What does mysql sub-conditional query statement mean?
In mysql, you can call another table expression in a table expression. This called table expression is called a subquery (subquery) statement, also called a subselect (subselect) or an inline selection ( inner select). The results of the subquery are passed to the table expression that called it for further processing.
Subquery classification
1. Classification by returned result set
Subqueries are divided into four types according to the returned result sets: table subquery, row subquery, column subquery and scalar subquery.
Table subquery: The returned result set is a set of rows, N rows and N columns (N>=1). Table subqueries are often used in the FROM clause of a parent query.
Row subquery: The returned result set is a set of columns, one row with N columns (N>=1). Row subqueries can be used in the FROM clause and WHERE clause of a query.
Column subquery: The returned result set is a set of rows, with N rows and one column (N>=1).
Scalar subquery: The returned result set is a scalar set, one row and one column, which is a scalar value. Anywhere you can specify a scalar expression, you can use a scalar subquery.
By definition, each scalar subquery is also a row subquery and a column subquery, but not vice versa; each row subquery and column subquery is also a table subquery, Nor vice versa.
2. According to the calling method of the returned result
Subquery can be divided into where type subquery and from type subquery according to the calling method of the returned result set. and exists type subquery.
Where type subquery: (use the inner query result as the comparison condition of the outer query)
Definition: where type subquery uses the inner query result as the outer query Query conditions.
from type subquery: (the inner query result is provided for the outer query again)
Definition: from subquery is to treat the result of the subquery (a table in memory) as Make a temporary table and then process it.
Exists subquery: (Get the outer query results to the inner layer to see if the inner query is true)
Definition: The exists subquery is to loop through the outer table, and then The inner table performs inner query. Similar to in (), but they are still different. It mainly depends on the size difference between the two tables. If the subquery table is large, use exists (inner index), and if the subquery table is small, use in (outer index);
Use the subquery principle
1. A subquery must be placed in parentheses.
2. Place the subquery to the right of the comparison condition to increase readability.
The subquery does not contain an ORDER BY clause. Only one ORDER BY clause can be used with a SELECT statement, and if specified it must be placed at the end of the main SELECT statement.
3. Two comparison conditions can be used in subqueries: single-line operators (>, =, >=, ,
Instance analysis
1. Create a test table
CREATE TABLE PLAYERS
(PLAYERNO INTEGER NOT NULL,
NAME CHAR(15) NOT NULL,
INITIALS CHAR(3) NOT NULL,
BIRTH_DATE DATE ,
SEX CHAR(1) NOT NULL,
JOINED SMALLINT NOT NULL,
STREET VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
HOUSENO CHAR(4) ,
POSTCODE CHAR(6) ,
TOWN VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
PHONENO CHAR(13) ,
LEAGUENO CHAR(4) ,
PRIMARY KEY (PLAYERNO));
CREATE TABLE PENALTIES
(PAYMENTNO INTEGER NOT NULL,
PLAYERNO INTEGER NOT NULL,
PAYMENT_DATE DATE NOT NULL,
AMOUNT DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (PAYMENTNO));Note: Table Players is a basic table of player information, and penalties is a list of players with fine records.
2. Insert test data
INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (2, 'Everett', 'R', '1948-09-01', 'M', 1975, 'Stoney Road','43', '3575NH', 'Stratford', '070-237893', '2411'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (6, 'Parmenter', 'R', '1964-06-25', 'M', 1977, 'Haseltine Lane','80', '1234KK', 'Stratford', '070-476537', '8467'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (7, 'Wise', 'GWS', '1963-05-11', 'M', 1981, 'Edgecombe Way','39', '9758VB', 'Stratford', '070-347689', NULL); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (8, 'Newcastle', 'B', '1962-07-08', 'F', 1980, 'Station Road','4', '6584WO', 'Inglewood', '070-458458', '2983'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (27, 'Collins', 'DD', '1964-12-28', 'F', 1983, 'Long Drive','804', '8457DK', 'Eltham', '079-234857', '2513'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (28, 'Collins', 'C', '1963-06-22', 'F', 1983, 'Old Main Road','10', '1294QK', 'Midhurst', '010-659599', NULL); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (39, 'Bishop', 'D', '1956-10-29', 'M', 1980, 'Eaton Square','78', '9629CD', 'Stratford', '070-393435', NULL); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (44, 'Baker', 'E', '1963-01-09', 'M', 1980, 'Lewis Street','23', '4444LJ', 'Inglewood', '070-368753', '1124'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (57, 'Brown', 'M', '1971-08-17', 'M', 1985, 'Edgecombe Way','16', '4377CB', 'Stratford', '070-473458', '6409'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (83, 'Hope', 'PK', '1956-11-11', 'M', 1982, 'Magdalene Road','16A', '1812UP', 'Stratford', '070-353548', '1608'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (95, 'Miller', 'P', '1963-05-14', 'M', 1972, 'High Street','33A', '5746OP', 'Douglas', '070-867564', NULL); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (100, 'Parmenter', 'P', '1963-02-28', 'M', 1979, 'Haseltine Lane','80', '6494SG', 'Stratford', '070-494593', '6524'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (104, 'Moorman', 'D', '1970-05-10', 'F', 1984, 'Stout Street','65', '9437AO', 'Eltham', '079-987571', '7060'); INSERT INTO PLAYERS VALUES (112, 'Bailey', 'IP', '1963-10-01', 'F', 1984, 'Vixen Road','8', '6392LK', 'Plymouth', '010-548745', '1319'); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (1, 6, '1980-12-08',100); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (2, 44, '1981-05-05', 75); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (3, 27, '1983-09-10',100); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (4,104, '1984-12-08', 50); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (5, 44, '1980-12-08', 25); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (6, 8, '1980-12-08', 25); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (7, 44, '1982-12-30', 30); INSERT INTO PENALTIES VALUES (8, 27, '1984-11-12', 75);
3. Table subquery example
For example: Get males with numbers less than 10 Player’s number
mysql> select playerno from (
select playerno, sex
from players
where playerno < 10)
as players10 where sex='M';
##4. Row subquery example
For example: Get the same gender as player No. 100 and live in the same place City's player number.mysql> select playerno
from players
where (sex, town) = (
select sex, town
from players
where playerno = 100);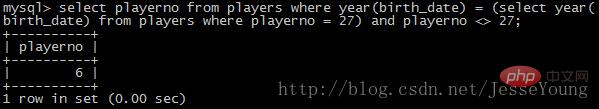
5 Scalar subquery example
Almost anywhere a scalar expression can be specified, a scalar subquery can be used. For example: Get the number of the player who was born in the same year as player No. 27mysql> select playerno
from players
where year(birth_date) =
(select year(birth_date)
from players
where playerno = 27)
and playerno <> 27;
mysql> select playerno from players where year(birth_date) = 1964 and playerno <> 27;
6 Column subquery example
Since the result set returned by the column subquery is N rows and one column, you cannot directly use = > < >= <= <> These comparison scalar results operator. IN, ANY (SOME) and ALL operators can be used in column subqueries: IN: Within the specified item, the same as IN (item 1, item 2,...).ANY:与比较操作符联合使用,ANY关键字必须接在一个比较操作符的后面,表示与子查询返回的任何值比较为 TRUE ,则返回 TRUE 。
SOME:ANY 的别名,较少使用。
ALL:与比较操作符联合使用,ALL关键字必须接在一个比较操作符的后面,表示与子查询返回的所有值比较都为 TRUE ,则返回 TRUE 。
实例1(in):获取球员性别为女的所有球员的球员号,名字及所在城市。
mysql> select playerno, name, town
from players
where playerno in
(select playerno
from players
where sex = 'F');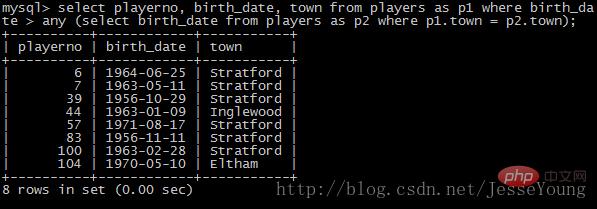
实例2(any):获取至少比同城的另一球员年轻的所有球员的号码,日期和居住城市。
mysql> select playerno, birth_date, town
from players as p1
where birth_date > any
(select birth_date
from players as p2
where p1.town = p2.town);
实例3(all):获取最老球员的号码,名字及生日。(即出生日期数值小于或等于所有其它球员的球员)
mysql> select playerno, name, birth_date
from players
where birth_date <= all
(select birth_date
from players);7、exists型子查询
EXISTS关键字表示存在。使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录,而是返回一个真假值,如果内层查询语句查询到满足条件的记录,只要子查询中至少返回一个值,则EXISTS语句的值就为True。就返回true,否则返回false。当返回的值为true时,外层查询语句将进行查询,否则不进行查询。NOT EXISTS刚好与之相反。exists的用法和in ()差不多,但是它们还是有区别的。主要是看两个张表大小差的程度。若子查询表大则用exists(内层索引),子查询表小则用in(外层索引);
实例1(exists):获取那些至少支付了一次罚款的球员的名字和首字母。
mysql> select name, initials
from players
where exists
(select * from penalties
where playerno = players.playerno);实例2(not exists):获取那些从来没有罚款的球员的名字和首字母。
mysql> select name, initials
from players
where not exists
(select * from penalties
where playerno = players.playerno);推荐教程:mysql视频教程
The above is the detailed content of What does mysql sub-conditional query statement mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.







