collect! What Spring must master
mysql tutorial column introduces what you must master about Spring.

Hello everyone! I am an enthusiastic member of the Chaoyang people.
The Spring framework is a must-ask question during interviews. What exactly does it contain? Let's take a look. This is also a question I often ask in interviews, and it also reflects a programmer's ability to understand the framework.
Introduce the Spring framework
Spring is a lightweight framework that aims to Improve the development efficiency of developers and the maintainability of the system.
What we generally call the Spring Framework is the Spring Framework. It is a collection of many modules. Using these modules can easily assist us in development. These modules are Core Containers, Data Access/Integration, Web, AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming), Tools, Messaging, and Testing modules. For example, the Core component in Core Container is the core of all Spring components, Beans components and Context components are the basis for implementing IOC and DI, and AOP components are used to implement aspect-oriented programming.
6 features of Spring:
Core technologies: Dependency Injection (DI), AOP, Events, resources, i18n, validation, data binding, type conversion, SpEL; Testing: Mock objects, TestContext framework, Spring MVC testing, WebTestClient; Data access: transactions, DAO support, JDBC, ORM, marshaling XML; Web support: Spring MVC and Spring WebFlux web framework; Integration: remoting, JMS, JCA, JMX, email, tasks, scheduling, caching; Language: Kotlin, Groovy, dynamic language;
List some important Spring modules
The picture below corresponds to the Spring 4.x version. The Portlet component of the Web module in the latest 5.x version has been abandoned and added WebFlux components for asynchronous reactive processing.

Spring Core: Basic, it can be said that all other functions of Spring depend on this class library. Mainly provides IOC and DI functions. Spring Aspects: This module provides support for integration with AspectJ. Spring AOP: Provides aspect-oriented programming implementation. Spring JDBC: Java database connection. Spring JMS: Java Message Service. Spring ORM: Used to support ORM tools such as Hibernate. Spring Web: Provides support for creating web applications. Spring Test: Provides support for JUnit and TestNG testing.
Talk about your understanding of Spring IOC and AOP
IOC
IOC (Inversion Of Controll, Inversion of Control) is a design idea, that is The control of manually created objects in the program is handed over to the Spring framework. IOC is also used in other languages and is not specific to Spring. The IOC container is the carrier used by Spring to implement IOC. The IOC container is actually a Map (key, value), and various objects are stored in the Map.
Leave the interdependencies between objects to be managed by the IOC container, and the IOC container completes the injection of the objects. This can greatly simplify application development and free applications from complex dependencies. The IOC container is like a factory. When we need to create an object, we only need to configure the configuration file/annotations without thinking about how the object is created. In actual projects, a Service class may have hundreds or even thousands of classes as its bottom layer. If we need to instantiate this Service, we may have to figure out the constructors of all the underlying classes of this Service every time, which may confuse people. Drive crazy. If you use IOC, you only need to configure it and reference it where needed, which greatly increases the maintainability of the project and reduces the difficulty of development.
In the Spring era, we usually configured beans through XML files. Later, developers felt that using XML files to configure beans was not good, so Spring Boot annotation configuration gradually became popular. 
AOP
##AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming, aspect-oriented programming ) can encapsulate the logic or responsibilities (such as transaction processing, log management, permission control, etc.) that have nothing to do with the business but are commonly called by the business modules, so as to reduce the duplication of code in the system, reduce the coupling between modules, and have Conducive to future scalability and maintainability.
Spring AOP is based on dynamic proxy. If the object to be proxied implements a certain interface, then Spring AOP will use JDK dynamic proxy to create the proxy object; but for objects that do not implement the interface, it cannot be used. JDK dynamic proxy instead uses CGlib dynamic proxy to generate a subclass of the proxy object as a proxy.
The difference between Spring AOP and AspectJ AOP
Spring AOP is a runtime enhancement , and AspectJ is a compile-time enhancement. Spring AOP is based on Proxying, while AspectJ is based on Bytecode Manipulation. Spring AOP has integrated AspectJ, which should be regarded as the most complete AOP framework in the Java ecosystem. AspectJ is more powerful than Spring AOP, but Spring AOP is relatively simpler. If we have fewer aspects, there will be little performance difference between the two. However, when there are too many aspects, it is best to choose AspectJ, which is much faster than SpringAOP.What are the scopes of beans in Spring?
singleton: The only bean instance, beans in Spring are all singletons by default. prototype: A new bean instance will be created with each request. request: Each HTTP request will generate a new bean, which is only valid within the current HTTP request. session: Each HTTP request will generate a new bean, which is only valid within the current HTTP session. global-session: The global session scope is only meaningful in portlet-based web applications and is no longer available in Spring 5. Portlets are small Java web plug-ins capable of generating snippets of semantic code (such as HTML). They are based on portlet containers and can handle HTTP requests like servlets. But unlike Servlets, each Portlet has a different session.
Do you understand the thread safety issues of singleton beans in Spring?
Most of the time we do not use multi-threading in the system, so few people pay attention to this issue. Singleton beans have threading problems, mainly because when multiple threads operate the same object, writing operations to the non-static member variables of this object will cause thread safety issues.
There are two common solutions:
Try to avoid defining variable member variables in the bean object (not very realistic). Define a ThreadLocal member variable in the class and save the required variable member variables in ThreadLocal (a recommended way).
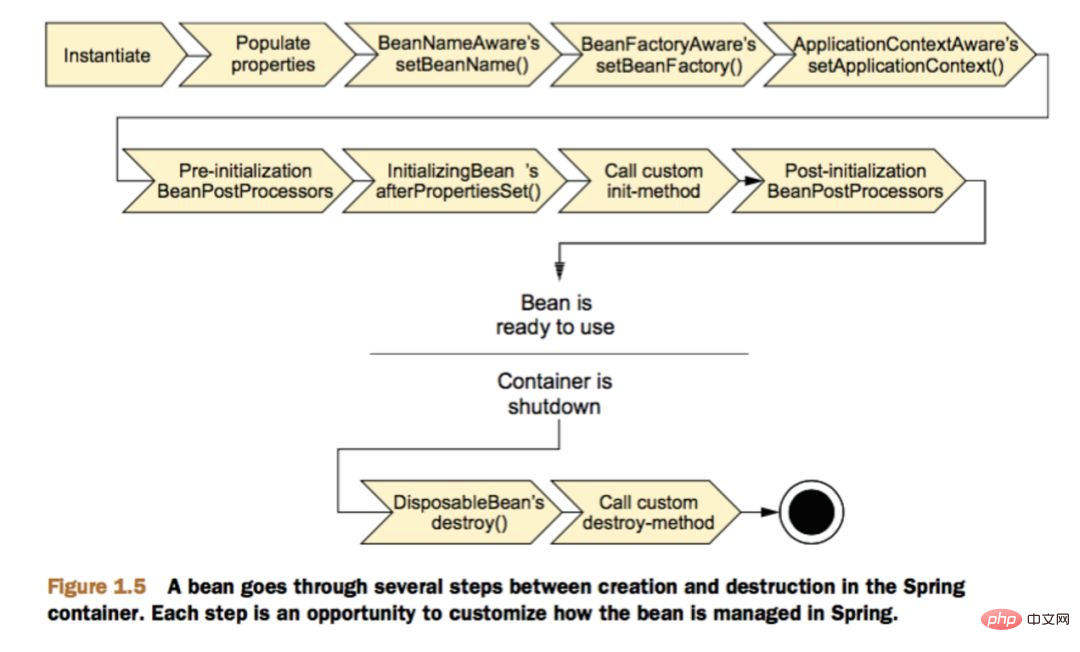
Bean life cycle in Spring?
The Bean container finds the definition of Spring Bean in the configuration file. The Bean container uses the Java Reflection API to create a Bean instance. If some attribute values are involved, use the set() method to set some attribute values. If the Bean implements the BeanNameAware interface, call the setBeanName() method and pass in the name of the Bean. If the Bean implements the BeanClassLoaderAware interface, call the setBeanClassLoader() method and pass in the instance of the ClassLoader object. If the Bean implements the BeanFactoryAware interface, call the setBeanClassFacotory() method and pass in the instance of the ClassLoader object. Similar to the above, if other *Aware interfaces are implemented, the corresponding methods are called. If there is a BeanPostProcessor object related to the Spring container that loads this Bean, execute the postProcessBeforeInitialization() method. If the Bean implements the InitializingBean interface, execute the afeterPropertiesSet() method. If the Bean definition in the configuration file contains the init-method attribute, execute the specified method. If there is a BeanPostProcess object related to the Spring container that loads this Bean, execute the postProcessAfterInitialization() method. When you want to destroy a Bean, if the Bean implements the DisposableBean interface, execute the destroy() method. When you want to destroy a Bean, if the definition of the Bean in the configuration file contains the destroy-method attribute, execute the specified method. 

Tell me about your understanding of Spring MVC?
Talking about this issue, we have to mention the previous eras of Model1 and Model2 without Spring MVC.
**Model1 era:** Many back-end programmers who learned Java late may not have been exposed to JavaWeb application development in the Model1 mode. In Model1 mode, the entire Web application is almost entirely composed of JSP pages, and only a small number of JavaBeans are used to handle database connection, access and other operations. In this mode, JSP is both the control layer and the presentation layer. Obviously, there are many problems with this model. For example, control logic and performance logic are mixed together, resulting in extremely low code reuse rate; another example is that the front-end and back-end are interdependent, making testing difficult and development efficiency extremely low.
Model2 Era: Friends who have studied Servlet and done related demos should understand the development model of Java Bean (Model) JSP (View) Servlet (Controller). This is the early Java Web MVC development model. Model is the data involved in the system, that is, dao and beans; View is used to display the data in the model, just for display; Controller sends user requests to Servlet for processing, returns the data to JSP and displays it to the user.
There are still many problems in the Model2 mode. The degree of abstraction and encapsulation of Model2 is far from enough. When using Model2 for development, it is inevitable to reinvent the wheel, which greatly reduces the maintainability and usability of the program. Reusability. As a result, many MVC frameworks related to Java Web development came into being, such as Struts2. However, because Struts2 is relatively cumbersome, with the popularity of Spring lightweight development framework, the Spring MVC framework appeared in the Spring ecosystem. Spring MVC is currently the best MVC framework. Compared with Struts2, Spring MVC is simpler and more convenient to use, has higher development efficiency, and Spring MVC runs faster.
MVC is a design pattern, and Spring MVC is an excellent MVC framework. Spring MVC can help us develop a more concise Web layer, and it is naturally integrated with the Spring framework. Under Spring MVC, we generally divide back-end projects into Service layer (processing business), Dao layer (database operations), Entity layer (entity classes), and Controller layer (control layer, returning data to the front-end page).
The simple schematic diagram of Spring MVC is as follows:
Talk about the working principle of Spring MVC
##Process description:1. The client (browser) sends a request directly to the DispatcherServlet. 2.DispatcherServlet calls HandlerMapping based on the request information and parses the Handler corresponding to the request. 3. Parse to the corresponding Handler (which is what we usually call the Controller). 4.HandlerAdapter will call the real processor according to the Handler to process the request and execute the corresponding business logic. 5. After the processor finishes processing the business, it will return a ModelAndView object. Model is the returned data object, and View is the logical View. 6.ViewResolver will find the actual View based on the logical View. 7.DispatcherServlet passes the returned Model to View (view rendering). 8. Return the View to the requester (browser).##What design patterns are used in the Spring framework?
Factory design pattern: Spring uses the factory pattern to create bean objects through BeanFactory and ApplicationContext. Proxy design pattern: Implementation of Spring AOP functionality. Single case design pattern: Beans in Spring are singletons by default. Template method pattern: jdbcTemplate, hibernateTemplate and other classes ending with Template in Spring that operate on the database use the template pattern. Wrapper design pattern: Our project needs to connect to multiple databases, and different customers will access different databases according to their needs during each visit. This model allows us to dynamically switch between different data sources according to customer needs. Observer pattern: The Spring event-driven model is a classic application of the observer pattern. Adapter mode: Spring AOP enhancement or advice (Advice) uses the adapter mode, and Spring MVC also uses the adapter mode to adapt the Controller.
What is the difference between @Component and @Bean?
The objects of action are different. The @Component annotation acts on classes, while the @Bean annotation acts on methods. @Component annotation is usually automatically detected and automatically assembled into the Spring container through class path scanning (we can use the @ComponentScan annotation to define the path to be scanned). The @Bean annotation is usually defined in the method marked with the annotation to generate this bean, telling Spring that this is an instance of a certain class and returned to me when I need to use it. @Bean annotation is more customizable than @Component annotation, and in many places beans can only be registered through @Bean annotation. For example, when a class that references a third-party library needs to be assembled into a Spring container, it can only be achieved through the @Bean annotation.
@Bean annotation usage example:
@Configurationpublic class AppConfig { @Bean public TransferService transferService() { return new TransferServiceImpl(); }}复制代码The above code is equivalent to the following XML configuration:
<beans> <bean id="transferService" class="com.common.TransferServiceImpl"/></beans>复制代码
The following example cannot be passed@ Implemented by Component annotation:
@Beanpublic OneService getService(status) { case (status) { when 1: return new serviceImpl1(); when 2: return new serviceImpl2(); when 3: return new serviceImpl3(); }}复制代码将一个类声明为Spring的bean的注解有哪些?
我们一般使用@Autowired注解去自动装配bean。而想要把一个类标识为可以用@Autowired注解自动装配的bean,可以采用以下的注解实现:
@Component注解。通用的注解,可标注任意类为Spring组件。如果一个Bean不知道属于哪一个层,可以使用@Component注解标注。 @Repository注解。对应持久层,即Dao层,主要用于数据库相关操作。 @Service注解。对应服务层,即Service层,主要涉及一些复杂的逻辑,需要用到Dao层(注入)。 @Controller注解。对应Spring MVC的控制层,即Controller层,主要用于接受用户请求并调用Service层的方法返回数据给前端页面。
Spring事务管理的方式有几种?
编程式事务:在代码中硬编码(不推荐使用)。 声明式事务:在配置文件中配置(推荐使用),分为基于XML的声明式事务和基于注解的声明式事务。
Spring事务中的隔离级别有哪几种?
在TransactionDefinition接口中定义了五个表示隔离级别的常量:
**ISOLATION_DEFAULT:**使用后端数据库默认的隔离级别,Mysql默认采用的REPEATABLE_READ隔离级别;Oracle默认采用的READ_COMMITTED隔离级别。
**ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:**最低的隔离级别,允许读取尚未提交的数据变更,可能会导致脏读、幻读或不可重复读。
**ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED: **Allow reading of data that has been submitted by concurrent transactions, which can prevent dirty reads, but phantom reads or non-repeatable reads may still occur
**ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:**For the same field The results of multiple reads are consistent, unless the data is modified by the own transaction itself, which can prevent dirty reads and non-repeatable reads, but phantom reads may still occur.
**ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE: **The highest isolation level, fully compliant with the ACID isolation level. All transactions are executed one after another in order, so that there is no possibility of interference between transactions. In other words, this level can prevent dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads. But this will seriously affect the performance of the program. Normally this level is not used.
#What are the types of transaction propagation behaviors in Spring transactions?
Eight constants representing transaction propagation behavior are defined in the TransactionDefinition interface.
Support current transaction situation:
**PROPAGATION_REQUIRED: **If a transaction currently exists, join the Transaction; if there is currently no transaction, create a new transaction.
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS: If a transaction currently exists, join the transaction; if there is currently no transaction, continue running in a non-transactional manner.
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY: If a transaction currently exists, join the transaction; if there is no transaction currently, throw an exception. (mandatory: mandatory).
If the current transaction is not supported:
##PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW: Create a new transaction , if a transaction currently exists, suspend the current transaction.
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED: Run in non-transactional mode. If a transaction currently exists, the current transaction will be suspended.
PROPAGATION_NEVER: Run in non-transactional mode, throwing an exception if a transaction currently exists.
Other situations:
PROPAGATION_NESTED: If a transaction currently exists, create a transaction to run as a nested transaction of the current transaction; if there is currently no transaction, Then this value is equivalent to PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
End
I hope you can master these contents and continue to support me, thank you.
More related free learning recommendations: mysql tutorial(Video)
The above is the detailed content of collect! What Spring must master. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
In 2023, AI technology has become a hot topic and has a huge impact on various industries, especially in the programming field. People are increasingly aware of the importance of AI technology, and the Spring community is no exception. With the continuous advancement of GenAI (General Artificial Intelligence) technology, it has become crucial and urgent to simplify the creation of applications with AI functions. Against this background, "SpringAI" emerged, aiming to simplify the process of developing AI functional applications, making it simple and intuitive and avoiding unnecessary complexity. Through "SpringAI", developers can more easily build applications with AI functions, making them easier to use and operate.
 Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
As an industry leader, Spring+AI provides leading solutions for various industries through its powerful, flexible API and advanced functions. In this topic, we will delve into the application examples of Spring+AI in various fields. Each case will show how Spring+AI meets specific needs, achieves goals, and extends these LESSONSLEARNED to a wider range of applications. I hope this topic can inspire you to understand and utilize the infinite possibilities of Spring+AI more deeply. The Spring framework has a history of more than 20 years in the field of software development, and it has been 10 years since the Spring Boot 1.0 version was released. Now, no one can dispute that Spring
 What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
How to implement spring programmatic transactions: 1. Use TransactionTemplate; 2. Use TransactionCallback and TransactionCallbackWithoutResult; 3. Use Transactional annotations; 4. Use TransactionTemplate in combination with @Transactional; 5. Customize the transaction manager.
 How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring
May 24, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring
May 24, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
Java implements scheduled tasks In the library that comes with Jdk, there are two ways to implement scheduled tasks, one is Timer, and the other is ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor. When Timer+TimerTask creates a Timer, it creates a thread, which can be used to schedule TimerTask tasks. Timer has four construction methods, and you can specify the name of the Timer thread and whether to set it as a daemon thread. The default name is Timer-number, and the default is not a daemon thread. There are three main methods: cancel(): terminate task scheduling, cancel all currently scheduled tasks, running tasks will not be affected purge(): remove tasks from the task queue
 The differences and connections between Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Jun 22, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
The differences and connections between Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Jun 22, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
SpringBoot and SpringCloud are both extensions of Spring Framework that help developers build and deploy microservice applications faster, but they each have different purposes and functions. SpringBoot is a framework for quickly building Java applications, allowing developers to create and deploy Spring-based applications faster. It provides a simple, easy-to-understand way to build stand-alone, executable Spring applications
 The 7 most commonly used annotations in Spring, the most powerful organization in history!
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
The 7 most commonly used annotations in Spring, the most powerful organization in history!
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
With the update and iteration of technology, Java5.0 began to support annotations. As the leading framework in Java, spring has slowly begun to abandon xml configuration since it was updated to version 2.5, and more annotations are used to control the spring framework.
 How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set the transaction isolation level in Spring: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation; 2. Set it in the Spring configuration file; 3. Use PlatformTransactionManager; 4. Set it in the Java configuration class. Detailed introduction: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation, add the @Transactional annotation to the class or method that requires transaction management, and set the isolation level in the attribute; 2. In the Spring configuration file, etc.
 Learn Spring Cloud from scratch
Jun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM
Learn Spring Cloud from scratch
Jun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM
As a Java developer, learning and using the Spring framework is an essential skill. With the popularity of cloud computing and microservices, learning and using Spring Cloud has become another skill that must be mastered. SpringCloud is a development toolset based on SpringBoot for quickly building distributed systems. It provides developers with a series of components, including service registration and discovery, configuration center, load balancing and circuit breakers, etc., allowing developers to build micro