 Common Problem
Common Problem
 What should I do if the computer enters the bios interface when it is turned on?
What should I do if the computer enters the bios interface when it is turned on?
What should I do if the computer enters the bios interface when it is turned on?
Solution to the problem of entering the BIOS interface when the computer is turned on: 1. Purchase a replacement motherboard battery and reset the correct parameters in the BIOS interface; 2. Press the DEL key to enter the BIOS, and then press F9 to load the predefined parameters ;3. Repair the hard disk master boot record or reinstall the system or replace the hard disk.

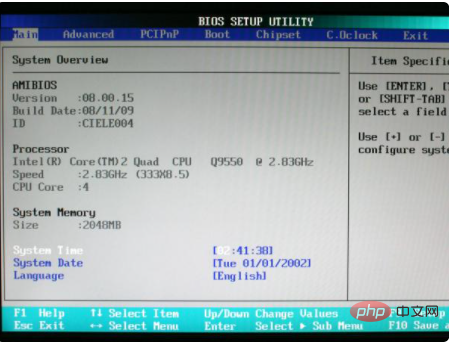
#1. Battery failure: You can check whether the system time is accurate in the BIOS interface. If it is not accurate, it can be determined that the motherboard battery has failed, causing the computer to call the BIOS default If the parameters are inconsistent with the local hardware environment, the computer cannot be started normally. You can purchase the motherboard battery to replace it, then turn on the computer and press the DEL key (F2 or other designated hotkeys for notebooks) to enter the BIOS interface, reset the correct parameters, and finally press F10 to save, exit and restart.
2. Configuration error: This situation may also occur because the manually configured BIOS parameters do not match the local hardware environment. If you don’t know how to set the parameters, generally you can press the F1 key to skip non-fatal errors and start the computer directly according to the white text prompts on the black background, or press the DEL key to enter the BIOS, and then press F9 to load the predefined parameters or select Load Optimized Defaults (load high-performance defaults) or Load Fail-Safe Defaults (load fail-safe defaults),
3. Hardware failure: If the above operations are invalid, it means there is a problem with the hardware. Generally, it is caused by poor contact between the memory and the hard disk or the hard disk master boot record is damaged. It is necessary to re-insert the memory or hard disk, repair the hard disk master boot record, reinstall the system or replace the hard disk.
BIOS is the abbreviation of "Basic Input Output System" in English. When translated literally, the Chinese name is "Basic Input Output System". In fact, it is a set of programs solidified on a ROM chip on the motherboard of the computer. It saves the computer's most important basic input and output programs, post-boot self-test programs and system self-starting programs. It can be read and written from CMOS. Specific information about system settings. Its main function is to provide the lowest and most direct hardware settings and control for the computer.
Related introduction:
Functionally, BIOS is divided into three parts:
Self-test and initialization
This part is responsible for starting the computer. There are three specific parts:
The first part is used to detect the hardware part when the computer is just powered on, also called Power On Self Test. POST for short), the function is to check whether the computer is in good condition. Usually a complete POST self-test will include the CPU, 640K basic memory, extended memory above 1M, ROM, motherboard, CMOS memory, serial and parallel ports, graphics card, soft and hard disk subsystem and The keyboard is tested. Once a problem is found during the self-test, the system will give a prompt message or sound a warning.
If an error is found during the self-test, it will be handled in two situations: for serious faults (fatal faults), the machine will be shut down. At this time, since various initialization operations have not been completed, no prompts or signals can be given. ; For non-serious faults, a prompt or sound alarm signal will be given, waiting for user processing.
The second part is initialization, including creating interrupt vectors, setting registers, initializing and detecting some external devices, etc. A very important part of it is BIOS settings, mainly some parameters of hardware settings. When the computer starts, it will read these parameters and compare them with the actual hardware settings. If they are not consistent, it will affect the startup of the system.
The third part is the boot program, whose function is to boot DOS or other operating systems. The BIOS first reads the boot record from the beginning sector of the floppy disk or hard disk. If it is not found, it will display on the monitor that there is no boot device. If the boot record is found, it will transfer control of the computer to the boot record, which will then control the operating system. After the computer starts successfully, this part of the BIOS task is completed.
The above is the detailed content of What should I do if the computer enters the bios interface when it is turned on?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What is the reason why PS keeps showing loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
What is the reason why PS keeps showing loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
PS "Loading" problems are caused by resource access or processing problems: hard disk reading speed is slow or bad: Use CrystalDiskInfo to check the hard disk health and replace the problematic hard disk. Insufficient memory: Upgrade memory to meet PS's needs for high-resolution images and complex layer processing. Graphics card drivers are outdated or corrupted: Update the drivers to optimize communication between the PS and the graphics card. File paths are too long or file names have special characters: use short paths and avoid special characters. PS's own problem: Reinstall or repair the PS installer.
 How to speed up the loading speed of PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
How to speed up the loading speed of PS?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
Solving the problem of slow Photoshop startup requires a multi-pronged approach, including: upgrading hardware (memory, solid-state drive, CPU); uninstalling outdated or incompatible plug-ins; cleaning up system garbage and excessive background programs regularly; closing irrelevant programs with caution; avoiding opening a large number of files during startup.
 How to solve the problem of loading when PS is always showing that it is loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:30 PM
How to solve the problem of loading when PS is always showing that it is loading?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:30 PM
PS card is "Loading"? Solutions include: checking the computer configuration (memory, hard disk, processor), cleaning hard disk fragmentation, updating the graphics card driver, adjusting PS settings, reinstalling PS, and developing good programming habits.
 Is slow PS loading related to computer configuration?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
Is slow PS loading related to computer configuration?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
The reason for slow PS loading is the combined impact of hardware (CPU, memory, hard disk, graphics card) and software (system, background program). Solutions include: upgrading hardware (especially replacing solid-state drives), optimizing software (cleaning up system garbage, updating drivers, checking PS settings), and processing PS files. Regular computer maintenance can also help improve PS running speed.
 How to solve the problem of loading when the PS opens the file?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
How to solve the problem of loading when the PS opens the file?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:33 PM
"Loading" stuttering occurs when opening a file on PS. The reasons may include: too large or corrupted file, insufficient memory, slow hard disk speed, graphics card driver problems, PS version or plug-in conflicts. The solutions are: check file size and integrity, increase memory, upgrade hard disk, update graphics card driver, uninstall or disable suspicious plug-ins, and reinstall PS. This problem can be effectively solved by gradually checking and making good use of PS performance settings and developing good file management habits.
 Is PS slow loading related to other programs that are running?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
Is PS slow loading related to other programs that are running?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
The secrets to mastering Office software include: understanding different versions and platforms, correctly installing and configuring, proficient in using the software interface, in-depth understanding of feature operations, application collaboration and sharing functions, utilizing templates and styles, mastering advanced skills, and solving common problems. In addition, you need to choose a version that suits your needs, make good use of templates and styles, develop backup habits, and learn shortcut keys and advanced techniques to improve efficiency.
 How to solve the problem of loading when PS is started?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
How to solve the problem of loading when PS is started?
Apr 06, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
A PS stuck on "Loading" when booting can be caused by various reasons: Disable corrupt or conflicting plugins. Delete or rename a corrupted configuration file. Close unnecessary programs or upgrade memory to avoid insufficient memory. Upgrade to a solid-state drive to speed up hard drive reading. Reinstalling PS to repair corrupt system files or installation package issues. View error information during the startup process of error log analysis.
 Does mysql need the internet
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
Does mysql need the internet
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
MySQL can run without network connections for basic data storage and management. However, network connection is required for interaction with other systems, remote access, or using advanced features such as replication and clustering. Additionally, security measures (such as firewalls), performance optimization (choose the right network connection), and data backup are critical to connecting to the Internet.




