API rate limiting via Node+Redi

Rate limiting protects and improves the availability of API-based services. If you are talking to an API and receive an HTTP 429 Too Many Requests response status code, you have been rate limited. This means you have exceeded the number of requests allowed in a given time. All you need to do is slow down, wait a moment, and try again.
Video tutorial recommendation: nodejs tutorial
Why rate limit?
When you consider limiting your own API-based services, you need to weigh the trade-offs between user experience, security, and performance.
#The most common reason to control data flow is to maintain the availability of API-based services. But there are also security benefits, as an accidental or intentional surge in inbound traffic can take up valuable resources and impact availability for other users.
By controlling the rate of incoming requests, you can:
- Ensure that services and resources are not "flooded."
- Mitigating Brute Force Attacks
- Preventing Distributed Denial of Service (DDOS) Attacks
How to implement rate limiting?
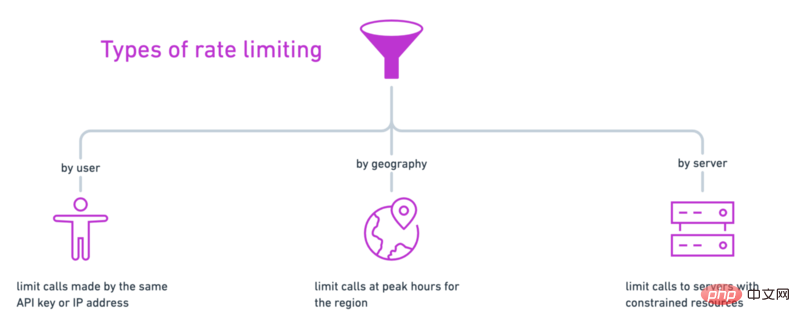
Rate limiting can be implemented at the client level, application level, infrastructure level, or anywhere in between. There are several ways to control inbound traffic to an API service:
- By User: Track calls made by a user using an API key, access token, or IP address
- By Geographic Region: For example lowering the rate limit for each geographic region during peak times of the day
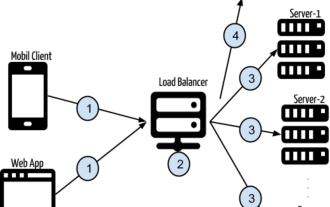
- By Server: If you have multiple servers to handle Different calls to the API, you might impose stricter rate limits on access to more expensive resources.
You can use any of these rate limits (or even a combination).
No matter how you choose to implement it, the goal of rate limiting is to establish a checkpoint that denies or passes requests to access your resources. Many programming languages and frameworks have built-in functionality or middleware to achieve this, as well as options for various rate limiting algorithms.
Here's one way to make your own rate limiter using Node and Redis:
Create a Node App
Adding a rate limiter using Redis
Testing in Postman
View code examples on GitHub.
Before you begin, make sure you have Node and Redis installed on your computer.
Step 1: Set up a Node application
Set up a new Node application from the command line. Accept the default options via the CLI prompt, or add the —yes flag.
$ npm init --yes
If you accepted the default options during project setup, create a file named index.js for the entry point.
$ touch index.js
Install the Express Web framework, and then initialize the server in index.js.
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000
app.get('/', (req, res) => res.send('Hello World!'))
app.listen(port, () => console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`))Start the server from the command line.
$ node index.js
Go back to index.js, create a route, first check the rate limit, and then allow the user to access the resource if it does not exceed the limit.
app.post('/', async (req, res) => {
async function isOverLimit(ip) {
// to define
}
// 检查率限制
let overLimit = await isOverLimit(req.ip)
if (overLimit) {
res.status(429).send('Too many requests - try again later')
return
}
// 允许访问资源
res.send("Accessed the precious resources!")
})
In the next step, we will define the rate limiter function isOverLimit.
Step 2: Add a rate limiter using Redis
Redis is an in-memory key-value database, so it can retrieve data very quickly. Implementing rate limiting with Redis is also very simple.
- Store a key like the user's IP address.
- Increase the number of calls made from this IP
- Expire records after a specified period of time
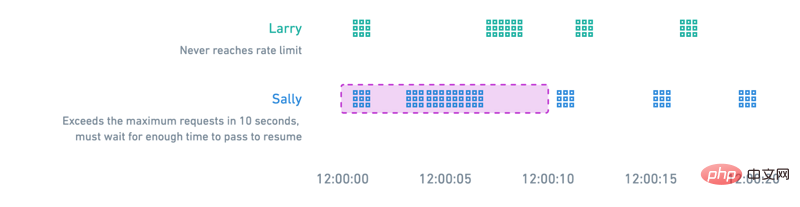
The rate limiting algorithm shown in the figure below is a Example of sliding window counter. A user will never hit the rate limit if they submit a moderate number of calls, or space them out over time. Users who exceed the maximum request within the 10 second window must wait sufficient time to resume their requests.

Install a Redis client named ioredis for Node from the command line.
$ npm install ioredis
Start the Redis server locally.
$ redis-server
Then require and initialize the Redis client in index.js.
const redis = require('ioredis')
const client = redis.createClient({
port: process.env.REDIS_PORT || 6379,
host: process.env.REDIS_HOST || 'localhost',
})
client.on('connect', function () {
console.log('connected');
});Define the isOverLimit function we started writing in the previous step. According to this mode of Redis, a counter is saved according to IP.
async function isOverLimit(ip) {
let res
try {
res = await client.incr(ip)
} catch (err) {
console.error('isOverLimit: could not increment key')
throw err
}
console.log(`${ip} has value: ${res}`)
if (res > 10) {
return true
}
client.expire(ip, 10)
}This is the rate limiter.
When a user calls the API, we check Redis to see if the user has exceeded the limit. If so, the API will immediately return an HTTP 429 status code with the message Too many requests — try again later . If the user is within limits, we continue to the next block of code where we can allow access to a protected resource (such as a database).
During rate limit checking, we find the user's record in Redis and increment its request count, if there is no record for that user in Redis, then we create a new record. Finally, each record will expire within 10 seconds of the most recent activity.
In the next step, please make sure our speed limiter is functioning properly.
Step 3: Test in Postman
Save the changes and restart the server. We will use Postman to send POST requests to our API server, which is running locally at http:// localhost:3000.
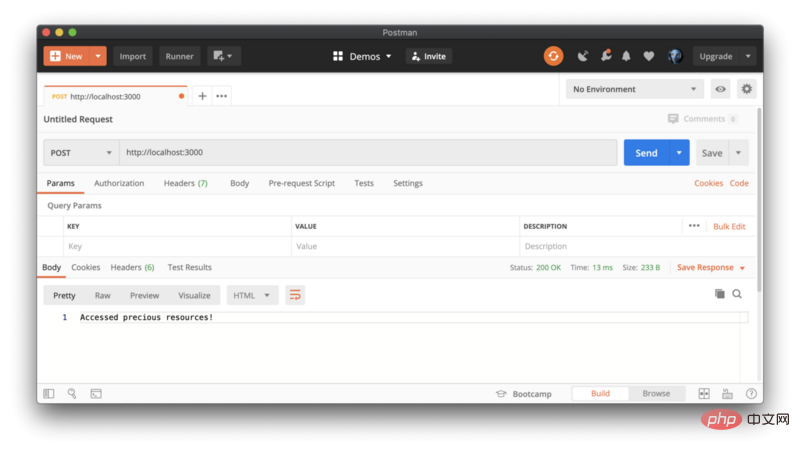
Continue sending requests in rapid succession to reach your rate limit.
Final Thoughts on Rate Limiting
This is a simple example of a rate limiter for Node and Redis, and this is just the beginning. There are a bunch of strategies and tools you can use to structure and implement your rate limits. And there are other enhancements that can be explored with this example, like:
- in the response body or as a
Retry-afterheader to let the user know before retrying How long should you wait - Log requests that hit the rate limit to understand user behavior and warn of malicious attacks
- Try using other rate limiting algorithms or other middleware
Remember that when you look at API limits, you are making trade-offs between performance, security, and user experience. Your ideal rate limiting solution will change over time, taking these factors into account.
English original address: https://codeburst.io/api-rate-limiting-with-node-and-redis-95354259c768
More programming related knowledge , please visit: Introduction to Programming! !
The above is the detailed content of API rate limiting via Node+Redi. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node with nvm: 1. Download "nvm-setup.zip" and install it on the C drive; 2. Configure environment variables and check the version number through the "nvm -v" command; 3. Use the "nvm install" command Install node; 4. Delete the installed node through the "nvm uninstall" command.
 How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to handle file upload? The following article will introduce to you how to use express to handle file uploads in the node project. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 How to do Docker mirroring of Node service? Detailed explanation of extreme optimization
Oct 19, 2022 pm 07:38 PM
How to do Docker mirroring of Node service? Detailed explanation of extreme optimization
Oct 19, 2022 pm 07:38 PM
During this period, I was developing a HTML dynamic service that is common to all categories of Tencent documents. In order to facilitate the generation and deployment of access to various categories, and to follow the trend of cloud migration, I considered using Docker to fix service content and manage product versions in a unified manner. . This article will share the optimization experience I accumulated in the process of serving Docker for your reference.
 An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will share with you Node's process management tool "pm2", and talk about why pm2 is needed, how to install and use pm2, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
How to package nodejs executable file with pkg? The following article will introduce to you how to use pkg to package a Node project into an executable file. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
npm node gyp fails because "node-gyp.js" does not match the version of "Node.js". The solution is: 1. Clear the node cache through "npm cache clean -f"; 2. Through "npm install -g n" Install the n module; 3. Install the "node v12.21.0" version through the "n v12.21.0" command.
 Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Authentication is one of the most important parts of any web application. This tutorial discusses token-based authentication systems and how they differ from traditional login systems. By the end of this tutorial, you will see a fully working demo written in Angular and Node.js. Traditional Authentication Systems Before moving on to token-based authentication systems, let’s take a look at traditional authentication systems. The user provides their username and password in the login form and clicks Login. After making the request, authenticate the user on the backend by querying the database. If the request is valid, a session is created using the user information obtained from the database, and the session information is returned in the response header so that the session ID is stored in the browser. Provides access to applications subject to





