What are the differences between ArrayList, LinkedList and Vector?

1. Analysis from the storage data structure
(Recommended tutorial: java introductory tutorial)
ArrayList: Array
Vector: Array
LinkedList: Doubly linked list
Array: You can quickly search based on the subscript, so in most cases, the query is fast.
But if you want to perform addition and deletion operations, you will need to move all the elements behind the modified element, so the overhead of additions and deletions is relatively large, and the execution efficiency of the array's addition and deletion operations is low. ArrayList and Vector, which use arrays as data storage structures, also have these characteristics. The query speed is fast (can be retrieved directly based on the subscript, which is faster than iterative search), and the addition and deletion are slow.
Linked list: It is convenient to add and delete elements. To add or delete an element, you only need to deal with the references between nodes. Just like people holding hands in a row, if you want to add or delete someone, you only need to change the two people nearby to hold hands with another person, and it will have no effect on the people who are already holding hands. The resources and time consumed by substitution are the same no matter where.
But the query is inconvenient. It needs to be compared one by one, and it cannot be directly searched based on the subscript. LinkedList, which is stored in a linked list structure, also has these characteristics. It is easy to add and delete, but slow to query (referring to random query, not sequential query).
2. Analysis from the perspective of inheritance
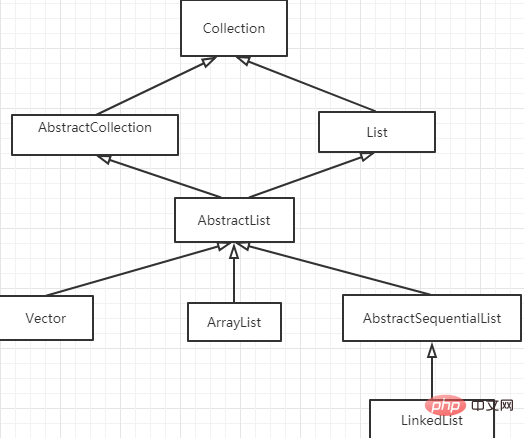
They all implement the List interface, which means they all implement get(int location ), remove(int location) and other "functions to obtain and delete nodes based on index values".
(Video tutorial recommendation: java video tutorial)
It is easy to get the value of the array structure according to the subscript, and the implementation of the LinkedList bidirectional list is also relatively simple, by counting the index value To implement, search starts from 1/2 the length of the linked list. If the subscript is larger, it will start searching from the head of the list. If it is smaller, it will start searching from the end of the list.
3. Analysis from the perspective of concurrency safety
Vector: thread safety
ArrayList: non-thread safety
LinkedList: non-thread Security
4. Data growth analysis
Vector: By default, the growth is twice the length of the original array. Speaking of default, it means that he can actually set the initialization size independently.
ArrayList: Automatically grows 50% of the original array.
The above is the detailed content of What are the differences between ArrayList, LinkedList and Vector?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is the difference between using foreach and iterator to delete elements when traversing Java ArrayList?
Apr 27, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
What is the difference between using foreach and iterator to delete elements when traversing Java ArrayList?
Apr 27, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
1. The difference between Iterator and foreach is the polymorphic difference (the bottom layer of foreach is Iterator) Iterator is an interface type, it does not care about the type of collection or array; both for and foreach need to know the type of collection first, even the type of elements in the collection; 1. Why is it said that the bottom layer of foreach is the code written by Iterator: Decompiled code: 2. The difference between remove in foreach and iterator. First, look at the Alibaba Java Development Manual, but no error will be reported in case 1, and an error will be reported in case 2 (java. util.ConcurrentModificationException) first
 How to check if ArrayList contains a certain element in Java?
Sep 03, 2023 pm 04:09 PM
How to check if ArrayList contains a certain element in Java?
Sep 03, 2023 pm 04:09 PM
You can use the contains() method of the List interface to check whether an object exists in the list. contains() method booleancontains(Objecto) Returns true if this list contains the specified element. More formally, returns true if and only if this list contains at least one element e such that (o==null?e==null:o.equals(e)). Parameter c - the element whose presence in this list is to be tested. Return Value Returns true if this list contains the specified element. Throws ClassCastException - if the specified element's type is incompatible with this list (optional). NullP
 Remove elements from ArrayList using java's ArrayList.remove() function
Jul 24, 2023 pm 01:21 PM
Remove elements from ArrayList using java's ArrayList.remove() function
Jul 24, 2023 pm 01:21 PM
Use java's ArrayList.remove() function to remove elements from an ArrayList. In Java, ArrayList is a commonly used collection class used to store and operate a set of elements. The ArrayList class provides many methods to add, delete, modify, and query elements in the collection. One of the more frequently used methods is remove(), which can remove elements from an ArrayList. The remove() method of ArrayList has two overloaded forms: one
 Use the removeLast() method of the LinkedList class to delete the last element in the linked list
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
Use the removeLast() method of the LinkedList class to delete the last element in the linked list
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
Use the removeLast() method of the LinkedList class to delete the last element in the linked list. LinkedList is a common data structure in the Java collection framework. It stores elements in the form of a doubly linked list. Through the methods provided by the LinkedList class, we can easily operate on the linked list, such as adding, deleting and modifying elements. In some scenarios, we may need to delete the last element in the linked list. LinkedList class provides removeLas
 What is the reason why the initial capacity of ArrayList in Java is 10?
May 10, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
What is the reason why the initial capacity of ArrayList in Java is 10?
May 10, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
Why is the initial capacity of HashMap 16? When talking about the initialization capacity of ArrayList, we must first review the initialization capacity of HashMap. Taking the Java8 source code as an example, there are two relevant factors in HashMap: initialization capacity and loading factor: /***Thedefaultinitialcapacity-MUSTbeapoweroftwo.*/staticfinalintDEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY=1>1);if(newCapacity-minCapacity0)newCapacity=hugeCapacity
 Use java's ArrayList.clear() function to clear the elements in the ArrayList
Jul 24, 2023 pm 02:04 PM
Use java's ArrayList.clear() function to clear the elements in the ArrayList
Jul 24, 2023 pm 02:04 PM
Use Java's ArrayList.clear() function to clear the elements in the ArrayList. In Java programming, ArrayList is a very commonly used data structure that can dynamically store and access elements. However, in some cases, we may need to clear all elements in the ArrayList in order to reuse or free the memory. At this time, you can use the clear() function of ArrayList to achieve it. ArrayList.clear()
 Java uses the contains() function of the ArrayList class to determine whether an element exists
Jul 24, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
Java uses the contains() function of the ArrayList class to determine whether an element exists
Jul 24, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
Java uses the contains() function of the ArrayList class to determine whether an element exists. ArrayList is a very commonly used data structure in Java programming. It provides a flexible way to store and manipulate a set of data. In addition to simply adding, deleting and accessing elements, ArrayList also provides some useful methods, such as the contains() function, which is used to determine whether an element exists in the ArrayList. contains() function is A
 Java program to add elements to LinkedList
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:21 PM
Java program to add elements to LinkedList
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:21 PM
LinkedList is a general class of JavaCollectionFramework, which implements three interfaces: List, Deque and Queue. It provides the functionality of the LinkedList data structure, a linear data structure in which each element is linked to each other. We can perform a variety of operations on a LinkedList, including adding, removing, and traversing elements. To add elements to the LinkedList collection, we can use various built-in methods such as add(), addFirst(), and addLast(). We will explore how to use these methods to add elements to a LinkedList. in Java




