 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL
Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL
Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL

[Related learning recommendations: python tutorial】
Experimental environment
1. Install Python 3.7
2. Install requests, bs4, pymysql module
Experimental steps 1. Installation environment and module
Please refer to https://www. jb51.net/article/194104.htm
2.Write code
# 51cto 博客页面数据插入mysql数据库
# 导入模块
import re
import bs4
import pymysql
import requests
# 连接数据库账号密码
db = pymysql.connect(host='172.171.13.229',
user='root', passwd='abc123',
db='test', port=3306,
charset='utf8')
# 获取游标
cursor = db.cursor()
def open_url(url):
# 连接模拟网页访问
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '
'Chrome/57.0.2987.98 Safari/537.36'}
res = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
return res
# 爬取网页内容
def find_text(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
# 博客名
titles = []
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_="tit")
for each in targets:
each = each.text.strip()
if "置顶" in each:
each = each.split(' ')[0]
titles.append(each)
# 阅读量
reads = []
read1 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl on")
read2 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl")
for each in read1:
reads.append(each.text)
for each in read2:
reads.append(each.text)
# 评论数
comment = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='comment fl')
for each in targets:
comment.append(each.text)
# 收藏
collects = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='collect fl')
for each in targets:
collects.append(each.text)
# 发布时间
dates=[]
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_='time fl')
for each in targets:
each = each.text.split(':')[1]
dates.append(each)
# 插入sql 语句
sql = """insert into blog (blog_title,read_number,comment_number, collect, dates)
values( '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s');"""
# 替换页面 \xa0
for titles, reads, comment, collects, dates in zip(titles, reads, comment, collects, dates):
reads = re.sub('\s', '', reads)
comment = re.sub('\s', '', comment)
collects = re.sub('\s', '', collects)
cursor.execute(sql % (titles, reads, comment, collects,dates))
db.commit()
pass
# 统计总页数
def find_depth(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
depth = soup.find('li', class_='next').previous_sibling.previous_sibling.text
return int(depth)
# 主函数
def main():
host = "https://blog.51cto.com/13760351"
res = open_url(host) # 打开首页链接
depth = find_depth(res) # 获取总页数
# 爬取其他页面信息
for i in range(1, depth + 1):
url = host + '/p' + str(i) # 完整链接
res = open_url(url) # 打开其他链接
find_text(res) # 爬取数据
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()3..MySQL creates the corresponding table
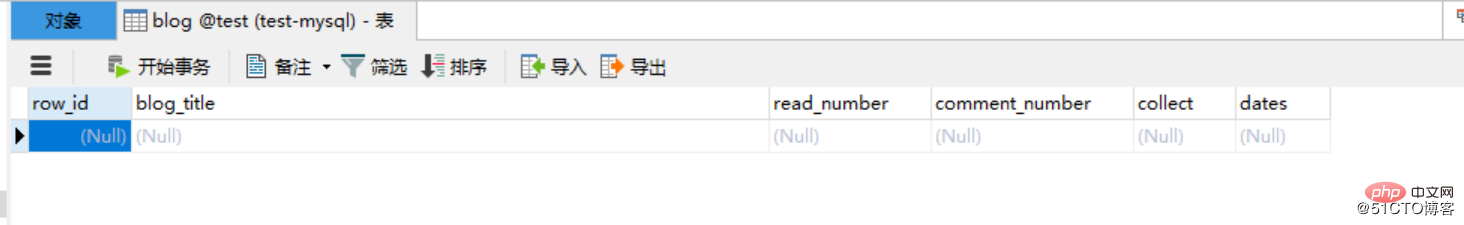
CREATE TABLE `blog` ( `row_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键', `blog_title` varchar(52) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '博客标题', `read_number` varchar(26) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '阅读数量', `comment_number` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '评论数量', `collect` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '收藏数量', `dates` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '发布日期', PRIMARY KEY (`row_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
import re
import bs4
import pymysql
import requests
# 连接数据库
db = pymysql.connect(host='172.171.13.229',
user='root', passwd='abc123',
db='test', port=3306,
charset='utf8')
# 获取游标
cursor = db.cursor()
def open_url(url):
# 连接模拟网页访问
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '
'Chrome/57.0.2987.98 Safari/537.36'}
res = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
return res
# 爬取网页内容
def find_text(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
# 博客标题
titles = []
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_="tit")
for each in targets:
each = each.text.strip()
if "置顶" in each:
each = each.split(' ')[0]
titles.append(each)
# 阅读量
reads = []
read1 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl on")
read2 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl")
for each in read1:
reads.append(each.text)
for each in read2:
reads.append(each.text)
# 评论数
comment = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='comment fl')
for each in targets:
comment.append(each.text)
# 收藏
collects = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='collect fl')
for each in targets:
collects.append(each.text)
# 发布时间
dates=[]
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_='time fl')
for each in targets:
each = each.text.split(':')[1]
dates.append(each)
# 插入sql 语句
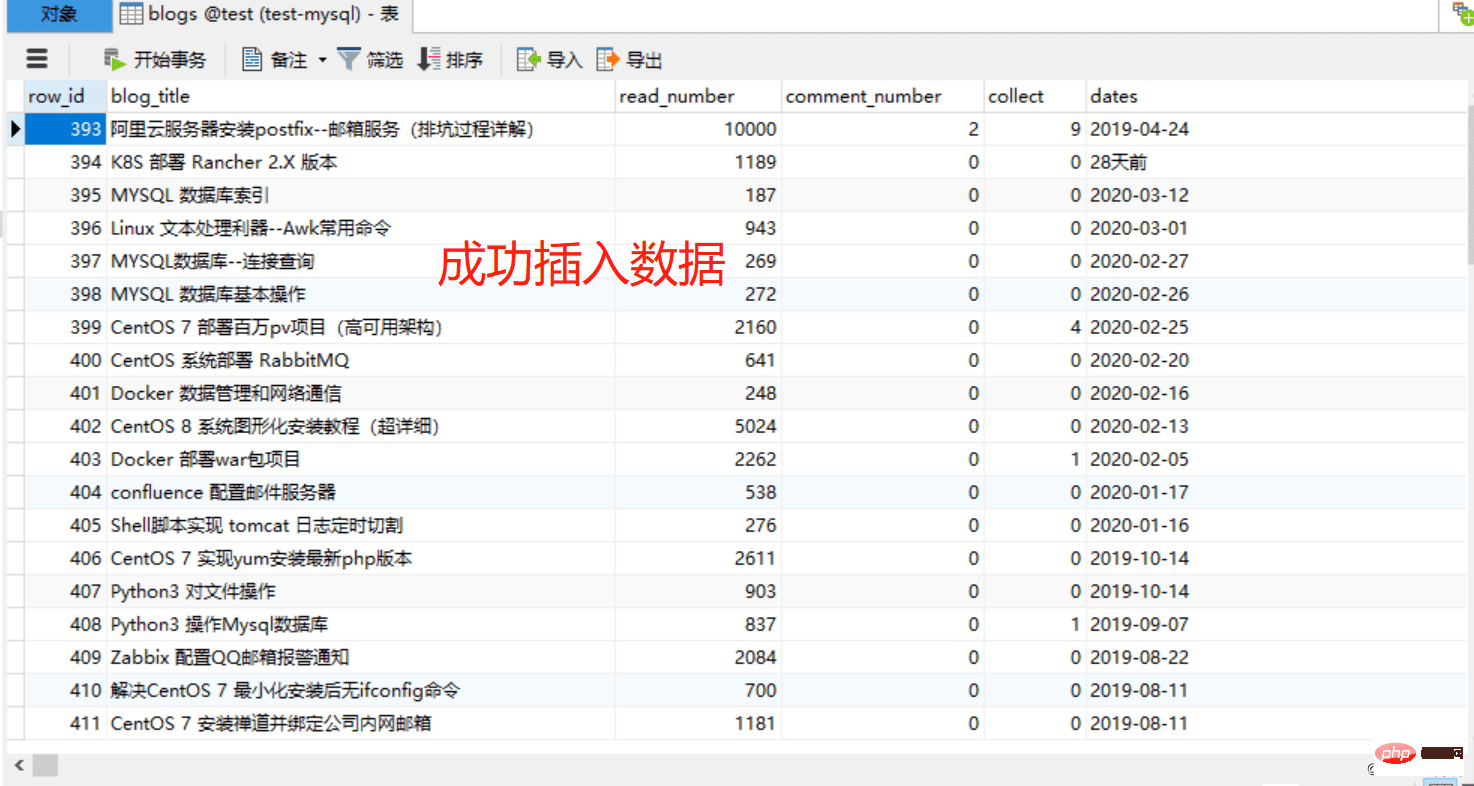
sql = """insert into blogs (blog_title,read_number,comment_number, collect, dates)
values( '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s');"""
# 替换页面 \xa0
for titles, reads, comment, collects, dates in zip(titles, reads, comment, collects, dates):
reads = re.sub('\s', '', reads)
reads=int(re.sub('\D', "", reads)) #匹配数字,转换为整型
comment = re.sub('\s', '', comment)
comment = int(re.sub('\D', "", comment)) #匹配数字,转换为整型
collects = re.sub('\s', '', collects)
collects = int(re.sub('\D', "", collects)) #匹配数字,转换为整型
dates = re.sub('\s', '', dates)
cursor.execute(sql % (titles, reads, comment, collects,dates))
db.commit()
pass
# 统计总页数
def find_depth(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
depth = soup.find('li', class_='next').previous_sibling.previous_sibling.text
return int(depth)
# 主函数
def main():
host = "https://blog.51cto.com/13760351"
res = open_url(host) # 打开首页链接
depth = find_depth(res) # 获取总页数
# 爬取其他页面信息
for i in range(1, depth + 1):
url = host + '/p' + str(i) # 完整链接
res = open_url(url) # 打开其他链接
find_text(res) # 爬取数据
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
#主程序入口
if __name__ == '__main__':
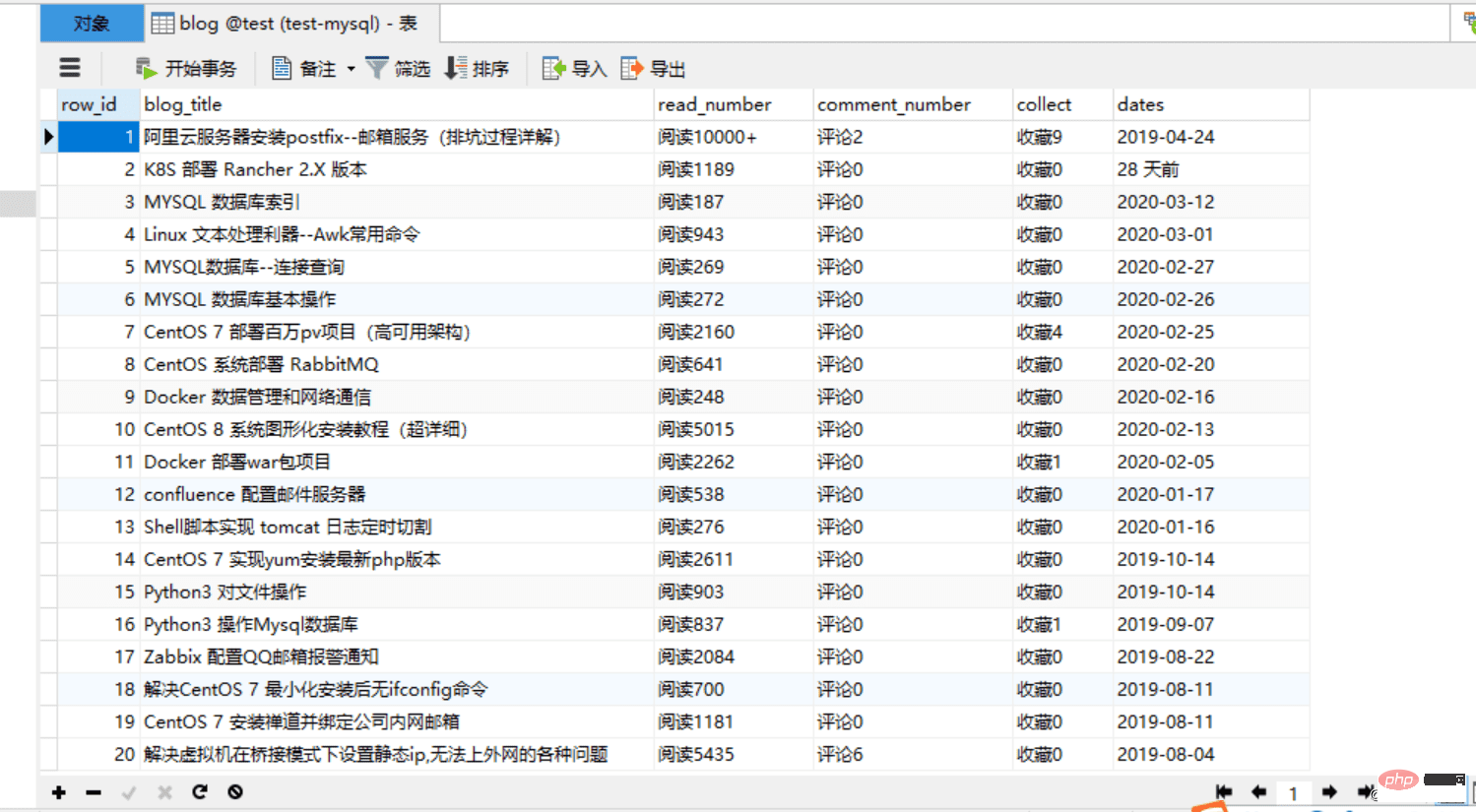
main()CREATE TABLE `blogs` ( `row_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键', `blog_title` varchar(52) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '博客标题', `read_number` int(26) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '阅读数量', `comment_number` int(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '评论数量', `collect` int(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '收藏数量', `dates` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '发布日期', PRIMARY KEY (`row_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
#末尾修改为:
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
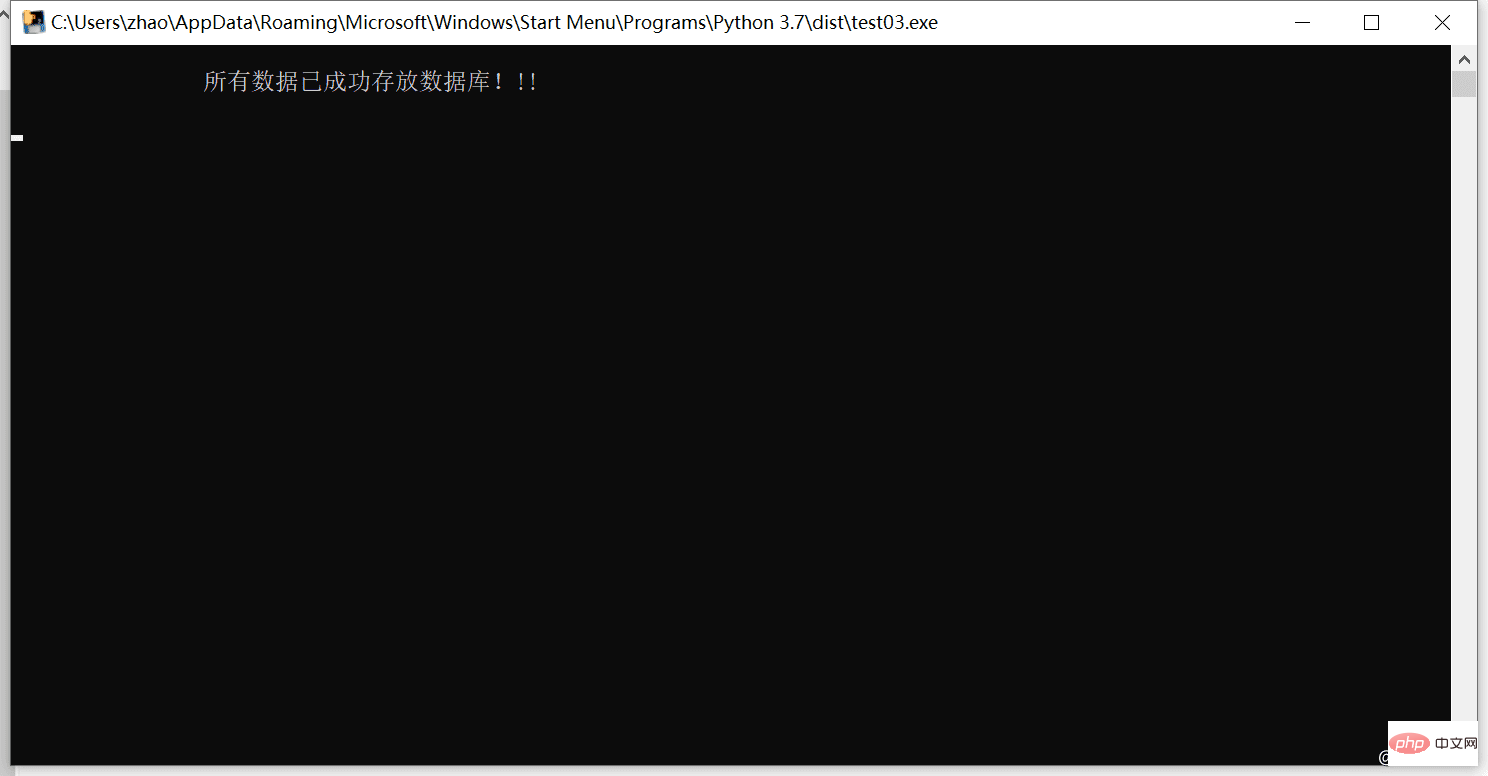
print("\n\t\t所有数据已成功存放数据库!!! \n")
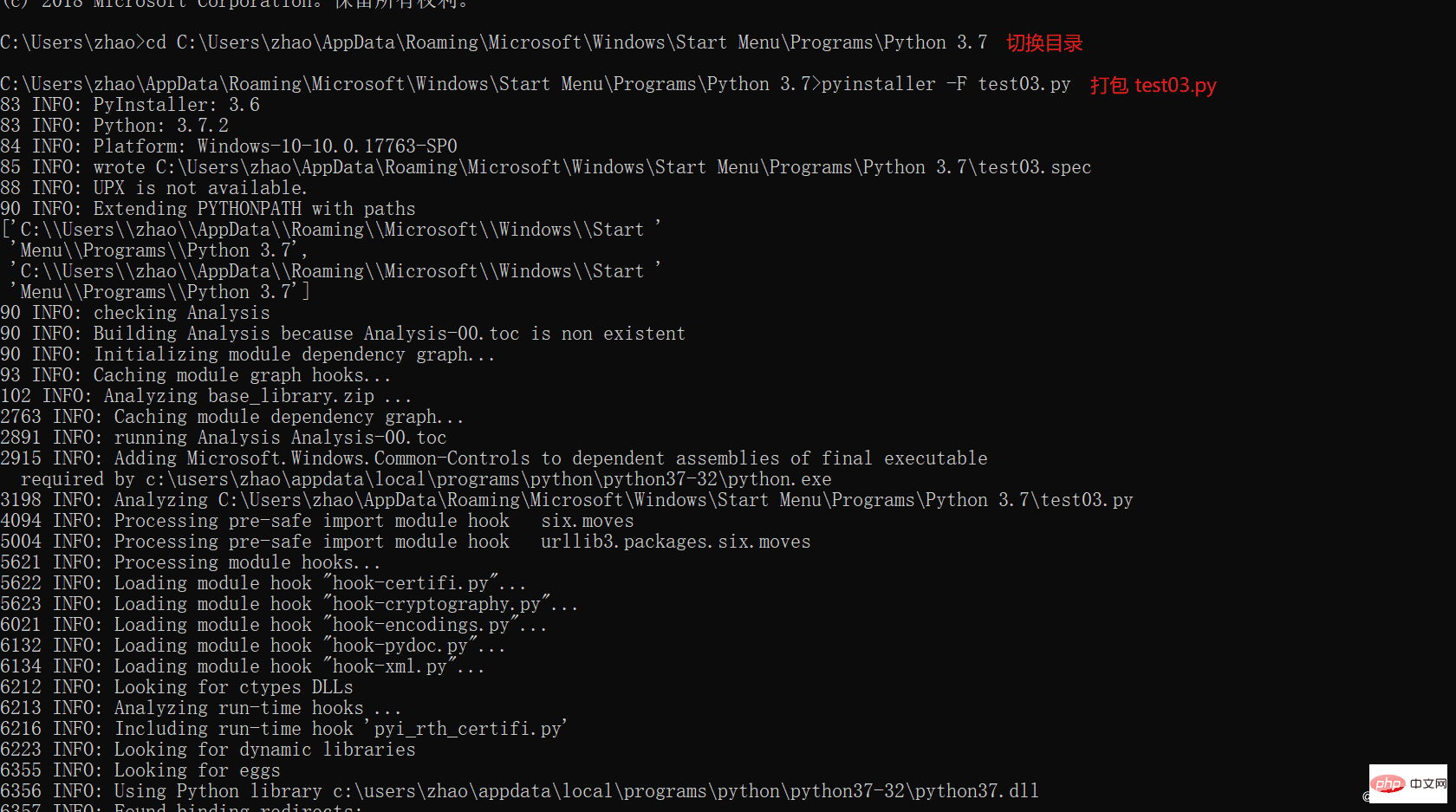
time.sleep(5)pip install pyinstaller -i https://pypi.tuna. tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
Related learning recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang and Python each have their own advantages: Golang is suitable for high performance and concurrent programming, while Python is suitable for data science and web development. Golang is known for its concurrency model and efficient performance, while Python is known for its concise syntax and rich library ecosystem.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".



