 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of the underlying operating mechanism and working principles of PHP
Detailed explanation of the underlying operating mechanism and working principles of PHP
Detailed explanation of the underlying operating mechanism and working principles of PHP

I recently set up a server, and suddenly I felt how the lamps work, or how they are connected? I usually just write programs, and I have never thought about the working principle between them:
The underlying working principle of PHP
Related learning recommendations: PHP programming from entry to proficiency
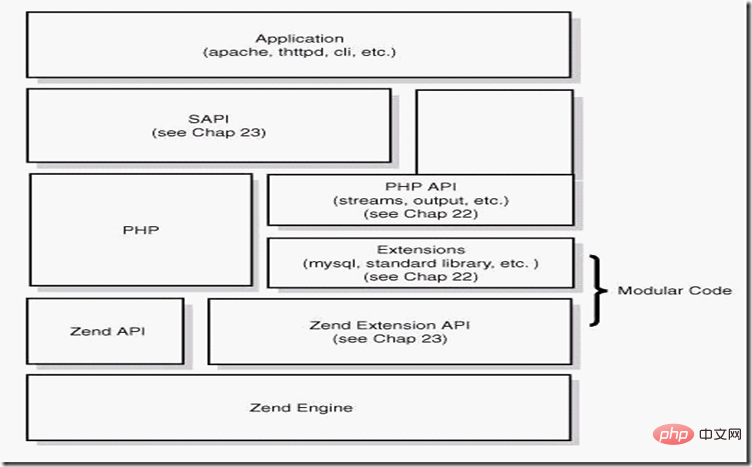
Figure 1 PHP structure
As can be seen from the picture, php It is a 4-layer system from bottom to top
①Zend engine
Zend is implemented in pure C and is the core part of PHP. It translates PHP code (lexical, syntax analysis, etc.) Process) processes executable opcodes and implements corresponding processing methods, implements basic data structures (such as hashtable, oo), memory allocation and management, and provides corresponding api methods for external calls. It is the core of everything. All peripheral functions are implemented around zend.
②Extensions
Around the zend engine, extensions provide various basic services in a component-based manner. Our common various built-in functions (such as array series), standard libraries, etc. are all through extensions To achieve this, users can also implement their own extensions as needed to achieve function expansion, performance optimization and other purposes (for example, the PHP middle layer and rich text parsing currently used by Tieba are typical applications of extensions).
③Sapi
The full name of Sapi is Server Application Programming Interface, which is the server application programming interface. Sapi allows PHP to interact with peripheral data through a series of hook functions. This is PHP's very elegant and A successful design successfully decouples and isolates PHP itself from upper-layer applications through SAPI. PHP can no longer consider how to be compatible with different applications, and the application itself can also implement different processing methods according to its own characteristics. We will introduce it later in the sapi chapter
④Upper-layer application
This is the PHP program we usually write. We can obtain various application modes through different sapi methods, such as implementing web through webserver Apply, run as a script from the command line, etc.
Architectural ideas:
The engine (Zend) component (ext) model reduces internal coupling
The middle layer (sapi) isolates the web server and php
************************************************ ******************************
If php is a car, then
the framework of the car It is php itself
Zend is the engine (engine) of the car
The various components below Ext are the wheels of the car
Sapi can be regarded as a road, and the car can run on different types of roads
The execution of a php program is like a car running on the road.
Therefore, we need: Excellent performance engine, suitable wheels, correct runway
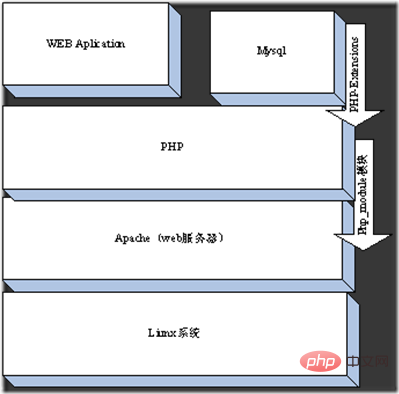
The relationship between Apache and php
Apache for php The analysis is completed through the php Module among many Modules.
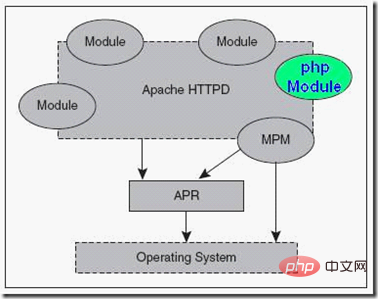
#To finally integrate php into the Apache system, you need to make some necessary settings for Apache. Here, we will take the mod_php5 SAPI operating mode of php as an example to explain. As for the concept of SAPI, we will explain it in detail later.
Assume that the versions we install are Apache2 and Php5, then you need to edit Apache’s main configuration file http.conf and add the following lines to it:
In Unix/Linux environment:
1 2 |
|
Note: modules/mod_php5.so is the installation location of the mod_php5.so file in the X system environment.
In Windows environment:
1 2 |
|
Note: d:/php/php5apache2.dll is the installation location of the php5apache2.dll file in Windows environment.
These two configurations tell Apache Server that any Url user requests received in the future with php as the suffix need to call the php5_module module (mod_php5.so/php5apache2.dll) for processing.
Apache’s life cycle
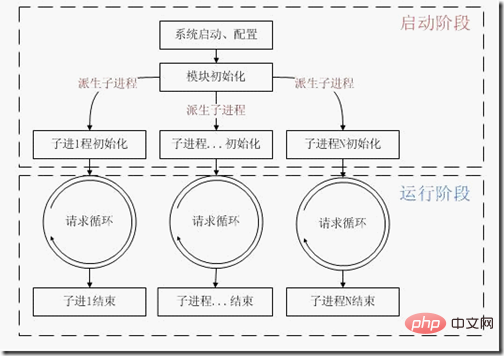
##Apache’s request processing process
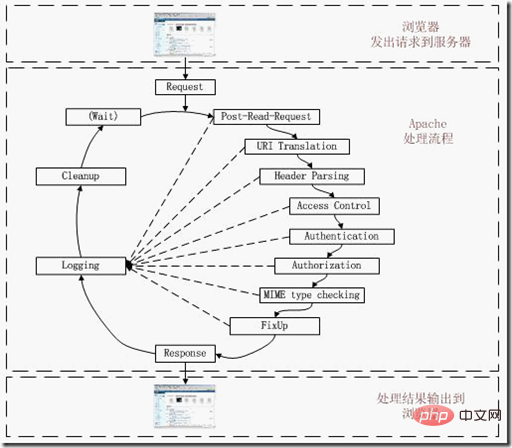
Detailed explanation of the Apache request processing cycle
In the normal request processing process, this is the first stage in which the module can insert hooks. This stage can be exploited for modules that want to get into processing requests very early.
Apache’s main job in this stage: mapping the requested URL to the local file system. Modules can insert hooks at this stage to execute their own mapping logic. mod_alias uses this phase to work.
3. Header Parsing stage
Apache’s main work in this stage: check the header of the request. Since the module can perform the task of checking request headers at any point in the request processing flow, this hook is rarely used. mod_setenvif uses this phase to work.
4. Access Control Phase
The main work of Apache in this phase: Check whether access to the requested resources is allowed according to the configuration file. Apache's standard logic implements allow and deny directives. mod_authz_host uses this phase to work.
5. Authentication stage
The main work of Apache in this stage: authenticate users according to the policy set in the configuration file, and set the user name area. Modules can insert hooks at this stage to implement an authentication method.
6. Authorization phase
The main work of Apache in this phase: Check whether authenticated users are allowed to perform the requested operation according to the configuration file. The module can insert hooks at this stage to implement a user rights management method.
7. MIME Type Checking stage
The main work of Apache in this stage: determine the content processing function to be used according to the relevant rules of the MIME type of the requested resource. The standard modules mod_negotiation and mod_mime implement this hook.
8. FixUp stage
This is a general stage that allows the module to run any necessary processing before the content generator. Similar to Post_Read_Request, this is a hook that can capture any information and is also the most commonly used hook.
9. Response stage
Apache’s main job in this stage is to generate content returned to the client and be responsible for sending an appropriate reply to the client. This stage is the core part of the entire process.
10. Logging phase
The main work of Apache in this phase: recording transactions after the reply has been sent to the client. Modules may modify or replace Apache's standard logging.
11. CleanUp Phase
The main work of Apache in this phase: clean up the environment left after the completion of this request transaction, such as the processing of files and directories or the closing of Socket, etc. This is the first time for Apache The final stage of request processing.
LAMP architecture:
Android system architecture diagram
Lamp and Android architecture Comparing the pictures, it seems to be somewhat similar to the lamp architecture. I don't know Android, but it feels a bit similar. Experts can point out the differences. I would be very grateful.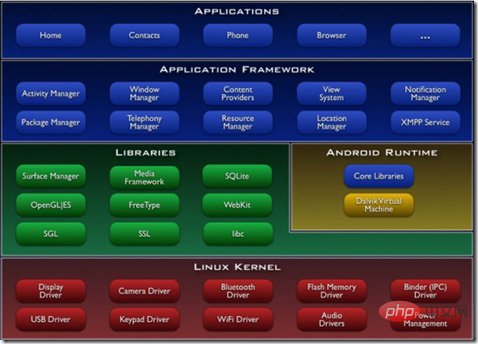
lamp and the inside of the computer
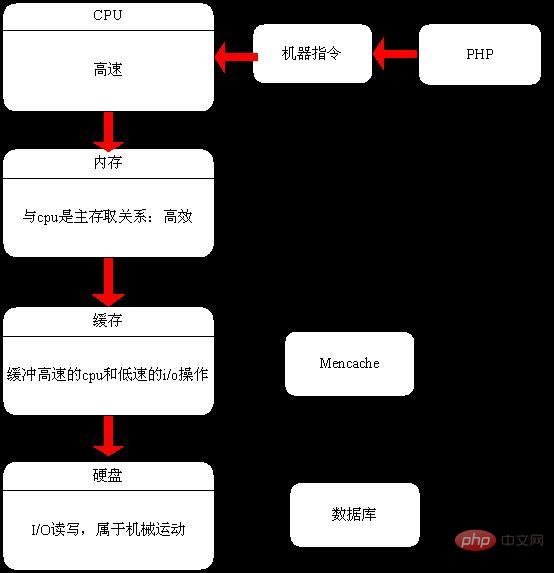
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the underlying operating mechanism and working principles of PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1205
1205
 24
24
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 7 PHP Functions I Regret I Didn't Know Before
Nov 13, 2024 am 09:42 AM
7 PHP Functions I Regret I Didn't Know Before
Nov 13, 2024 am 09:42 AM
If you are an experienced PHP developer, you might have the feeling that you’ve been there and done that already.You have developed a significant number of applications, debugged millions of lines of code, and tweaked a bunch of scripts to achieve op
 How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How To Set Up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for PHP Development
Dec 20, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Visual Studio Code, also known as VS Code, is a free source code editor — or integrated development environment (IDE) — available for all major operating systems. With a large collection of extensions for many programming languages, VS Code can be c
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently process XML documents using PHP. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a versatile text-based markup language designed for both human readability and machine parsing. It's commonly used for data storage an
 PHP Program to Count Vowels in a String
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
PHP Program to Count Vowels in a String
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
A string is a sequence of characters, including letters, numbers, and symbols. This tutorial will learn how to calculate the number of vowels in a given string in PHP using different methods. The vowels in English are a, e, i, o, u, and they can be uppercase or lowercase. What is a vowel? Vowels are alphabetic characters that represent a specific pronunciation. There are five vowels in English, including uppercase and lowercase: a, e, i, o, u Example 1 Input: String = "Tutorialspoint" Output: 6 explain The vowels in the string "Tutorialspoint" are u, o, i, a, o, i. There are 6 yuan in total
 Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Static binding (static::) implements late static binding (LSB) in PHP, allowing calling classes to be referenced in static contexts rather than defining classes. 1) The parsing process is performed at runtime, 2) Look up the call class in the inheritance relationship, 3) It may bring performance overhead.
 What are PHP magic methods (__construct, __destruct, __call, __get, __set, etc.) and provide use cases?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What are PHP magic methods (__construct, __destruct, __call, __get, __set, etc.) and provide use cases?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What are the magic methods of PHP? PHP's magic methods include: 1.\_\_construct, used to initialize objects; 2.\_\_destruct, used to clean up resources; 3.\_\_call, handle non-existent method calls; 4.\_\_get, implement dynamic attribute access; 5.\_\_set, implement dynamic attribute settings. These methods are automatically called in certain situations, improving code flexibility and efficiency.



