Is mysql single-threaded or multi-threaded?
mysql is multi-threaded. Mysql is a single-process multi-thread database. There are about three types of threads in innodb: 1. Master Thread; 2. IO Thread thread, used to process write requests asynchronously; 3. Purge Thread thread, used to delete undo logs .

(Recommended tutorial: mysql video tutorial)
mysql is a single-process multi-thread database, in innodb There are probably the following types of threads in it:
(1) Master Thread: This is the main thread, very core. Its purpose is mainly to do some periodic tasks, in different innodb versions Their functions are different, here is the earliest version. The early innodb Master thread will have two frequency tasks, one is once every 1 second, and the other is once every 10 seconds.
Work every second:
1. Refresh the log;
2. Refresh up to 100 dirty pages
3. Merge the insert buffer;
4. If idle, switch to background.
In fact, the most important ones are the first two. And only refreshing the log must be done every time, and the rest will only be done if conditions are met. For example, refreshing dirty pages will only be refreshed if the proportion of dirty pages in the cache exceeds a threshold.
Work every 10 seconds:
1. Refresh log;
2. Refresh dirty pages;
3. Delete undo log;
4. Merge insert buffer
(2) IO Thread: Mainly used for asynchronous processing of write requests.
(3) purge Thread: is used to delete undo logs. This is the subsequent innodb version that separates this matter from the Master thread.
Finally, a memory map of innodb:
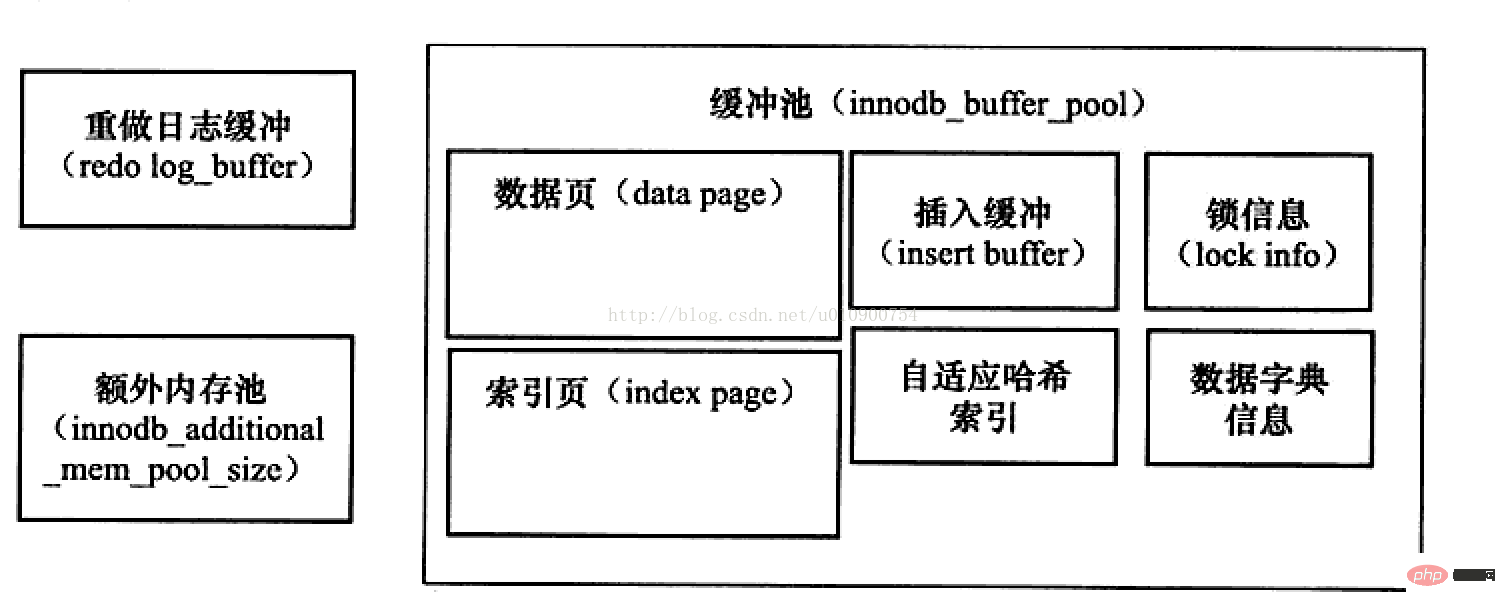
Related recommendations: php training
The above is the detailed content of Is mysql single-threaded or multi-threaded?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 How to deal with shared resources in multi-threading in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 am 10:28 AM
How to deal with shared resources in multi-threading in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 am 10:28 AM
Mutexes are used in C++ to handle multi-threaded shared resources: create mutexes through std::mutex. Use mtx.lock() to obtain a mutex and provide exclusive access to shared resources. Use mtx.unlock() to release the mutex.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 Challenges and countermeasures of C++ memory management in multi-threaded environment?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 01:08 PM
Challenges and countermeasures of C++ memory management in multi-threaded environment?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 01:08 PM
In a multi-threaded environment, C++ memory management faces the following challenges: data races, deadlocks, and memory leaks. Countermeasures include: 1. Use synchronization mechanisms, such as mutexes and atomic variables; 2. Use lock-free data structures; 3. Use smart pointers; 4. (Optional) implement garbage collection.






