

【Related learning recommendations: javascript learning tutorial】
HTMLSizeThe so-called HTML size of an element refers to the size style set in the HTML tag.
For example:
<p></p>复制代码
The page effect is as shown below:

This size can be passedelem.style.width or elem.style.height gets
For example:
let box = document.querySelector('.box');console.log(box.style.width); // 200pxconsole.log(box.style.heihgt); // 200px复制代码 But for CSS dimensions, they are Unobtainable.
For example:
.box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background: lightpink;
}复制代码As shown below:
In order to separate the style and structure, we will Write the style separately into the CSS file. If the above method cannot obtain the size of the element, then what method should we use to obtain it?
Then look down.
In the element object of JavaScript, three read-only properties are provided, which can be used to obtain the size of the element.
They are:
and offsetWidth and clientWidthandscrollWidth and offsetWidthoffsetHeight are used to get the real height of the element (border-box), which contains the Vertical padding and borders, if there is a horizontal scroll bar (the height of the horizontal scroll bar is 17px, which is generally included in the content height height), you also need to add horizontal scrolling The height of the bar.
offsetWidth is used to get the real width of the element (border-box), which includes the horizontal padding and border of the element, if there is a vertical scroll bar. (The height of the horizontal scroll bar is 17px, which is generally included in the content width width). The width of the vertical scroll bar also needs to be added.
p element has the following style
.box { margin: 10px auto; padding: 10px; width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid #000; background: lightpink;
}复制代码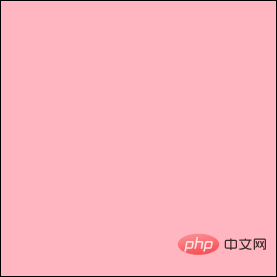

obtains the element The real height of #1px * 2, for 222pxoffsetWidth obtains the real width of the element, then its width is width padding * 2 border * 2, which is 200px
1px * 2, which is 222px<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">let box = document.querySelector('.box');let height = box.offsetHeight;let width = box.offsetWidth;console.log(height); // 222pxconsoel.log(width); // 222px复制代码</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>When a scroll bar is includedWhen a scroll bar is included, since the height of the horizontal scroll bar is 17px, it will generally be included in the content height height, that is, the actual value of the content height is 17px less than the set value. The two
.father { margin: 10px auto; padding: 10px; width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid; background: lightsalmon; /* 滚动条高度和宽度被计算到content中 */
overflow: auto;
}.son { width: 220px; height: 220px; background: plum;
}复制代码The page effect is as follows:
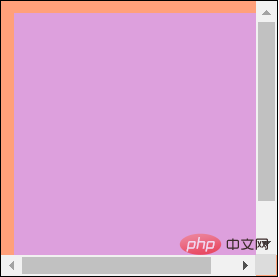 183px
183px 17px
. The same goes for the height of the content area. But when there is a scroll bar, the values of
But when there is a scroll bar, the values of need to include the height and width of the scroll bar in addition to the padding and border values. Although the scroll bar occupies part of the width and height space of the content area, it is added in the final calculation. <p>所以真实宽度还是相当于原来设置的<code>width+ padding * 2+ border * 2,即200px + 10px * 2+1px * 2,为222px。高度亦然。
let f_box = document.querySelector('.father');let f_height = f_box.offsetHeight;let f_width = f_box.offsetWidth;console.log(f_height); // 220pxconsole.log(f_width); // 220px复制代码clientHeight和clientWidth
clientHeight和clientWidth表示可视区域的高度和宽度,包括元素内容本身的宽度和高度以及padding。但是,如果有滚动条的话,需要减去滚动条的宽度和高度。
一个p有如下样式:
.box { margin: 10px auto; padding: 10px; width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid #000; background: lightpink;
}复制代码页面效果如下:
其盒模型如下:

该元素的clientHeight为width+padding * 2,即200px+10px * 2,为220px,高度亦然。
let box = document.querySelector('.box');let height = box.clientHeight;let width = box.clientWidth;console.log(height); // 220pxconsoel.log(width); // 220px复制代码当含有滚动条时,需要减去滚动条的宽度和高度。
父子p有如下样式:
.father { margin: 10px auto; padding: 10px; width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid; background: lightsalmon; /* 滚动条高度和宽度被计算到content中 */
overflow: auto;
}.son { width: 220px; height: 220px; background: plum;
}复制代码页面效果如下:
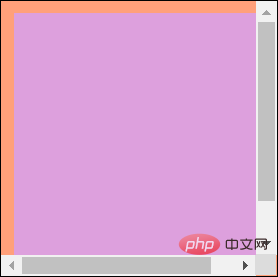
其盒模型如下:

那么,clientWidth的值为width+padding * 2-17px,即200px+10px * 2-17px,为203px
所谓可视区域,就是我们最终能看到的部分。就像下图一样,原来的元素如果没有滚动条,它的尺寸应该是红色框线所包裹的尺寸。
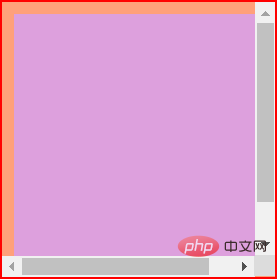
但是,由于多了滚动条,可视区域就减小了,如下所示。在原有尺寸基础上减去滚动条的宽度和高度就是可视区域的宽度和高度了。
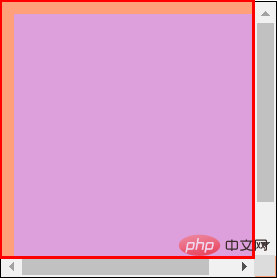
scrollHeight与scrollWidth
scrollHeight用于获取一个元素的内容高度,包括溢出的部分。scrollWidth用于获取一个元素的内容宽度,包括溢出的部分。当然,在没有溢出,即没有滚动条的情况下,这两个值等同于clientHeight和clientWidth,也是包括元素本身的尺寸以及padding,但不包括border和margin
父子p有如下样式:
.father { margin: 10px auto; padding: 10px; /* 父元素的内容宽度:320px + 10px = 330px */
width: 200px; /* 父元素的内容高度:200px - 17px = 203px */
height: 200px; border: 1px solid #000; overflow: auto;
}.son { padding: 10px; /* 子元素的真实宽度:300px + 10px * 2 = 320px */
width: 300px; height: 100px; background: plum;
}复制代码页面效果如下:
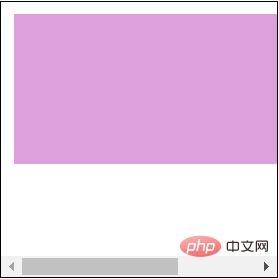
由于子元素的高度只有100px,没有发生溢出,因此,父元素的scrollHeight就等同于clientHeight:width+padding-水平滚动条高度17px,即200px+10px*2-17px=203px
子元素真实占据的宽度有300px+10px*2 = 320px,外加父元素设置的左侧内边距还是10px,右侧内边距失效。因此父元素的scrollWidth的值为320px+10px,为330px
let f_box = document.querySelector('.father');let height = f_box.scrollHeight;let width = f_box.scrollWidth;console.log(height); // 203pxconsole.log(width); // 330px复制代码overflow造成右内边距失效的问题关于父元素设置overflow: auto时,造成的右内边距失效,有以下图片可以佐证。

As shown above: the parent element has 10px padding on the left and top sides, but not on the right side.
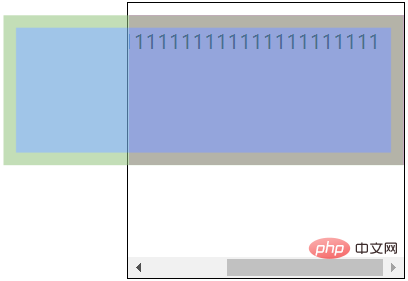
As shown above: Because the child element is not set overflow, you can see that the right inner margin of the child element is still is effective.
When the width of the child element is greater than the width of the parent element, the margin-right of the child element or the padding-right of the parent element is calculated as 0. Not detailed here.
If you want to know more about programming learning, please pay attention to the php training column!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of JavaScript to obtain the size of an element. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!