

Over the past ten years, one of my biggest passions has been front-end development (specifically JavaScript). As a "craftsman", I like to specialize in various tools. In this article, I will introduce you to some debugging techniques using the old-fashioned console.
Yes, we all know the following basic skills:
console.log(‘Hello World!’); console.info(‘Something happened…’); console.warn(‘Something strange happened…’); console.error(‘Something horrible happened…’);
From now on, I will teach you some skills you don’t know and let you become an experienced driver!
If you want to know where the message is printed, use console.trace() to get the stacktrace of the data to be printed. .
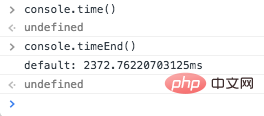
If you want to analyze the performance of the function, you can use console.time() to time, console.timeEnd() to end the time, the console will print out the time difference between the two times.
If you find that the performance problem is difficult to analyze, and you may also want to consider whether there is a memory leak, you can use console.memory (note that memory is a property of console, not a function) to check the current heap usage.

Fundebug helps you debug better, welcome to try it!
Although it is not a standard approach, it is widely accepted and used. You can use these two commands to start and stop profiling. This helps you do accurate profiling in your code. Rather than relying on manual mouse clicks. You can find the profile just now in the browser consoleJavascript Profiler.
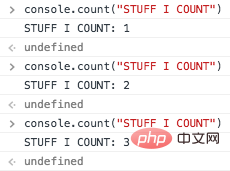
Sometimes in order to record how many times a function or a piece of code has been executed repeatedly, you can Use console.count('?') to record. Every time this code is executed, it will automatically increase by 1.
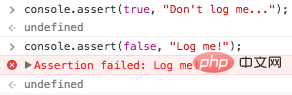
You can use console.assert to Output messages if some conditions are false instead of using if-else.
Note: An Assertion Error will be reported under Node.js.
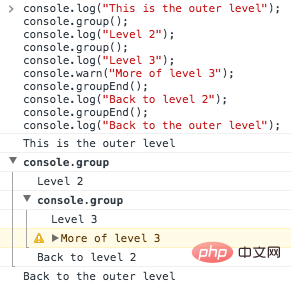
If you want to format the printed log For organized organization, you can use console.group() and console.groupEnd(). Use console.group to aggregate logs into groups and form nested hierarchies. Please see the example:
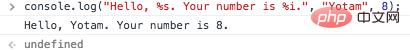
You can use console.log to print variables (%s = string, % i = integer, %o = object, %f = float).
We have output a lot of records on the console, use console.clear()Clear it.

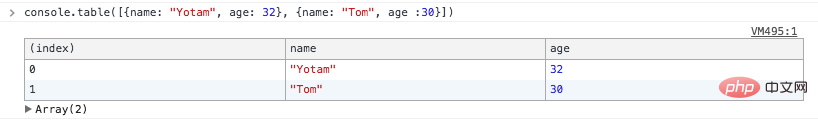
The last one! You can use console.table() to print the object in table form.
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Introduction to Programming! !
The above is the detailed content of 10 Advanced Tips for Using Console for JavaScript Debugging. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!