 Common Problem
Common Problem
 What does it take to convert a source program written in a high-level language into an executable program?
What does it take to convert a source program written in a high-level language into an executable program?
What does it take to convert a source program written in a high-level language into an executable program?
Converting a source program written in a high-level language into an executable program requires "compilation and linking". Source programs written in high-level languages cannot be directly executed on the machine and must be compiled and linked.

To run a program, it must go through four steps: preprocessing, compilation, assembly and linking. Next, we will explain these processes in detail through a few simple examples.
We need to explain some of the options used above.
If you use the gcc command without any options, the entire process of preprocessing, compilation, assembly, and linking will be performed by default. If the program is correct, you will get an executable file, which defaults to a.out
-E option: prompts the compiler to stop after performing preprocessing, and subsequent compilation, assembly, and linking will not be executed.
-S option: prompts the compiler to stop after compilation and not to perform assembly and linking.
-c option: prompts the compiler to stop after executing assembly.
So, these three options are equivalent to limiting the stop time of the compiler execution operation, rather than taking out a certain step separately for execution.
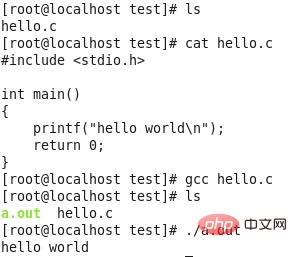
#Everyone should be familiar with the execution process of the above program, so I won’t waste any time.
1. Preprocessing:
Use the -E option to indicate that only precompilation will be performed, and a .i file will be generated accordingly.
Operations performed during the preprocessing process:
- Delete all "#define" and expand all macro definitions
- Process all conditional compilation instructions, For example, "#if", "#ifdef", "#elif", "#else", "#endif"
- processes the "#include" precompilation directive and inserts the included header file into the compilation The location of the instruction. (This process is recursive, because the included file may also contain other files)
- Remove all comments "//" and "/* */".
- Add line number and file name identifiers to facilitate the compiler to generate line number ideas for debugging later during compilation and to display the line number when compilation errors or warnings occur during compilation.
- Keep all #pragma pragmas as the compiler needs them.
Use a simple program to verify whether the facts are as mentioned above
Write a simple program, and then use the -E option to perform the preprocessing process and open the generated Compare the .i file with the source file, and the result is clear at a glance

Adding line numbers to the code will not be demonstrated here. We will not do it manually when writing code When adding line numbers, the line numbers we see are automatically added by the editing tools we use, and these line numbers cannot be seen by the compilation system. However, we find that if there is a problem with any line of our code, When compiling, a prompt will be given to tell which line of code has a problem. This has proven that the compiler will automatically add line numbers.
2. Compilation:
Use the -S option to indicate that the compilation operation will end after execution. A .s file is generated accordingly.
The compilation process is the core part of the entire program construction. If the compilation is successful, the source code will be converted from text form into machine language. The compilation process is to perform a series of lexical analysis, syntax analysis, and semantic analysis on the preprocessed files. After analysis and optimization, the corresponding assembly code file is generated.
- Lexical analysis:
Lexical analysis uses a program called lex to implement lexical scanning. It will analyze the input string according to the lexical rules previously described by the user. Divide it into individual tokens. The generated tokens are generally divided into: keywords, identifiers, literals (including numbers, strings, etc.) and special symbols (operators, equal signs, etc.), and then they are placed in the corresponding tables.
- Grammar analysis: The grammar analyzer parses the token sequence generated by lexical analysis according to the grammar rules given by the user, and then forms a grammar tree from them. For different languages, only their grammatical rules are different. There is also a ready-made tool for syntax analysis called: yacc.
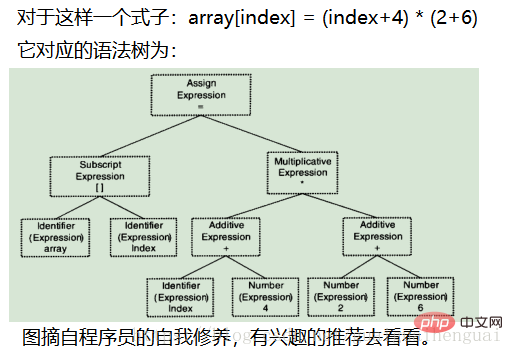
- Semantic analysis:
Grammatical analysis completes the analysis of the syntax level of the expression, but it does not understand whether the statement is truly meaningful. Some statements are grammatically legal, but have no practical meaning. For example, when two pointers are multiplied, semantic analysis is required. However, the only semantics that the compiler can analyze are static semantics.
Static semantics: Semantics that can be determined at compile time. Usually includes declaration and type matching and type conversion. For example, when a floating-point expression is assigned to an integer expression, it implies a conversion from floating-point to integer, and semantic analysis needs to complete this conversion. For another example, converting a floating-point type into Assigning an expression to a pointer is definitely not possible. During semantic analysis, it will be found that the two types do not match, and the compiler will report an error.
Dynamic semantics: Semantics that can only be determined at runtime. For example, if you divide two integers, there is no problem with the syntax and the types match. It sounds like there is nothing wrong with it. However, if the divisor is 0, there will be a problem. This problem is not known in advance and can only be done during operation. Only when the time comes can we find out that there is something wrong with him. This is dynamic semantics.
- Intermediate code generation
Our code can be optimized. For some values that can be determined during compilation, they will be optimized, such as Speaking of 2 6 in the above example, its value can be determined to be 8 during compilation, but it is more difficult to directly optimize the syntax. In this case, the optimizer will first convert the syntax tree into intermediate code. Intermediate code is generally independent of the target machine and operating environment. (Does not include data size, variable address, register name, etc.). Intermediate codes have different forms in different compilers. The more common ones are three-address code and P-code.
The intermediate code allows the compiler to be divided into front-end and back-end. The compiler front-end is responsible for generating machine-independent intermediate code, and the compiler back-end converts the intermediate code into machine code.
- Target code generation and optimization
The code generator converts the intermediate code into machine code. This process depends on the target machine, because different machines have different Word length, register, data type, etc.
Finally, the target code optimizer optimizes the target code, such as selecting appropriate addressing methods, using unique ones to replace multiplication and division, and deleting redundant instructions.
3. Assembly
The assembly process is completed by calling the assembler as, which is used to convert the assembly code into instructions that the machine can execute. Almost every assembly statement Corresponds to a machine instruction.
Use the command as hello.s -o hello.o or use gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o to execute until the end of the assembly process, and the corresponding generated file is an .o file.
4. Links
The main content of the link is to correctly connect the parts that reference each other between the modules. Its job is to correct the references of some instructions to other symbol addresses. The linking process mainly includes address and space allocation, symbol resolution and redirection
Symbol resolution: sometimes also called symbol binding, name binding, name resolution, or address binding, it actually refers to the use of symbols Come and go to identify an address.
For example, Int A = 6; such a code, use A to identify a 4 -byte size space in the space. The content stored in the space is 4.
The process of addressing each target is called relocation.
The most basic link is called static linking, which is to compile the source code file of each module into a target file (Linux: .o Windows: .obj), and then link the target file and library together to form the final executable file. A library is actually a package of a set of target files. Some of the most commonly used codes are mutated into target files and then packaged and stored. The most common library is the runtime library, which is a collection of basic functions that support program running.
For more related knowledge, please visit: PHP Chinese website!
The above is the detailed content of What does it take to convert a source program written in a high-level language into an executable program?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 What are the characteristics of machine language, assembly language, and high-level language?
Apr 22, 2021 pm 04:00 PM
What are the characteristics of machine language, assembly language, and high-level language?
Apr 22, 2021 pm 04:00 PM
Characteristics of machine language: difficult to learn, understand, and understand; not universal; requires manual allocation of memory; and runs fastest. The characteristics of assembly language: the execution efficiency of the program is very high, it takes up little storage space, and it runs fast; it lacks versatility and the program is not easy to transplant. Characteristics of high-level languages: easy, certain versatility, and cannot be directly recognized and executed by computers.
 What is the system software that can translate source programs written in high-level languages into target programs?
Jan 22, 2021 pm 05:36 PM
What is the system software that can translate source programs written in high-level languages into target programs?
Jan 22, 2021 pm 05:36 PM
System software that can translate source programs written in high-level languages into target programs is a "compiler". A compiler is a translation program implemented using a generative implementation approach; it takes a source program written in a high-level programming language as input, and uses a target program expressed in assembly language or machine language as output.
 Is assembly language a high-level language?
Jan 30, 2023 pm 03:14 PM
Is assembly language a high-level language?
Jan 30, 2023 pm 03:14 PM
Assembly language is not a high-level language; it is a low-level language like machine language. The difference between assembly language and high-level language: 1. The programming efficiency of assembly language is not high, while the programming efficiency of high-level language is higher than that of assembly language; 2. The readability of high-level language is higher than that of assembly language; 3. Assembly language is a Machine language, while high-level language is simplified and close to human natural language.
 What is needed to convert a program written in a high-level programming language into an equivalent executable program?
Jan 12, 2021 pm 02:41 PM
What is needed to convert a program written in a high-level programming language into an equivalent executable program?
Jan 12, 2021 pm 02:41 PM
Converting a program written in a high-level programming language into an equivalent executable program requires compilation and linking. High-level programming languages can get rid of the different constraints of computer instruction systems and machine language random machines, and convert source programs into target codes that the CPU can recognize.
 Is machine language a high-level language?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
Is machine language a high-level language?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
Machine language is not a high-level language. It is a low-level language used for computer hardware. It interacts directly with the underlying hardware of the computer. Machine language uses binary encoding to represent instructions and data. Each instruction corresponds to an operation or function of the computer hardware. , High-level language is a programming language that is closer to human language, providing higher abstraction capabilities and development efficiency. Machine language and high-level language play different roles in programming, each with their own advantages and applicable scenarios.
 Released the world's first open source Hongmeng-based humanoid robot that supports JS/ArkTS high-level language
Nov 17, 2023 pm 08:07 PM
Released the world's first open source Hongmeng-based humanoid robot that supports JS/ArkTS high-level language
Nov 17, 2023 pm 08:07 PM
Kuai Technology reported on November 17 that this morning, Shenzhen Kaihong announced that the first KaihongOS humanoid robot based on the open source Hongmeng, jointly developed by it and Leju Robot, was officially released. According to the official introduction, this is an all-things intelligent teaching system equipped with KaihongOS and using robots as the carrier, covering multiple scenarios such as industry and services. This robot is equipped with a blood oxygen heart rate sensor, temperature and humidity sensor, infrared temperature sensor, human body induction sensor, NFC, OLED display, and LED lights. Through multiple joint sensing, it can intelligently execute decisions. At the same time, the robot can also be interconnected with mobile phones, tablets, computers and other devices in real time, getting rid of the traditional wire harness connection method and improving teaching efficiency. At the same time, this robot also has 17
 What is the location of the main function in the c source program?
Nov 19, 2020 am 11:06 AM
What is the location of the main function in the c source program?
Nov 19, 2020 am 11:06 AM
C language stipulates that in a source program, the position of the main function can be arbitrary; when executing a program written in C language, the main function is equivalent to the entrance to the execution program; regardless of the position of the main function in the entire process , a C program always starts execution from the mam function.
 Feature analysis of Go language: Is it a high-level language?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Feature analysis of Go language: Is it a high-level language?
Mar 23, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Feature analysis of Go language: Is it a high-level language? Go language is a statically strongly typed programming language developed by Google. It is designed to be simple, easy to read and write, and has efficient concurrency features. So, according to the definition of high-level language, let's analyze whether Go language is a high-level language. Definition of high-level language A high-level language is a programming language that is closer to human language than machine language. It has the characteristics of concise syntax, easy to read and write, and high level of abstraction, which allows programmers to focus more on solving the problem itself.


