Redis download and install
The following column Redis Tutorial will introduce you to the specific steps of Redis download and Redis installation. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!

Redis Download and Install
Redis has an active community on GitHub. Over the years, a large number of pull requests have been raised and merged, and the author Antirez always provides timely responses in the issues section of GitHub. Therefore, the release cycle of Redis is very fast. They are widely used from the early versions 2.6/2.8 to 3.0/3.2 to the latest 4 versions. Each version provides some basic enhancements and bugfixes. Therefore, it is one of the best practices to use the latest version of Redis if possible.
In this book, we use the latest version of Redis 4.0.1.
Redis is an open software written in pure C language, so we can install it by compiling. Major operating systems also include Redis binary packages in their software repositories, although the Redis versions are often out of date.
1: Prepare!
You can find the download link and basic installation steps at https://redis.io/download. If you want to build Redis by compiling source code in Linux/Unix/macOS, you need the gcc compiler and the C standard library libc in your environment. When installing the OS repository, all you need is an Internet connection and the correct repository configuration.
2: How to do it?
We will demonstrate the compilation and installation of Redis in Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS (Xenial Xerus). The download and build steps are as follows:
Set up the build tool:
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential
Create a directory and enter Redis:
$ mkdir /redis $ cd /redis
Then, download Redis:
$ wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-4.0.1.tar.gz
Solution Zip and enter the directory:
$ tar zxvf redis-4.0.1.tar.gz $ cd redis-4.0.1
Create a directory for the Redis configuration file and copy the default configuration file into it:
$ mkdir /redis/conf $ cp redis.conf /redis/conf/
Establish dependencies:
$ cd deps $ make hiredis lua jemalloc linenoise $ cd ..
Note
Due to differences between the various operating systems and libraries installed on them, the above steps will be required when an error occurs indicating that something is not met. For example, you may encounter the error message: zmalloc.h:50:31: fatal error: jemalloc/jemalloc.h: No such file or directory. For most environments, this step is not necessary if there are no issues with the dependencies in question. .
Compiling:
$ make
If all goes well, the following message will be displayed. This means that the compilation was completed successfully:
It's a good idea to run 'make test' ;) make[1]: Leaving directory '/redis/redis-4.0.1/src'
Installing Redis:
$ make PREFIX=/redis install
The following message means that the installation was successful:
Enter the /redis directory and verify that the Redis binary has been generated:
$ ls /redis/bin redis-benchmark redis-check-aof redis-check-rdb redis-cli redis-sentinel redis-server
Congratulations! You have completed the compilation and installation of Redis.
Compared with compiling and installing, apt-get is much easier to install Redis in Ubuntu. Let’s take a look:
First, update the software repository index:
$ sudo apt-get update
Then start the installation:
$ sudo apt-get install redis-server
Once completed, check if Redis is set up in your environment :
$ which redis-server
Three: How does this work?
When choosing a Redis version, remember that Redis follows standard versioning conventions, which is the major.minor.patch level. Even-numbered minors represent stable versions, while odd-numbered minors represent unstable versions, although some versions of Redis use odd-numbered minors.
The difference between building Redis by compiling and building from a software repository is that the former can add optimization or debugging options at compile time and also has the flexibility to specify the installation location during the installation process.
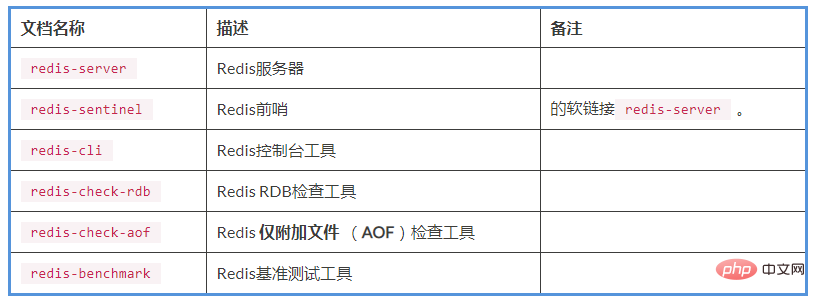
After installation, there are some executable files in the bin directory. Their descriptions and instructions are shown in the table below:
Four: And more!
For Windows, you can get the Redis version for Windows, which is maintained by the Microsoft Open Technologies group:
https://github.com/MicrosoftArchive/redis/releases .
Simply download the .msi executable file and double-click to install, keeping the default configuration.
For macOS, the process is not much different than in Linux. You can also install Redis by issuing the brew install redis command on macOS.
The above is the detailed content of Redis download and install. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
To view all keys in Redis, there are three ways: use the KEYS command to return all keys that match the specified pattern; use the SCAN command to iterate over the keys and return a set of keys; use the INFO command to get the total number of keys.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.




