, as there is always the possibility of something going wrong. It is always a good practice to have backups. However, the process usually works fine, just make sure to shut down your machine before continuing. There are two ways to increase disk size in VirtualBox. Expand VirtualBox disk size using GUI using CL
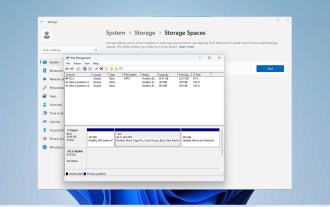 Three ways to implement mirrored volumes on Windows 11
Sep 18, 2023 pm 04:25 PM
Three ways to implement mirrored volumes on Windows 11
Sep 18, 2023 pm 04:25 PM
Drive failure is a serious issue that may render your files unrecoverable or your boot drive non-working, so that is why many users choose to create a mirrored volume on Windows 11 as a way to prevent this. If you're not familiar, a mirrored volume is an exact copy of another drive that can be used as a backup in the event of a disk failure. It's a great backup solution, and today we'll show you how to create it on your PC. What are the prerequisites for setting up a mirrored volume? Two dynamic disks of similar size. The mirror drive can be larger than the source drive. RAID support is available on almost every modern PC. The mirror drive should be unallocated and do not have any volumes. How to create a mirrored volume in Windows 11? 1.Use



