The latest version of 2023 68 Redis interview questions (collection)
The article is too long, it is recommended to save it first and read it slowly!
Redis (Remote Dictionary Server) is an open source (BSD licensed) high-performance non-relational (NoSQL) key-value database written in C language.

#Redis can store mappings between keys and five different types of values. The key type can only be string, and only five data types are supported: string, list, set, hash table, and ordered set.
Different from traditional databases, Redis data is stored in memory, so the read and write speed is very fast. Therefore, redis is widely used in the cache direction and can handle more than 100,000 reads and writes per second. Operation, it is the fastest Key-Value DB known to perform. In addition, Redis is often used for distributed locks. In addition, Redis supports transactions, persistence, LUA scripts, LRU driven events, and various cluster solutions.
Today I will talk about Redis interview questions to prepare for the interview after returning to work.
1. Overview
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of Redis
Advantages
Reading and writing performance Excellent, Redis can read at a speed of 110,000 times/s and write at a speed of 81,000 times/s.
Supports data persistence and supports two persistence methods: AOF and RDB.
Supports transactions. All operations of Redis are atomic. At the same time, Redis also supports atomic execution after merging several operations.
Rich data structures, in addition to supporting string type value, it also supports hash, set, zset, list and other data structures.
Supports master-slave replication, the host will automatically synchronize data to the slave, and read and write can be separated.
Disadvantages
The database capacity is limited by physical memory and cannot be used for high-performance reading and writing of massive data. Therefore, the scenarios suitable for Redis are mainly limited to small amounts of data. High-performance operations and calculations.
Redis does not have automatic fault tolerance and recovery functions. The downtime of the host and slave machines will cause some front-end read and write requests to fail. You need to wait for the machine to restart or manually switch the front-end IP to recover.
The host machine is down. Some data could not be synchronized to the slave machine in time before the machine went down. After switching IP, data inconsistency will be introduced, which reduces the availability of the system.
Redis is difficult to support online expansion. When the cluster capacity reaches the upper limit, online expansion will become very complicated. In order to avoid this problem, operation and maintenance personnel must ensure that there is enough space when the system goes online, which causes a great waste of resources.
2. Why use Redis/Why use cache
We mainly look at this problem from the two points of "high performance" and "high concurrency".
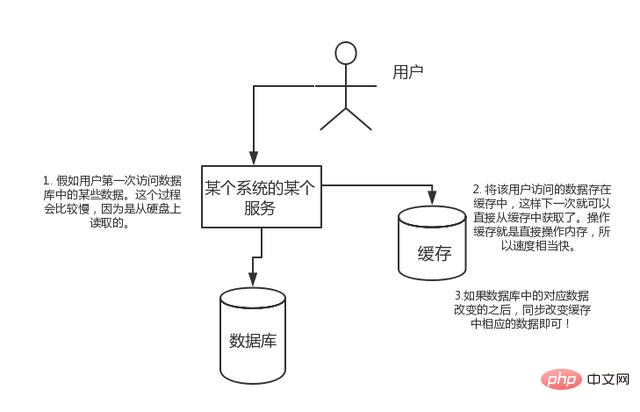
High performance:
If the user accesses some data in the database for the first time. This process will be slower because it is read from the hard disk. Store the data accessed by the user in the cache, so that the next time the data is accessed, it can be obtained directly from the cache. Operation cache is to directly operate the memory, so the speed is quite fast. If the corresponding data in the database changes, just change the corresponding data in the cache synchronously!
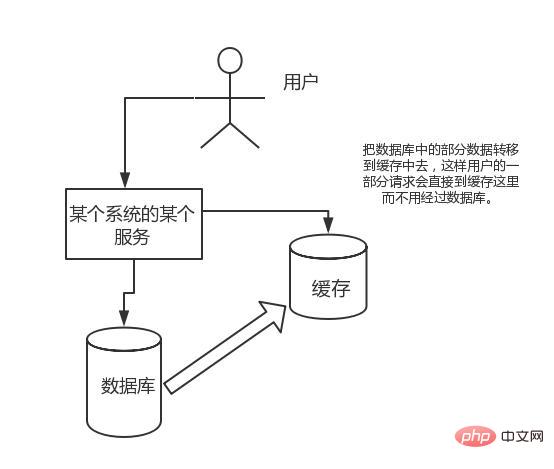
High concurrency:
The requests that the direct operation cache can withstand are much greater than the direct access to the database, so We can consider transferring some data in the database to the cache, so that some of the user's requests will go directly to the cache without going through the database.
3. Why use Redis instead of map/guava for caching?
The cache is divided into local cache and distributed cache . Taking Java as an example, local caching is implemented using the built-in map or guava. The main feature is that it is lightweight and fast. The life cycle ends with the destruction of the jvm, and in the case of multiple instances, each instance Each cache needs to be saved, and the cache is not consistent.
Using redis or memcached is called distributed cache. In the case of multiple instances, each instance shares a cache of data, and the cache is consistent. The disadvantage is that the redis or memcached service needs to be kept highly available, and the entire program architecture is relatively complex.
4. Why is Redis so fast?
1) Completely based on memory, most requests are pure memory operations, very fast. The data is stored in memory, similar to HashMap. The advantage of HashMap is that the time complexity of search and operation is O(1);
2) The data structure is simple, and the data operation is also simple. The data structure in Redis It is specially designed;
3) Using a single thread avoids unnecessary context switching and competition conditions, and there is no need to switch between multiple processes or threads to consume the CPU. There is no need to consider various lock issues, and there is no need to lock or release locks. Operation, there is no performance consumption caused by possible deadlock;
4) Use multi-channel I/O multiplexing model, non-blocking IO;
5 Use the underlying model differently, between them The underlying implementation method and the application protocol for communication with the client are different. Redis directly builds its own VM mechanism, because if the general system calls system functions, it will waste a certain amount of time to move and request;
2. Data types
5. What data types does Redis have?
Redis mainly has 5 data types, including String, List, Set, Zset, and Hash, which can meet the needs of most users. Part of the usage requirements

6. Redis application scenarios
Summary 1
Counter: You can perform increment and decrement operations on String to realize the counter function. Redis, an in-memory database, has very high read and write performance and is very suitable for storing counts of frequent reads and writes.
Cache: Put hotspot data into memory, set the maximum memory usage and elimination strategy to ensure the cache hit rate.
Session Cache: Redis can be used to uniformly store session information for multiple application servers. When the application server no longer stores the user's session information, it no longer has state. A user can request any application server, making it easier to achieve high availability and scalability.
Full Page Cache (FPC): In addition to basic session tokens, Redis also provides a very simple FPC platform. Taking Magento as an example, Magento provides a plugin to use Redis as a full-page cache backend. In addition, for WordPress users, Pantheon has a very good plug-in wp-redis, which can help you load the pages you have browsed as quickly as possible.
Lookup table: For example, DNS records are very suitable for storage using Redis. The lookup table is similar to the cache and also takes advantage of the fast lookup feature of Redis. But the contents of the lookup table cannot be invalidated, while the contents of the cache can be invalidated, because the cache does not serve as a reliable source of data.
Message queue (publish/subscribe function): List is a two-way linked list that can write and read messages through lpush and rpop. However, it is best to use messaging middleware such as Kafka and RabbitMQ.
Distributed lock implementation: In a distributed scenario, locks in a stand-alone environment cannot be used to synchronize processes on multiple nodes. You can use the SETNX command that comes with Redis to implement distributed locks. In addition, you can also use the officially provided RedLock distributed lock implementation.
Others: Set can implement operations such as intersection and union, thereby realizing functions such as mutual friends. ZSet can implement ordered operations to achieve functions such as rankings.
Summary 2
Compared with other caches, Redis has a very big advantage, that is, it supports multiple data types.
Data type description string string, the simplest k-v storage hashhash format, value is field and value, suitable for scenarios such as ID-Detail. list is a simple list, a sequential list, supports inserting data at the first or last position, unordered list, fast search speed, suitable for intersection, union, and difference processing sorted set ordered set
In fact, through the above data Based on the characteristics of the type, you can basically think of suitable application scenarios.
string——Suitable for the simplest k-v storage, similar to memcached storage structure, SMS verification code, configuration information, etc., use this type to store.
hash - Generally, the key is an ID or a unique identifier, and the value corresponds to the details. Such as product details, personal information details, news details, etc.
list——Because list is ordered, it is more suitable for storing some ordered and relatively fixed data. Such as province and city table, dictionary table, etc. Because the list is ordered, it is suitable to be sorted according to the writing time, such as the latest ***, message queue, etc.
set——It can be simply understood as an ID-List model, such as which friends a person has on Weibo. The best thing about set is that it can provide intersection between two sets. , union and difference operations. For example: Find common friends between two people, etc.
Sorted Set——is an enhanced version of set, adding a score parameter, which will automatically sort according to the score value. It is more suitable for data such as top 10 that is not sorted according to the insertion time.
As mentioned above, although Redis is not as complex a data structure as a relational database, it can also be suitable for many scenarios, including more than general cache data structures. Understanding the business scenarios suitable for each data structure will not only help improve development efficiency, but also effectively utilize the performance of Redis.
3. Persistence
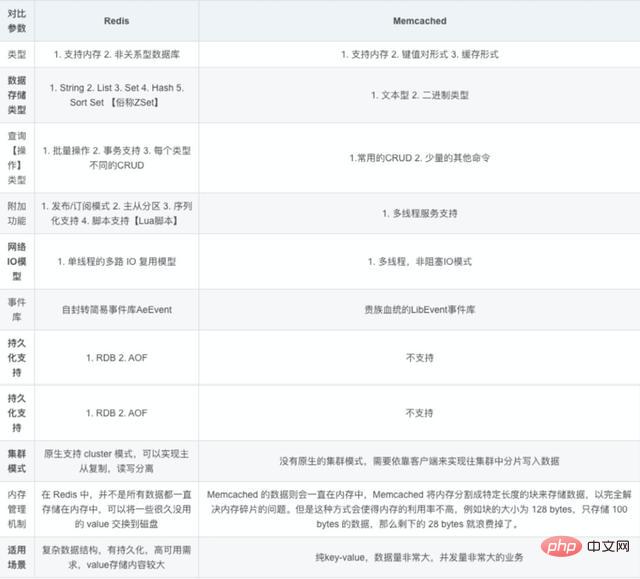
7. What is Redis persistence?
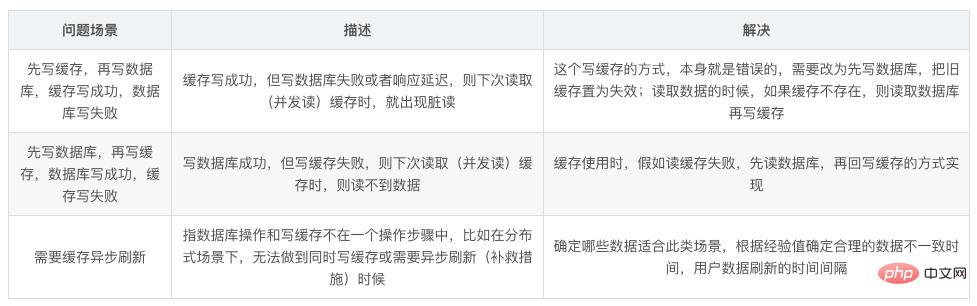
Persistence is to write the memory data to the disk to prevent the memory data from being lost if the service goes down.
8. What is the persistence mechanism of Redis? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
Redis provides two persistence mechanisms RDB (default) and AOF mechanism:
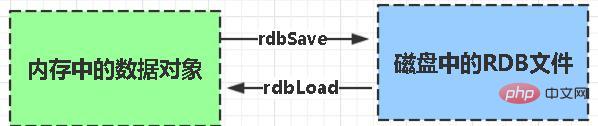
RDB: is the abbreviation of Redis DataBase snapshot
RDB It is the default persistence method of Redis. The memory data is saved to the hard disk in the form of a snapshot according to a certain period of time, and the corresponding data file is dump.rdb. The snapshot period is defined through the save parameter in the configuration file.
Advantages:
1. There is only one file dump.rdb, which is convenient for persistence.
2. Good disaster tolerance, a file can be saved to a safe disk.
3. To maximize performance, fork the child process to complete the write operation and allow the main process to continue processing commands, so IO is maximized. Use a separate sub-process for persistence, and the main process will not perform any IO operations, ensuring the high performance of redis
4. When the data set is large, the startup efficiency is higher than AOF.
Disadvantages:
1. Low data security. RDB is persisted at intervals. If redis fails between persistence, data loss will occur. Therefore, this method is more suitable when the data requirements are not strict)
2. AOF (Append-only file) persistence method: refers to all command line records being completely persistently stored in the format of the redis command request protocol ) is saved as an aof file.
AOF: Persistence
AOF persistence (i.e. Append Only File persistence) records each write command executed by Redis to a separate log file , when Redis is restarted, the data in the persistent log file will be restored.
When both methods are enabled at the same time, data recovery Redis will give priority to AOF recovery.
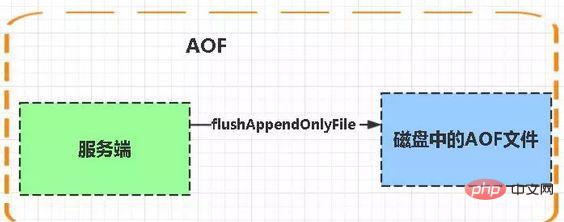
Advantages:
1. Data security, aof persistence can be configured with appendfsync attribute, always, every time a command operation is performed Just record it once in the aof file.
2. Write files in append mode. Even if the server goes down in the middle, you can use the redis-check-aof tool to solve the data consistency problem.
3. Rewrite mode of AOF mechanism. Before the AOF file is rewritten (commands will be merged and rewritten when the file is too large), you can delete some of the commands (such as flushall by mistake))
Disadvantages:
1. AOF files are larger than RDB files, and the recovery speed is slow.
2. When the data set is large, the startup efficiency is lower than rdb.
What are the advantages and disadvantages?
AOF files are updated more frequently than RDB, so AOF is used first to restore data.
AOF is more secure and larger than RDB
RDB performance is better than AOF
If both are configured, AOF is loaded first
9 , How to choose the appropriate persistence method
Generally speaking, if you want to achieve data security comparable to PostgreSQL, you should use both persistence functions at the same time. In this case, when Redis is restarted, the AOF file will be loaded first to restore the original data, because under normal circumstances, the data set saved by the AOF file is more complete than the data set saved by the RDB file.
If you care deeply about your data, but can still afford data loss within a few minutes, then you can just use RDB persistence.
Many users only use AOF persistence, but this method is not recommended because regularly generating RDB snapshots is very convenient for database backup, and RDB data set recovery is faster than AOF recovery. The speed is faster. In addition, using RDB can also avoid bugs in AOF programs.
If you only want your data to exist when the server is running, you can also not use any persistence method.
10. How to expand Redis persistent data and cache?
If Redis is used as a cache, use consistent hashing to achieve dynamic expansion and contraction.
If Redis is used as a persistent storage, a fixed keys-to-nodes mapping relationship must be used, and the number of nodes cannot be changed once determined. Otherwise (that is, when Redis nodes need to change dynamically), a system that can rebalance data at runtime must be used, and currently only Redis cluster can do this.
4. Memory related
14. There are 20 million data in MySQL, but only 200 thousand data are stored in redis. How to ensure that the data in redis are hot data?
When the size of the redis memory data set increases to a certain size, the data elimination strategy will be implemented.
15. What are the memory elimination strategies of Redis?
Redis's memory elimination strategy refers to how to handle data that needs to be newly written and requires additional space application when Redis's memory for caching is insufficient.
Global key space selective removal
noeviction: When the memory is not enough to accommodate the newly written data, the new write operation will Report an error.
allkeys-lru: When the memory is insufficient to accommodate newly written data, in the key space, remove the least recently used key. (This is the most commonly used)
allkeys-random: When the memory is insufficient to accommodate newly written data, a key is randomly removed from the key space.
Selective removal of key space with expiration time
volatile-lru: When the memory is not enough to accommodate the newly written data, in In the key space with an expiration time set, remove the least recently used key.
volatile-random: When the memory is insufficient to accommodate newly written data, a key is randomly removed from the key space with an expiration time set.
volatile-ttl: When the memory is insufficient to accommodate newly written data, in the key space with an expiration time set, keys with earlier expiration times will be removed first.
Summary
The selection of Redis’s memory elimination strategy will not affect the processing of expired keys. The memory elimination policy is used to handle data that requires additional space when memory is insufficient; the expiration policy is used to handle expired cached data.
16. What physical resources does Redis mainly consume?
Memory.
17. What happens when Redis runs out of memory?
If the set upper limit is reached, the Redis write command will return an error message (but the read command can still return normally.) Or you can configure the memory elimination mechanism, and Redis will flush it when it reaches the upper memory limit. Old content.
18. How does Redis optimize memory?
You can make good use of collection type data such as Hash, list, sorted set, set, etc., because usually many small Key-Values can be stored together in a more compact way. Use hashes as much as possible. Hash tables (meaning that the number stored in a hash table is small) use very small memory, so you should abstract your data model into a hash table as much as possible. For example, if there is a user object in your web system, do not set a separate key for the user's name, surname, email, and password. Instead, store all the user's information in a hash table.
5. Threading model
19. Redis threading model
Redis developed a network event processor based on the Reactor mode. This processor is called File event handler. Its structure is composed of 4 parts: multiple sockets, IO multiplexer, file event dispatcher, and event processor. Because the consumption of the file event dispatcher queue is single-threaded, Redis is called a single-threaded model.
The file event processor uses I/O multiplexing (multiplexing) procedures to listen to multiple sockets at the same time, and associate different event processing for the socket according to the task currently performed by the socket. device.
When the monitored socket is ready to perform operations such as connection response (accept), read (read), write (write), close (close), etc., the file event corresponding to the operation is will occur, then the file event handler will call the event handler previously associated with the socket to handle these events.
Although the file event processor runs in a single-threaded manner, by using an I/O multiplexer to listen to multiple sockets, the file event processor not only implements a high-performance network communication model, It can also be well connected with other modules in the redis server that also run in a single-threaded manner, which maintains the simplicity of the single-threaded design within Redis.
6. Threading model
19. Redis threading model
Redis developed a network event processor based on the Reactor mode. This processor is called File event handler. Its structure is composed of 4 parts: multiple sockets, IO multiplexer, file event dispatcher, and event processor. Because the consumption of the file event dispatcher queue is single-threaded, Redis is called a single-threaded model.
The file event processor uses I/O multiplexing (multiplexing) procedures to listen to multiple sockets at the same time, and associate different event processing for the socket according to the task currently performed by the socket. device.
When the monitored socket is ready to perform operations such as connection response (accept), read (read), write (write), close (close), etc., the file event corresponding to the operation is will occur, then the file event handler will call the event handler previously associated with the socket to handle these events.
Although the file event processor runs in a single-threaded manner, by using an I/O multiplexer to listen to multiple sockets, the file event processor not only implements a high-performance network communication model, It can also be well connected with other modules in the redis server that also run in a single-threaded manner, which maintains the simplicity of the single-threaded design within Redis.
7. Transactions
20. What is a transaction?
A transaction is a single isolated operation: all commands in the transaction will be serialized and executed in order. During the execution of the transaction, it will not be interrupted by command requests sent by other clients.
A transaction is an atomic operation: either all commands in the transaction are executed, or none of them are executed.
21. The concept of Redis transaction
The essence of Redis transactions is a collection of commands such as MULTI, EXEC, and WATCH. Transactions support executing multiple commands at one time, and all commands in a transaction will be serialized. During the transaction execution process, the commands in the queue will be executed serially in order, and command requests submitted by other clients will not be inserted into the transaction execution command sequence.
To summarize: a redis transaction is a one-time, sequential, and exclusive execution of a series of commands in a queue.
22. Three stages of Redis transaction
Transaction starts MULTI
Command enqueue
Transaction execution EXEC
During transaction execution, if the server receives a request other than EXEC, DISCARD, WATCH, and MULTI, it will put the request into Queuing in queue.
23. Redis transaction related commands
The Redis transaction function is implemented through the four primitives MULTI, EXEC, DISCARD and WATCH.
Redis will serialize all commands in a transaction and then execute them in order.
1) redis does not support rollback, "Redis does not rollback when a transaction fails, but continues to execute the remaining commands", so the internals of Redis can remain simple and fast.
2) If an error occurs in the command in a transaction, then all commands will not be executed;
.3)If in If a runtime error occurs in a transaction, the correct command will be executed.
The WATCH command is an optimistic lock that provides check-and-set (CAS) behavior for Redis transactions. One or more keys can be monitored. Once one of the keys is modified (or deleted), subsequent transactions will not be executed, and monitoring continues until the EXEC command.
The MULTI command is used to start a transaction and it always returns OK. After MULTI is executed, the client can continue to send any number of commands to the server. These commands will not be executed immediately, but will be placed in a queue. When the EXEC command is called, all commands in the queue will be executed.
EXEC: Execute commands within all transaction blocks. Returns the return values of all commands within the transaction block, arranged in the order of command execution. When the operation is interrupted, the empty value nil is returned.
By calling DISCARD, the client can clear the transaction queue and give up executing the transaction, and the client will exit from the transaction state.
The UNWATCH command can cancel watch’s monitoring of all keys.
24. Overview of Transaction Management (ACID)
Atomicity: Atomicity means that a transaction is an indivisible unit of work , either all operations in the transaction occur or none occur.
Consistency: The integrity of the data before and after the transaction must be consistent.
Isolation: When multiple transactions are executed concurrently, the execution of one transaction should not affect the execution of other transactions.
Durability: Durability means that once a transaction is committed, its changes to the data in the database are permanent. Even if the database fails, no changes should be made. It has any impact
Redis transactions always have consistency and isolation in ACID, Other features are not supported. Transactions are also durable when the server is running in AOF persistence mode and the value of the appendfsync option is always.
25. Does Redis transaction support isolation?
Redis is a single-process program, and it guarantees that the transaction will not be interrupted when executing the transaction. The transaction can run until all commands in the transaction queue are executed. Therefore, Redis transactions are always isolated.
26. Does Redis transaction guarantee atomicity, and does it support rollback?
In Redis, a single command is executed atomically, but transactions are not guaranteed to be atomic and there is no rollback. If any command in the transaction fails to execute, the remaining commands will still be executed.
27. Other implementations of Redis transactions
Based on Lua scripts, Redis can ensure that the commands in the script are executed once and in sequence, and it does not provide transaction execution at the same time. Error rollback, if some commands run incorrectly during execution, the remaining commands will continue to run to completion
Based on the intermediate mark variable, another mark variable is used to identify whether the transaction is completed. When reading data First read the mark variable to determine whether the transaction execution is completed. But this will require additional code to be implemented, which is more cumbersome.
8. Cluster solution
28. Sentinel mode
Introduction to Sentinel:
sentinel, the Chinese name is sentinel. Sentinel is a very important component in the redis cluster organization. It mainly has the following functions:
Cluster Monitoring: Responsible for monitoring whether the redis master and slave processes are working normally.
Message Notification: If a redis instance fails, Sentinel is responsible for sending messages as alarm notifications to the administrator.
Failover: If the master node hangs, it will automatically be transferred to the slave node.
Configuration Center: If failover occurs, notify the client of the new master address.
Sentinels are used to achieve high availability of redis clusters. They are also distributed and run as a sentinel cluster to work together.
During failover, determining whether a master node is down requires the consent of most sentinels, which involves the issue of distributed election.
Even if some sentinel nodes hang up, the sentinel cluster can still work normally, because if a failover system itself, which is an important part of the high availability mechanism, is a single point, it will be very confusing.
Core knowledge of Sentinel
Sentinel requires at least 3 instances to ensure its robustness.
The Sentinel redis master-slave deployment architecture does not guarantee zero data loss, but can only guarantee the high availability of the redis cluster.
For the complex deployment architecture of Sentinel redis master-slave, try to conduct sufficient testing and drills in both the test environment and the production environment.
29. Official Redis Cluster solution (server-side routing query)

Can you explain the working principle of redis cluster mode? In cluster mode, how is the key of redis addressed? What are the algorithms for distributed addressing? Do you know the consistent hash algorithm?
Introduction
Redis Cluster is a server-side Sharding technology, officially available in version 3.0. Redis Cluster does not use consistent hashing, but uses the concept of slot, which is divided into 16384 slots in total. Send the request to any node, and the node that receives the request will send the query request to the correct node for execution
Program description
Through hashing, the Data sharding, each node evenly stores data in a certain hash slot (hash value) range, with 16384 slots allocated by default
Each data shard will be stored in multiple mutual master-slave On multiple nodes
Data is written to the master node first, and then synchronized to the slave node (supports configuration of blocking synchronization)
Data between multiple nodes in the same shard does not maintain consistency
When reading data, when the key operated by the client is not allocated on the node, redis will return the steering instruction and point to the correct node.
When expanding, it is necessary to migrate the data of the old node. Part of it goes to the new node
Under the redis cluster architecture, each redis must open two port numbers, such as one is 6379, and the other is the port number plus 1w, such as 16379.
16379 The port number is used for communication between nodes, that is, cluster bus communication. It is used for fault detection, configuration updates, and failover authorization. The cluster bus uses another binary protocol, the gossip protocol, for efficient data exchange between nodes, occupying less network bandwidth and processing time.
Internal communication mechanism between nodes
(Basic communication principle) There are two ways to maintain cluster metadata: centralized and gossip protocol. The gossip protocol is used to communicate between redis cluster nodes.
Distributed addressing algorithm
hash algorithm (mass cache reconstruction)
Consistent hash algorithm (automatic cache migration) Virtual node (automatic load Balanced)
Hash slot algorithm of redis cluster
Advantages
No central architecture, supports dynamic expansion, and is transparent to the business
Equipped with Sentinel's monitoring and automatic Failover (failover) capabilities
The client does not need to connect to all nodes in the cluster, just connect to any available node in the cluster
High performance, the client is directly connected to redis Service, eliminating the loss of proxy
Disadvantages
Operation and maintenance are also very complicated, data migration requires manual intervention
Only number 0 can be used Database
Does not support batch operations (pipeline operations)
Distributed logic and storage module coupling, etc.
30, Client-based allocation
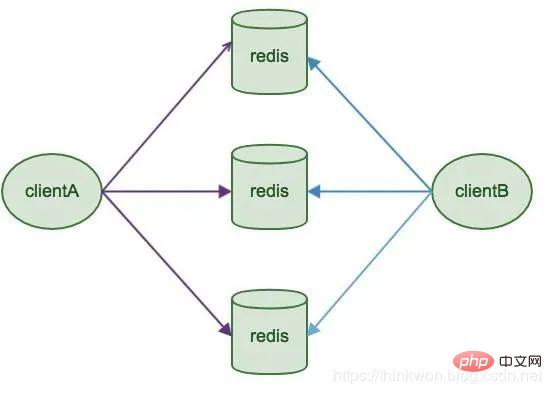
Introduction
Redis Sharding is a multi-Redis instance clustering method commonly used in the industry before Redis Cluster came out. The main idea is to use a hash algorithm to hash the key of Redis data. Through the hash function, a specific key will be mapped to a specific Redis node. The Java redis client drives jedis and supports the Redis Sharding function, that is, ShardedJedis and ShardedJedisPool combined with the cache pool
Advantages
The advantage is that it is very simple and the Redis instances on the server are independent of each other , unrelated to each other, each Redis instance runs like a single server, it is very easy to expand linearly, and the system is very flexible
Disadvantages
Due to the sharding processing On the client side, further expansion will bring challenges to operation and maintenance.
Client-side sharding does not support dynamic addition and deletion of nodes. When the topology of the server's Redis instance group changes, each client needs to be updated and adjusted. Connections cannot be shared. When the application scale increases, resource waste restricts optimization
31. Sharding based on proxy server

Introduction
The client sends a request to a proxy component, the proxy parses the client's data and forwards the request to the correct node, and finally Reply the results to the client
Features
Transparent access, the business program does not need to care about the back-end Redis instance, and the switching cost is low
Proxy logic It is isolated from the storage logic
The proxy layer has one more forwarding, and the performance is somewhat lost
Industry open source solution
Twtter open source Twemproxy
Wandoujia open source Codis
32. Redis master-slave architecture
The single-machine redis can carry QPS of tens of thousands to tens of thousands. No wait. For caches, they are generally used to support high read concurrency. Therefore, the architecture is made into a master-slave architecture, with one master and multiple slaves. The master is responsible for writing and copying data to other slave nodes, and the slave nodes are responsible for reading. All read requests go to the slave nodes. This can also easily achieve horizontal expansion, supports high read concurrency.
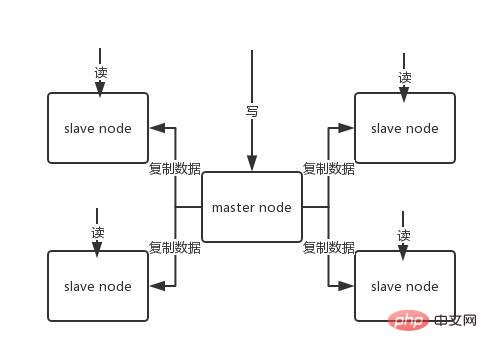
The core mechanism of redis replication
redis replicates data to the slave node asynchronously, but starting from redis2.8, the slave node will periodically confirm the amount of data it replicates each time;A master node can be configured with multiple slave nodes; slave node can also connect to other slave nodes; When the slave node replicates, it will not block the normal work of the master node. ;slave node will not block its own query operations when copying. It will use the old data set to provide services; but when the copy is completed, it needs to delete the old data set and load the new one. Data set, external services will be suspended at this time; slave node is mainly used for horizontal expansion and separation of reading and writing. The expanded slave node can improve the read throughput. Note that if a master-slave architecture is adopted, it is recommended that the persistence of the master node must be turned on. It is not recommended to use the slave node as the data hot backup of the master node, because in that case, if you turn off the persistence of the master , the data may be empty when the master crashes and restarts, and then the data of the slave node may be lost as soon as it is replicated. In addition, various backup plans for the master also need to be done. In case all the local files are lost, select an rdb from the backup to restore the master, so as toensure that there is data when starting, even if the high availability mechanism explained later is adopted, the slave node The master node can be automatically taken over, but it is also possible that the master node will automatically restart before sentinel detects the master failure, or it may cause all the slave node data above to be cleared.
The core principle of redis master-slave replicationWhen a slave node is started, it will send a PSYNC command to the master node.
If this is the first time that the slave node connects to the master node, a full resynchronization full copy will be triggered. At this time, the master will start a background thread and start generating an RDB snapshot file.
At the same time, all newly received write commands from the client client will be cached in memory. After the RDB file is generated, the master will send the RDB to the slave, and the slave will
write it to the local disk first, and then load it from the local disk into the memory.Then the master will send the write commands cached in the memory to the slave, and the slave will also synchronize the data.
If there is a network failure between the slave node and the master node and the connection is disconnected, it will automatically reconnect. After the connection, the master node will only copy the missing data to the slave.
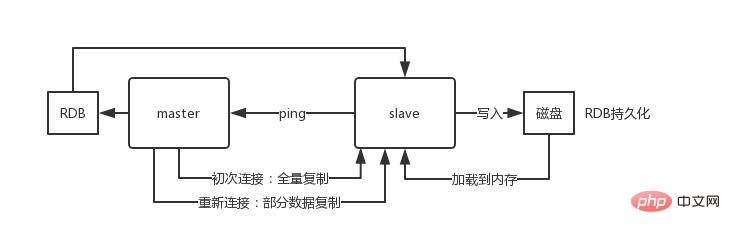
When the slave database and the master database establish the MS relationship, the SYNC command will be sent to the master database
After receiving the SYNC command, the main library will start to save the snapshot in the background (RDB persistence process) and cache the write commands received during the period.
When the snapshot is completed, the main Redis will save the snapshot file And all cached write commands are sent to slave Redis
After receiving from slave Redis, the snapshot file will be loaded and the received cached command will be executed.
After that, whenever the master Redis receives a write When commanding, the command will be sent from Redis to ensure data consistency
DisadvantagesAll slave node data replication and synchronization are handled by the master node. If the master node is under too much pressure, use the master-slave structure to solve the problem.
33. What is the master-slave replication model of the Redis cluster?In order to make the cluster still available when some nodes fail or most nodes cannot communicate, the cluster uses a master-slave replication model, and each node will have N-1 replicas
34. How is redis deployed in the production environment?redis cluster, 10 machines, 5 machines are deployed with redis master instances, and the other 5 machines are deployed with redis slave instances. Each master instance has a slave instance, and 5 nodes provide external read and write services. The read and write peak qps of one node may reach 50,000 per second, and the maximum read and write request/s for 5 machines is 250,000. What is the configuration of the machine? 32G memory, 8-core CPU, 1T disk, but the memory allocated to the redis process is 10g. In general online production environments, the memory of redis should not exceed 10g. If it exceeds 10g, there may be problems. 5 machines provide external reading and writing, with a total of 50g of memory. Because each master instance has a slave instance, it is highly available. If any master instance goes down, it will automatically failover and the redis slave instance will automatically become the master instance and continue to provide read and write services. . What data are you writing into the memory? What is the size of each piece of data? Product data, each piece of data is 10kb. 100 pieces of data is 1mb, and 100,000 pieces of data is 1g. There are 2 million pieces of product data resident in the memory, and the memory occupied is 20g, which is only less than 50% of the total memory. The current peak period is about 3,500 requests per second. In fact, large companies will have an infrastructure team responsible for the operation and maintenance of the cache cluster. 35. Talk about the concept of Redis hash slot? The Redis cluster does not use consistent hashing, but introduces the concept of hash slots. The Redis cluster has 16384 hash slots. Each key is determined by taking the modulo 16384 after passing the CRC16 check. Which slot to place, each node in the cluster is responsible for a part of the hash slot. 36. Will write operations be lost in the Redis cluster? Why? Redis does not guarantee strong consistency of data, which means that in practice, the cluster may lose write operations under certain conditions. 37. How are Redis clusters replicated? Asynchronous replication 38. What is the maximum number of nodes in a Redis cluster? 16384 39. How to choose a database for Redis cluster? Redis cluster currently cannot select database, and defaults to database 0. 9. Partition 40. Redis is single-threaded. How to improve the utilization of multi-core CPU? You can deploy multiple Redis instances on the same server and use them as different servers. At some point, one server is not enough anyway, so if you want With multiple CPUs, you can consider sharding. 41. Why do you need Redis partitioning? Partitioning allows Redis to manage larger memory, and Redis will be able to use the memory of all machines. Without partitions, you can only use up to one machine's memory. Partitioning allows Redis's computing power to be doubled by simply adding computers, and Redis's network bandwidth will also increase exponentially with the addition of computers and network cards. 42. Do you know what Redis partition implementation solutions are available? Client-side partitioning means that the client has already decided which redis node the data will be stored in or read from. Most clients already implement client-side partitioning. Agent partitioning means that the client sends the request to the agent, and then the agent decides which node to write or read data to. The agent decides which Redis instances to request based on partition rules, and then returns them to the client based on the Redis response results. A proxy implementation of redis and memcached is Twemproxy Query routing (Query routing) means that the client randomly requests any redis instance, and then Redis forwards the request to the correct Redis node. Redis Cluster implements a hybrid form of query routing, but instead of forwarding requests directly from one redis node to another redis node, it redirects directly to the correct redis node with the help of the client. 43. What are the disadvantages of Redis partitioning? Operations involving multiple keys are generally not supported. For example, you cannot intersect two collections because they may be stored in different Redis instances (actually there is a way for this situation, but the intersection command cannot be used directly). If you operate multiple keys at the same time, you cannot use Redis transactions. The granularity used in partitioning is key, and you cannot use a very long sorting key to store a data set (The partitioning granularity is the key , so it is not possible to shard a dataset with a single huge key like a very big sorted set) When using partitions, data processing will be very complicated, for example, in order to back up, you must start from different Redis instances Collect RDB/AOF files simultaneously with the host. Dynamic expansion or contraction when partitioning can be very complicated. Redis cluster adds or deletes Redis nodes at runtime, which can achieve data rebalancing that is transparent to users to the greatest extent. However, some other client partitioning or proxy partitioning methods do not support this feature. However, there is a pre-sharding technology that can also solve this problem better. 10. Distributed Issues 44. Redis implements distributed locks Redis is a single-process single-thread mode and uses queue mode to access concurrently It becomes serial access, and there is no competition between multiple clients' connections to Redis. You can use the SETNX command to implement distributed locks in Redis. If and only if key does not exist, set the value of key to value. If the given key already exists, SETNX does nothing. SETNX is the abbreviation of "SET if Not eXists" (if it does not exist, then SET). Return value: If the setting is successful, 1 is returned. Setup fails and returns 0. The process and matters for using SETNX to complete the synchronization lock are as follows: Use the SETNX command to obtain the lock. If 0 is returned (the key has been exists, the lock already exists), the acquisition fails, otherwise the acquisition succeeds. In order to prevent exceptions in the program after acquiring the lock, causing other threads/processes to always return 0 when calling the SETNX command and enter a deadlock state, a "reasonable" expiration time needs to be set for the key. Release the lock and use the DEL command to delete the lock data. 45. How to solve the problem of concurrent competition for Key in Redis The so-called problem of concurrent competition for Key in Redis is that multiple systems operate on a key at the same time, but in the end The order of execution is different from the order we expect, which leads to different results! Recommend a solution: distributed lock (both zookeeper and redis can implement distributed locks). (If there is no concurrent competition for Key in Redis, do not use distributed locks, which will affect performance) Distributed locks based on zookeeper temporary ordered nodes. The general idea is: when each client locks a certain method, a unique instantaneous ordered node is generated in the directory of the specified node corresponding to the method on zookeeper. The way to determine whether to acquire a lock is very simple. You only need to determine the smallest sequence number among the ordered nodes. When the lock is released, just delete the transient node. At the same time, it can avoid deadlock problems caused by locks that cannot be released due to service downtime. After completing the business process, delete the corresponding child node to release the lock. In practice, reliability is of course the main priority. Therefore, Zookeeper is recommended first. 46. Should distributed Redis be done in the early stage or done in the later stage when the scale is increased? Why? Since Redis is so lightweight (a single instance only uses 1M memory), the best way to prevent future expansion is to start more instances at the beginning. Even if you only have one server, you can have Redis run in a distributed manner from the beginning, using partitions to start multiple instances on the same server. Set up a few more Redis instances at the beginning, such as 32 or 64 instances. This may be troublesome for most users, but it is worth the sacrifice in the long run. In this case, when your data continues to grow and you need more Redis servers, all you need to do is just migrate the Redis instance from one service to another server (without considering repartitioning The problem). Once you add another server, you need to migrate half of your Redis instances from the first machine to the second machine. 47. What is RedLock The Redis official website proposed an authoritative way to implement distributed locks based on Redis called Redlock. This method is better than the original The single-node approach is more secure. It can guarantee the following features: Safety features: Mutually exclusive access, that is, only one client can always get the lock Avoid deadlock: In the end, the client may get the lock, and no deadlock will occur, even if the client that originally locked a resource crashes or a network partition occurs Fault tolerance: As long as most Redis As long as the node is alive, it can provide services normally 11. Cache exception 48. Cache avalanche Cache avalanche refers to caching a large area at the same time Failure, therefore, subsequent requests will fall on the database, causing the database to withstand a large number of requests in a short period of time and collapse. Solution: Set the expiration time of cached data randomly to prevent a large number of data from expiring at the same time. Generally, when the amount of concurrency is not particularly large, the most commonly used solution is lock queuing. Add a corresponding cache tag to each cached data and record whether the cache is invalid. If the cache tag is invalid, update the data cache. 49. Cache penetration Cache penetration refers to data that is neither in the cache nor in the database, causing all requests to fall on the database, causing the database to be short. It crashed due to a large number of requests within a short period of time. Solution: Add verification at the interface layer, such as user authentication verification, basic verification of id, and direct interception of id The data that cannot be obtained from the cache is not obtained in the database. At this time, the key-value pair can also be written as key-null. The cache validity time can be set shorter, such as 30 seconds (the setting is too long) It will make it impossible to use it under normal circumstances). This can prevent attacking users from repeatedly using the same ID to brute force attacks Use a Bloom filter to hash all possible data into a large enough bitmap. Data that must not exist will be hashed by this bitmap Intercept it, thereby avoiding query pressure on the underlying storage system Additional: The utilization of space has reached an extreme level, that is, Bitmap and Bloom Filter. Bitmap: Typically it is a hash table The disadvantage is that Bitmap can only record 1 bit of information for each element. If you want to complete additional functions, I am afraid only It can be accomplished by sacrificing more space and time. Bloom filter (recommended) introduces k(k>1)k(k>1) independent hash functions to ensure that Under a given space and misjudgment rate, the process of element weight determination is completed. Its advantage is that space efficiency and query time are much higher than the general algorithm, but its disadvantage is that it has a certain misrecognition rate and difficulty in deletion. The core idea of the Bloom-Filter algorithm is to use multiple different Hash functions to resolve "conflicts". Hash has a conflict (collision) problem. The values of two URLs obtained by using the same Hash may be the same. In order to reduce conflicts, we can introduce several more hashes. If we find that an element is not in the set through one of the hash values, then the element is definitely not in the set. Only when all Hash functions tell us that the element is in the set can we be sure that the element exists in the set. This is the basic idea of Bloom-Filter. Bloom-Filter is generally used to determine whether an element exists in a large data collection. 50. Cache breakdown Cache breakdown refers to data that is not in the cache but is in the database (usually the cache time has expired ), at this time, due to the large number of concurrent users, the read cache did not read the data at the same time, and at the same time went to the database to fetch the data, causing the database pressure to increase instantly, causing excessive pressure. Different from cache avalanche, cache breakdown refers to concurrent query of the same data. Cache avalanche means that different data have expired, and a lot of data cannot be found, so the database is searched. Solution Set hotspot data to never expire. Add mutex lock, mutex lock 51. Cache preheating Cache preheating means that after the system goes online, the relevant cache data Load directly into the cache system. In this way, you can avoid the problem of querying the database first and then caching the data when the user requests it! Users directly query cached data that has been preheated! Solution: Write a cache refresh page directly, and do it manually when going online; The amount of data is not large, and it can be done when the project is started Automatically load when needed; Refresh the cache regularly; 52. Cache downgrade When the number of visits increases sharply and service problems occur (such as response time When slow or unresponsive) or non-core services affect the performance of core processes, it is still necessary to ensure that the service is still available, even if the service is impaired. The system can automatically downgrade based on some key data, or configure switches to achieve manual downgrade. , The ultimate goal of cache downgrade is to ensure that the core service is available, even if it is lossy. And some services cannot be downgraded (such as adding to shopping cart, checkout). Before downgrading, the system should be sorted out to see if the system can lose soldiers and retain commanders; thereby sorting out what must be protected to the death and what can be downgraded; for example, you can refer to the log level setting plan: General: For example, some services occasionally time out due to network jitter or the service is going online, and can be automatically downgraded; Warning: Some services have fluctuating success rates over a period of time (such as 95~100%), you can automatically downgrade or manually downgrade, and send an alarm; Error: For example, the availability rate is lower than 90%, or the database connection pool is exhausted. Or the number of visits suddenly surges to the maximum threshold that the system can bear. At this time, it can be automatically downgraded or manually downgraded according to the situation; Serious error:For example, if the data is wrong due to special reasons, this Emergency manual downgrade is required. The purpose of service downgrade is to prevent Redis service failure from causing avalanche problems in the database. Therefore, for unimportant cached data, a service downgrade strategy can be adopted. For example, a common approach is that if there is a problem with Redis, instead of querying the database, it directly returns the default value to the user. 53. Hot data and cold data Only hot data and cache are valuable. For cold data, most of the data may have been squeezed out of the memory before it is accessed again, which not only takes up memory, but also has little value. For frequently modified data, consider using cache depending on the situation For hot data, such as one of our IM products, birthday greeting module, and birthday list of the day, the cache may be read hundreds of thousands of times. For another example, in a navigation product, we cache navigation information and may read it millions of times in the future. Cache is meaningful only if the data is read at least twice before updating. This is the most basic strategy. If the cache fails before it takes effect, it will not be of much value. What about the scenario where the cache does not exist and the frequency of modification is very high, but caching has to be considered? have! For example, this reading interface puts a lot of pressure on the database, but it is also hot data. At this time, you need to consider caching methods to reduce the pressure on the database, such as the number of likes, collections, and shares of one of our assistant products. This is very typical hot data, but it keeps changing. At this time, the data needs to be saved to the Redis cache synchronously to reduce the pressure on the database. 54. Cache hotspot key When a Key in the cache (such as a promotional product) expires at a certain point in time, it happens to be correct at this point in time. This Key has a large number of concurrent requests. When these requests find that the cache has expired, they usually load data from the back-end DB and reset it to the cache. At this time, large concurrent requests may instantly overwhelm the back-end DB. Solution: Lock the cache query. If the KEY does not exist, lock it, then check the DB into the cache, and then unlock it; if other processes find that there is Just wait for the lock, and then wait for the unlock to return the data or enter the DB query Common tools 55. What are the Java clients supported by Redis? Which one is officially recommended? Redisson, Jedis, lettuce, etc., the official recommendation is to use Redisson. 56. What is the relationship between Redis and Redisson? Redisson is an advanced distributed coordination Redis client that can help users easily implement some Java objects (Bloom filter, BitSet, Set, SetMultimap, ScoredSortedSet, SortedSet, Map) in a distributed environment , ConcurrentMap, List, ListMultimap, Queue, BlockingQueue, Deque, BlockingDeque, Semaphore, Lock, ReadWriteLock, AtomicLong, CountDownLatch, Publish / Subscribe, HyperLogLog). 57. What are the advantages and disadvantages of Jedis and Redisson? Jedis is a client implemented by Redis in Java. Its API provides relatively comprehensive support for Redis commands; Redisson implements a distributed and scalable Java data structure. Compared with Jedis, its functions It is relatively simple, does not support string operations, and does not support Redis features such as sorting, transactions, pipelines, and partitions. The purpose of Redisson is to promote the separation of users' concerns from Redis, so that users can focus more on processing business logic Other issues 58, Redis and The difference between Memcached Both are non-relational memory key-value databases. Now companies generally use Redis to implement caching, and Redis itself is becoming more and more powerful! Redis and Memcached have the following main differences: #(1) All values in memcached are simple strings, and redis, as its replacement, supports richer data types (2) redis is much faster than memcached (3) redis can persist its data 59. How to ensure double writing of cache and database data consistency? As long as you use cache, it may involve dual storage and double writing of cache and database. As long as you use dual writing, there will definitely be data consistency problems. So how do you solve the consistency problem? ? Generally speaking, if your system does not strictly require the cache database to be consistent, the cache may occasionally be slightly inconsistent with the database. It is best not to do this solution. Read request and write request strings Serialize and serialize it into a memory queue, so as to ensure that there will be no inconsistency. After serialization, the throughput of the system will be greatly reduced, and the usage will be significantly lower than that under normal conditions. Download several times more machines to support an online request. Another way is to temporarily produce inconsistencies, but the probability of occurrence is very small, which is to update the database first and then delete the cache. #60. Redis common performance problems and solutions? Master is best not to do any persistence work, including memory snapshots and AOF log files, especially do not enable memory snapshots for persistence. If the data is critical, a Slave enables AOF backup data, and the policy is to synchronize once per second. For the speed of master-slave replication and the stability of the connection, it is best for Slave and Master to be in the same LAN. Try to avoid adding slave libraries to the stressed main library Master calls BGREWRITEAOF to rewrite the AOF file. AOF will occupy a large amount of CPU and memory resources during rewriting, resulting in service failure. The load is too high and the service is temporarily suspended. For the sake of the stability of the Master, do not use a graph structure for master-slave replication. It is more stable to use a one-way linked list structure, that is, the master-slave relationship is: Master 61. Why doesn’t Redis officially provide a Windows version? Because the current Linux version is quite stable and has a large number of users, there is no need to develop a windows version, which will cause compatibility and other problems. 62. What is the maximum capacity that a string type value can store? 512M 63. How does Redis insert large amounts of data? Starting with Redis 2.6, redis-cli supports a new mode called pipe mode for performing large amounts of data insertion work. 64. Suppose there are 100 million keys in Redis, and 100,000 keys start with a fixed, known prefix. How to find them all? Use the keys command to scan out the key list of the specified mode. The other party then asked: If this redis is providing services to online businesses, what are the problems with using the keys command? At this time you have to answer one of the key features of redis: redis's single thread. The keys instruction will cause the thread to block for a period of time and the online service will pause. The service cannot be restored until the instruction is executed. At this time, you can use the scan command. The scan command can extract the key list of the specified mode without blocking, but there will be a certain probability of duplication. Just do it once on the client, but the overall time spent will be longer than using it directly. The keys command is long. 65. Have you ever used Redis to create an asynchronous queue? How was it implemented? Use the list type to save data information, rpush produces messages, and lpop consumes messages. When lpop has no messages, you can sleep for a period of time, and then check whether there is any information. If you do not want to sleep, you can use blpop , when there is no information, it will block until the information arrives. Redis can implement one producer and multiple consumers through the pub/sub topic subscription model. Of course, there are certain shortcomings. When the consumer goes offline, the produced messages will be lost. 66. How does Redis implement delay queue? Use sortedset, use timestamp as score, message content as key, call zadd to produce messages, and consumers use zrangbyscore to obtain data n seconds ago for polling processing. 67. How does the Redis recycling process work? A client ran a new command and added new data. Redis checks the memory usage. If it is greater than the limit of maxmemory, it will be recycled according to the set policy. A new command is executed, etc. So we keep crossing the boundary of the memory limit by constantly reaching the boundary and then constantly recycling back below the boundary. If the result of a command causes a large amount of memory to be used (such as saving the intersection of a large set to a new key), it will not take long for the memory limit to be exceeded by this memory usage. 68. What algorithm is used for Redis recycling? LRU algorithm. Okay, Redis interview questions will be shared here. If it is helpful to you, please give it a "like" to encourage it~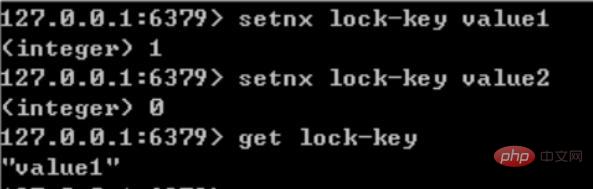
The above is the detailed content of The latest version of 2023 68 Redis interview questions (collection). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.



