A simple and easy-to-understand introduction to Redis caching principles
The following Redis Tutorial column will introduce you to the Redis caching principle. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!

##1. What is Redis
Redis is a high-performance open source Nosql (non-relational database) written in C language, and the data is stored in memory. Redis is stored in key-value format, which is different from traditional relational databases. It does not necessarily follow some basic requirements of traditional databases, for example, it does not follow SQL standards, transactions, table structures, etc. Non-relational databases are strictly not a database, but a collection of structured data storage methods. Data structures in Java: String, array, list, set map... Redis provides many methods that can be used to access data in various data structures.2. Features (Advantages)
1. Data is stored in memory, with fast access speed and strong concurrency capability 2. It supports stored value types There are relatively more, including string (string), list (linked list), set (set), zset (sorted set - ordered set) and hash (hash type).
3. The emergence of redis has largely compensated for the shortcomings of key/value storage such as memcached. In some cases, it can play a very good supplementary role to relational databases (such as MySQL).
4. It provides Java, C/C, C#, PHP, JavaScript and other clients, which is very convenient to use.
5.Redis supports clustering (master-slave synchronization, load balancing). Data can be synchronized from the master server to any number of slave servers, and the slave server can be the master server associated with other slave servers.
6. Supports persistence and can save data in files on the hard disk
7. Supports subscription/publish function QQ group
1. Data storage: stored in memory, and also Occasionally persist to disk. The access speed is fast, the concurrency capability is strong, and the data will not be lost after power failure.
2. Supports more Value types.
3. Multiple clients (language java php c# js)
4. Support cluster to expand space 8G 8G 16G
5. Open source (free and maintained by many people)
3. Install the Redis server
The official download site of Redis is http://redis.io/download, you can go there to download the latest installation program 3.1. Under windows Installation and use
1. Download the redis program software
Use redisbin32 or redisbin64
2. Green software, no installation required, use directly 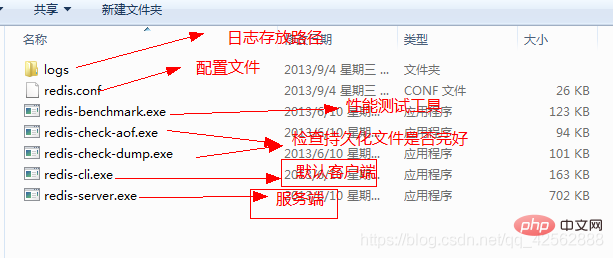 3. Start the redis service (with configuration File startup, and startup without configuration file)
3. Start the redis service (with configuration File startup, and startup without configuration file) 4. Connect to redis for operation
4. Connect to redis for operation
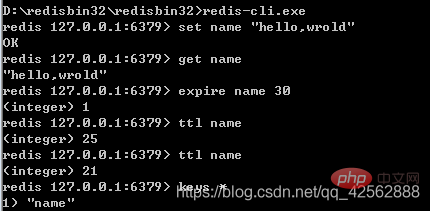
cmd>{%redis%}/redis-cli -h ip address-p port number
ip defaults to local -p defaults to 6379
redis-cli -h 172.16.6.248 -p 6379
cmd>{%redis%}/redis-cli
- Basic usage
-

2. Redis persistence configuration

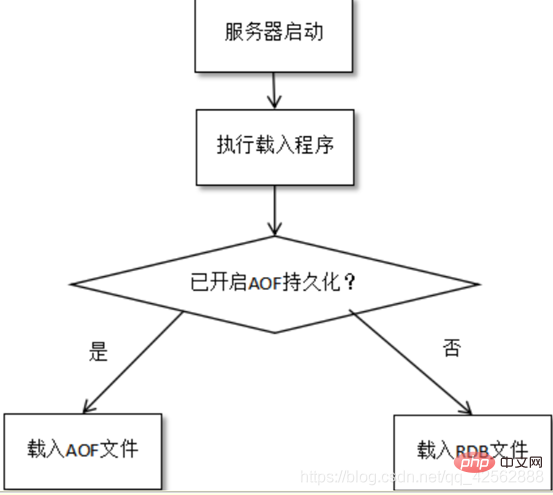 When the persistence conditions are met, persistence will be saved. Data that has not yet been saved will be stored in the AOF log format. Save it.
When the persistence conditions are met, persistence will be saved. Data that has not yet been saved will be stored in the AOF log format. Save it.
When Redis starts, it first parses the log file (a bunch of commands) and restores the data. Then also load the rdb file (take the union).
4.RDB mode
RDB persistence can generate point-in-time snapshots of the data set within a specified time interval. This mode is enabled by default. How to turn it off rdb mode:
save ""
save 900 1 //At least one change of storage synchronization is required within a period of 900 seconds
save xxx save 60 10000
5 .AOF log append mode
AOF persistently records all write operation commands executed by the server, and restores the data set by re-executing these commands when the server starts. This mode is turned off by default.
How to turn on aof mode:
appendonly yes //yes to turn on, no to turn off
#appendfsync always //Execute fsync every time there is a new command, and put the buffer data into the aof file
#Here we enable everysec
appendfsync everysec //fsync once per second
#appendfsync no //Never fsync (leave it to the operating system to handle, it may take a long time to execute fsync)
Please provide other parameters Let’s take a look at the detailed explanation of the redis.conf configuration file
6. Redis classic practical scenario-caching
-
6.1 Why use caching
Store frequently queried data and rarely modified data in the cache to reduce database access and reduce database pressure. The cache is generally in memory and the access speed is relatively fast.
-
6.2 Which data is suitable to be placed in the cache
Frequent query: Caching is to provide efficient access to data queries.
Rarely modified: the cache and database must be modified simultaneously when modifying
For example: regional data, product classification, data dictionary menu (regardless of permissions) -
6.3 Choose the appropriate one Cache
Hibernate second-level cache, mybatis second-level cache, redis central cache
Hibernate second-level cache, mybatis second-level cache does not support cluster cache by default, use redis -
6.4 How to store data
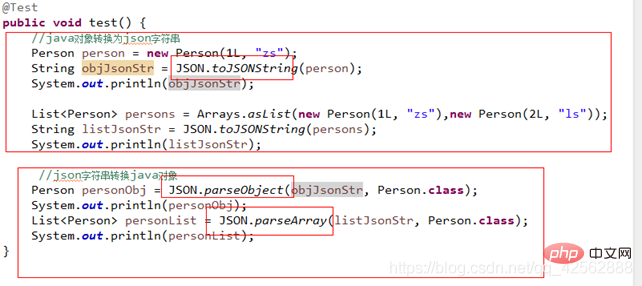
1) json: Convert the data to be stored into a json type string
When saving the cache:
Java Object--------- -->json string
Get cache:
json string-------->Java Object-
Json framework: jdk-json-lib jackson gson fastjson 2) Binary storage: Serialize the data to be stored into a binary serialization framework to implement
2) Binary storage: Serialize the data to be stored into a binary serialization framework to implement
7. Implement menu caching
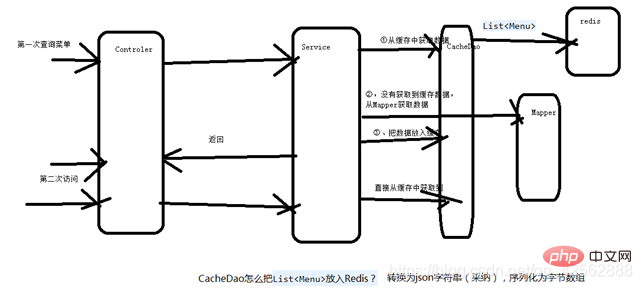
The above is the detailed content of A simple and easy-to-understand introduction to Redis caching principles. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




 2) Binary storage: Serialize the data to be stored into a binary serialization framework to implement
2) Binary storage: Serialize the data to be stored into a binary serialization framework to implement 