Introduction to some common basic algorithms in JS

An algorithm is just a function that converts the input of a certain data structure into the output of a certain data structure. The internal logic of the algorithm determines how to convert.
Basic Algorithm
1. Sorting
1. Bubble sorting
//冒泡排序function bubbleSort(arr) {
for(var i = 1, len = arr.length; i < len - 1; ++i) {
for(var j = 0; j <= len - i; ++j) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
let temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}2. Insertion sorting
//插入排序 过程就像你拿到一副扑克牌然后对它排序一样
function insertionSort(arr) {
var n = arr.length;
// 我们认为arr[0]已经被排序,所以i从1开始
for (var i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// 取出下一个新元素,在已排序的元素序列中从后向前扫描来与该新元素比较大小
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (arr[i] >= arr[j]) { // 若要从大到小排序,则将该行改为if (arr[i] <= arr[j])即可
// 如果新元素arr[i] 大于等于 已排序的元素序列的arr[j],
// 则将arr[i]插入到arr[j]的下一位置,保持序列从小到大的顺序
arr.splice(j + 1, 0, arr.splice(i, 1)[0]);
// 由于序列是从小到大并从后向前扫描的,所以不必再比较下标小于j的值比arr[j]小的值,退出循环
break;
} else if (j === 0) {
// arr[j]比已排序序列的元素都要小,将它插入到序列最前面
arr.splice(j, 0, arr.splice(i, 1)[0]);
}
}
}
return arr;
}When the goal is ascending sorting, the best case is that the sequence is already sorted in ascending order, then It only needs to be compared n-1 times, and the time complexity is O(n). The worst case scenario is that the sequence is originally sorted in descending order, so n(n-1)/2 times need to be compared, and the time complexity is O(n^2).
So on average, the time complexity of insertion sort is O(n^2). Obviously, the power-level time complexity means that insertion sort is not suitable for situations where there is a lot of data. Generally speaking, insertion sort is suitable for sorting small amounts of data.
3. Quick sort
//快速排序
function qSort(arr) {
//声明并初始化左边的数组和右边的数组
var left = [], right = [];
//使用数组第一个元素作为基准值
var base = arr[0];
//当数组长度只有1或者为空时,直接返回数组,不需要排序
if(arr.length <= 1) return arr;
//进行遍历
for(var i = 1, len = arr.length; i < len; i++) {
if(arr[i] <= base) {
//如果小于基准值,push到左边的数组
left.push(arr[i]);
} else {
//如果大于基准值,push到右边的数组
right.push(arr[i]);
}
}
//递归并且合并数组元素
return [...qSort(left), ...[base], ...qSort(right)];
//return qSort(left).concat([base], qSort(right));}Supplement:
In this code, we can see that this The code realizes distinguishing the left and right parts through pivot, and then recursively continues pivot sorting on the left and right parts, realizing the text description of quick sorting. In other words, there is no problem in the implementation of this algorithm.
Although this implementation is very easy to understand. However, this implementation also has room for improvement. In this implementation, we found that two arrays, left/right, are defined within the function to store temporary data. As the number of recursions increases, more and more temporary data will be defined and stored, requiring Ω(n) additional storage space.
Therefore, like many algorithm introductions, the in-place partitioning version is used to implement quick sort. Let us first introduce what an in-place partitioning algorithm is.
Description of in-place partitioning algorithm
Pick out an element from the sequence, called "pivot" , the position of the first element of the array is used as the index.
Traverse the array. When the array number is less than or equal to the base value, exchange the number at the index position with the number and index 1
Exchange the base value with the current index position
After the above three steps, the base value will be centered, and the numbers on the left and right sides of the array will be smaller or larger than the base value respectively. . At this time, the sorted array can be obtained by recursively partitioning in place.
Implementation of in-place partitioning algorithm
// 交换数组元素位置
function swap(array, i, j) {
var temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
function partition(array, left, right) {
var index = left;
var pivot = array[right]; // 取最后一个数字当做基准值,这样方便遍历
for (var i = left; i < right; i++) {
if (array[i] <= pivot) {
swap(array, index, i);
index++;
}
}
swap(array, right, index);
return index;
}Because we need to recursively partition in-place multiple times, and at the same time, we do not want additional address space, so when implementing the partitioning algorithm There will be three parameters, namely the original array array, the starting point left of the array that needs to be traversed, and the end point of the array right that needs to be traversed.
Finally, a sorted index value is returned for the next recursion. The value corresponding to this index must be smaller than the array element on the left side of the index and larger than all the array elements on the right side.
Basically again, we can further optimize the partitioning algorithm. We found that <=pivot can be changed to In-situ partition version is fast Sorting implementation 2. String 1. Palindrome string 2. Flip the string 3. The character that appears the most times in the string 3. Array 1. Array deduplication 4. Search 1. Binary search Apply binary search to the previous insertion sort to form a binary insertion sort, which is said to improve efficiency. But when I tested, maybe the amount of data was too small, and I didn't find too obvious a gap. . You can try it yourself ~ (for example, use console.time('Insertion sorting takes time') and console.timeEnd('Insertion sorting takes time') at the beginning and end of the function call) 5. Tree search/traversal 1. Depth-first search 2. Breadth-first search High-order function derivation algorithm 1. Filter deduplication filter is also a commonly used operation, which is used Filter out certain elements of Array and return the remaining elements. It can also be understood this way. The callback function of filter processes each element of Array. If the processing result returns false, the filter result will remove the element. If true, it will remain. Use the high-order function filter(). The key is It lies in correctly implementing a "filter" function. In fact, this filtering function has multiple parameters, filter(function (element, index, self)), which demonstrates the use of filter to remove duplicates, like this: 2, sort sorting algorithm 排序也是在程序中经常用到的算法。无论使用冒泡排序还是快速排序,排序的核心是比较两个元素的大小。如果是数字,我们可以直接比较,但如果是字符串或者两个对象呢? 直接比较数学上的大小是没有意义的,因此,比较的过程必须通过函数抽象出来。通常规定,对于两个元素x和y,如果认为x < y,则返回-1,如果认为x == y,则返回0,如果认为x > y,则返回1,这样,排序算法就不用关心具体的比较过程,而是根据比较结果直接排序。 值得注意的例子: 解释原因 第二个排序把apple排在了最后,是因为字符串根据ASCII码进行排序,而小写字母a的ASCII码在大写字母之后。 第三个排序结果,简单的数字排序都能错。 这是因为Array的sort()方法默认把所有元素先转换为String再排序,结果’10’排在了’2’的前面,因为字符’1’比字符’2’的ASCII码小。 因此我们把结合这个原理: 上面的代码解读一下:传入x,y,如果x 还有一个,sort()方法会直接对Array进行修改,它返回的结果仍是当前Array,一个例子: 相关免费学习推荐:js视频教程 The above is the detailed content of Introduction to some common basic algorithms in JS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!function quickSort(array) {
function swap(array, i, j) {
var temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
function partition(array, left, right) {
var index = left;
var pivot = array[right]; // 取最后一个数字当做基准值,这样方便遍历
for (var i = left; i < right; i++) {
if (array[i] < pivot) {
swap(array, index, i);
index++;
}
}
swap(array, right, index);
return index;
}
function sort(array, left, right) {
if (left > right) {
return;
}
var storeIndex = partition(array, left, right);
sort(array, left, storeIndex - 1);
sort(array, storeIndex + 1, right);
}
sort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
return array;
}//判断回文字符串
function palindrome(str) {
var reg = /[\W\_]/g;
var str0 = str.toLowerCase().replace(reg, "");
var str1 = str0.split("").reverse().join("");
return str0 === str1;
}function reverseString(str) {
return str.split("").reverse().join("");
}function findMaxDuplicateChar(str) {
var cnt = {}, //用来记录所有的字符的出现频次
c = ''; //用来记录最大频次的字符
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
var ci = str[i];
if (!cnt[ci]) {
cnt[ci] = 1;
} else {
cnt[ci]++;
}
if (c == '' || cnt[ci] > cnt[c]) {
c = ci;
}
}
console.log(cnt) return c;
}//数组去重
function uniqueArray(arr) {
var temp = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (temp.indexOf(arr[i]) == -1) {
temp.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return temp;
//or
return Array.from(new Set(arr));
}//二分查找
function binary_search(arr, l, r, v) {
if (l > r) {
return -1;
}
var m = parseInt((l + r) / 2);
if (arr[m] == v) {
return m;
} else if (arr[m] < v) {
return binary_search(arr, m+1, r, v);
} else {
return binary_search(arr, l, m-1, v);
}
}//深搜 非递归实现
function dfs(node) {
var nodeList = [];
if (node) {
var stack = [];
stack.push(node);
while(stack.length != 0) {
var item = stack.pop();
nodeList.push(item);
var children = item.children;
for (var i = children.length-1; i >= 0; i--) {
stack.push(children[i]);
}
}
} return nodeList;
}
//深搜 递归实现
function dfs(node, nodeList) {
if (node) {
nodeList.push(node);
var children = node.children;
for (var i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
dfs(children[i], nodeList);
}
}
return nodeList;
}//广搜 非递归实现
function bfs(node) {
var nodeList = [];
if (node != null) {
var queue = [];
queue.unshift(node);
while (queue.length != 0) {
var item = queue.shift();
nodeList.push(item);
var children = item.children;
for (var i = 0; i < children.length; i++)
queue.push(children[i]);
}
}
return nodeList;
}
//广搜 递归实现
var i=0;
//自增标识符
function bfs(node, nodeList) {
if (node) {
nodeList.push(node);
if (nodeList.length > 1) {
bfs(node.nextElementSibling, nodeList); //搜索当前元素的下一个兄弟元素
}
node = nodeList[i++];
bfs(node.firstElementChild, nodeList); //该层元素节点遍历完了,去找下一层的节点遍历
} return nodeList;
}var r,
arr = ['apple', 'strawberry', 'banana', 'pear', 'apple', 'orange', 'orange', 'strawberry'];
r = arr.filter(function (element, index, self) {
return self.indexOf(element) === index;
//拿到元素,判断他在数组里第一次出现的位置,是不是和当前位置一样,
//一样的话返回true,不一样说明重复了,返回false。
});// 看上去正常的结果:
['Google', 'Apple', 'Microsoft'].sort(); // ['Apple', 'Google', 'Microsoft'];
// apple排在了最后:
['Google', 'apple', 'Microsoft'].sort(); // ['Google', 'Microsoft", 'apple']
// 无法理解的结果:
[10, 20, 1, 2].sort(); // [1, 10, 2, 20]
var arr = [10, 20, 1, 2];
arr.sort(function (x, y) {
if (x < y) {
return -1;
}
if (x > y) {
return 1;
} return 0;
});
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 10, 20]var a1 = ['B', 'A', 'C'];var a2 = a1.sort();
a1; // ['A', 'B', 'C']
a2; // ['A', 'B', 'C']
a1 === a2; // true, a1和a2是同一对象

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
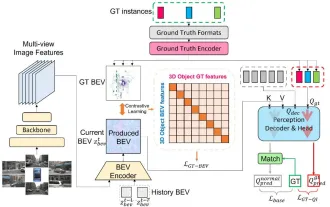 CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: At present, in the entire autonomous driving system, the perception module plays a vital role. The autonomous vehicle driving on the road can only obtain accurate perception results through the perception module. The downstream regulation and control module in the autonomous driving system makes timely and correct judgments and behavioral decisions. Currently, cars with autonomous driving functions are usually equipped with a variety of data information sensors including surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, and millimeter-wave radar sensors to collect information in different modalities to achieve accurate perception tasks. The BEV perception algorithm based on pure vision is favored by the industry because of its low hardware cost and easy deployment, and its output results can be easily applied to various downstream tasks.
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
The bottom layer of the C++sort function uses merge sort, its complexity is O(nlogn), and provides different sorting algorithm choices, including quick sort, heap sort and stable sort.
 Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
Can artificial intelligence predict crime? Explore CrimeGPT's capabilities
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and law enforcement opens up new possibilities for crime prevention and detection. The predictive capabilities of artificial intelligence are widely used in systems such as CrimeGPT (Crime Prediction Technology) to predict criminal activities. This article explores the potential of artificial intelligence in crime prediction, its current applications, the challenges it faces, and the possible ethical implications of the technology. Artificial Intelligence and Crime Prediction: The Basics CrimeGPT uses machine learning algorithms to analyze large data sets, identifying patterns that can predict where and when crimes are likely to occur. These data sets include historical crime statistics, demographic information, economic indicators, weather patterns, and more. By identifying trends that human analysts might miss, artificial intelligence can empower law enforcement agencies
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
1. Background of the Construction of 58 Portraits Platform First of all, I would like to share with you the background of the construction of the 58 Portrait Platform. 1. The traditional thinking of the traditional profiling platform is no longer enough. Building a user profiling platform relies on data warehouse modeling capabilities to integrate data from multiple business lines to build accurate user portraits; it also requires data mining to understand user behavior, interests and needs, and provide algorithms. side capabilities; finally, it also needs to have data platform capabilities to efficiently store, query and share user profile data and provide profile services. The main difference between a self-built business profiling platform and a middle-office profiling platform is that the self-built profiling platform serves a single business line and can be customized on demand; the mid-office platform serves multiple business lines, has complex modeling, and provides more general capabilities. 2.58 User portraits of the background of Zhongtai portrait construction
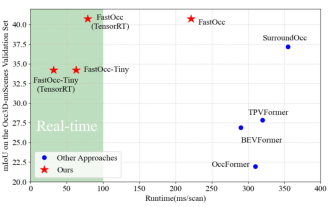 Add SOTA in real time and skyrocket! FastOcc: Faster inference and deployment-friendly Occ algorithm is here!
Mar 14, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
Add SOTA in real time and skyrocket! FastOcc: Faster inference and deployment-friendly Occ algorithm is here!
Mar 14, 2024 pm 11:50 PM
Written above & The author’s personal understanding is that in the autonomous driving system, the perception task is a crucial component of the entire autonomous driving system. The main goal of the perception task is to enable autonomous vehicles to understand and perceive surrounding environmental elements, such as vehicles driving on the road, pedestrians on the roadside, obstacles encountered during driving, traffic signs on the road, etc., thereby helping downstream modules Make correct and reasonable decisions and actions. A vehicle with self-driving capabilities is usually equipped with different types of information collection sensors, such as surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, millimeter-wave radar sensors, etc., to ensure that the self-driving vehicle can accurately perceive and understand surrounding environment elements. , enabling autonomous vehicles to make correct decisions during autonomous driving. Head




