Consolidate your JavaScript knowledge system
People don’t talk much, so the javascript column helps you consolidate your JavaScript knowledge system.

##
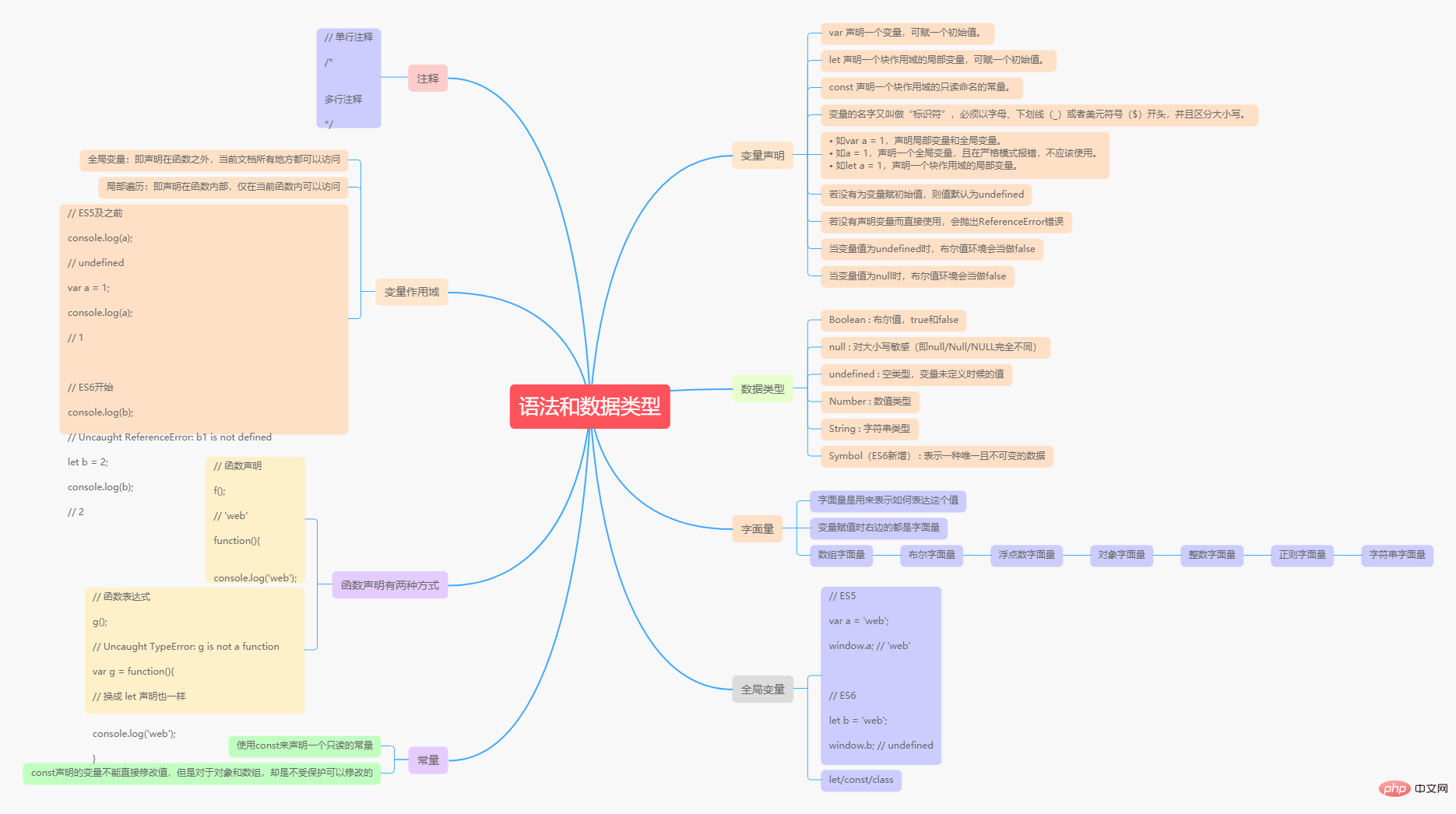
var a = [1, 2, 5];
for(var k in a){
console.log(k); // k 为当前元素的下标
}
for(var m of a){
console.log(m); // m 为当前元素的值
}
VM215:3 0
VM215:3 1
VM215:3 2
VM215:6 1
VM215:6 2
VM215:6 5复制代码 Variable declaration
Variable declaration
- var
- Declare a variable , can be assigned an initial value.
- Declare a block-scoped local variable and assign an initial value.
- Declare a block-scoped read-only named constant.
The name of a variable is also called an "identifier". must start with a letter, underscore (_) or dollar sign ($), and is case-sensitive - .
If no initial value is assigned to the variable, the value defaults toundefined -
If the variable is not declared and used directly,ReferenceError - Error# will be thrown
##When the variable value isundefined , the Boolean value environment is treated as - false
When the variable value isnull , the Boolean value The environment is treated as - false
Data type
Boolean Boolean value, true and false
- null is case sensitive
- undefined empty type, the value when the variable is undefined
- Number value type
- String string type
- Symbol (new in ES6) represents a unique and unavailable Variable data
- Literal
Literal is used to express how to express the value
- When assigning a variable, the right side is all literal
- Array literal
- Boolean literal
- Floating point literal
- Object literal
- Integer literal
- Regular literal
- String literal
- Global variable
// ES5
var a = 'web';
window.a; // 'web'
// ES6
let b = 'web';
window.b; // undefined复制代码
Copy after login
CommentsCode:// ES5 var a = 'web'; window.a; // 'web' // ES6 let b = 'web'; window.b; // undefined复制代码
// 单行注释
/*
多行注释
*/复制代码
Copy after login
Variable scope
// 单行注释 /* 多行注释 */复制代码
Global variables: that is, declared outside the function, can be accessed from all places in the current document
- Local traversal: that is, declared inside the function, only Can be accessed within the current function
- Code:
// ES5及之前 console.log(a); // undefined var a = 1; console.log(a); // 1 // ES6开始 console.log(b); // Uncaught ReferenceError: b1 is not defined let b = 2; console.log(b); // 2复制代码
// 函数声明
f(); // 'web'
function(){
console.log('web');
};复制代码Copy after login
// 函数表达式
g(); // Uncaught TypeError: g is not a function
var g = function(){ // 换成 let 声明也一样
console.log('web');
}复制代码Copy after login
Constant
// 函数声明
f(); // 'web'
function(){
console.log('web');
};复制代码// 函数表达式
g(); // Uncaught TypeError: g is not a function
var g = function(){ // 换成 let 声明也一样
console.log('web');
}复制代码Use const to declare a read-only constant
- Variables declared with const cannot directly modify the value, but for objects and arrays, they are not protected and can be modified
- A complete
- implementation consists of 3 parts: Core
- ECMAScript
, Document Object ModelDOM, Browser Object ModelBOM.JavaScript is a literal scripting language, a dynamically typed, weakly typed, prototype-based language with built-in support for types. -
JavaScript Features: An interpretive scripting language, mainly used to add interactive behaviors to HTML pages. It can be directly embedded in HTML pages, but writing it as a separate js file is conducive to structure and behavior. Separation, cross-platform features, supported by most browsers, can run on multiple platforms.- JavaScript Grammar differences: case-sensitive, variables are weakly typed, the trailing semicolon is optional, the explanation is the same as in
- java, c and php
languages Annotations are the same, curly braces indicate blocks of code.Example
Contains content that represents a block of code
Code:if(test1=="red") { test1 = "blue"; alert(test1); }复制代码Copy after login
JavaScript
Keywords:break,else,new,var case,finally,return,void catch,for,switch,while continue,function,this,with default,if,throw delete,in,try do,instanceof,typeof复制代码
In javascript
, variables are containers for storing information. There are two types of variables. The value is the original value and the reference value.
-
JavaScript的原始类型,即Undefined,Null,Boolean,Number和String型。 - 字符串
String是JavaScript的基本数据类型。 - 数据类型表示数据的类型,
JavaScript语言的每个值都属于某一种数据类型。 -
JavaScript的数据类型分两类:值类型(原始值),引用数据类型(引用值)。 - 值类型:字符串string,数字number,布尔boolean,对空null,未定义undefined,symbol为es6引入的一钟新的原始数据类型,表示独一无二的值。
- 引用数据类型:对象object,数组array,函数function。
-
JavaScript提供typeof运算符用于判断一个值是否在某种类型的范围内。 -
Undefined类型只有一个值,即为undefined。 - 当声明的变量未初始化时,该变量的默认值是
undefined。 -
Null类型只有一个值为null,值undefined实际上是从值null派生来的,所以JavaScript将他们定义为相等的。 -
null与undefined表示这两个值相等,但含义不同。 -
undefined是声明了变量但未对其初始化时赋予该变量的值,null表示尚未存在的对象。
代码:
console.log( null == undefined); // true复制代码
-
Boolean类型的两个值是true和false。 -
Number类型,所有数学运算返回的都是十进制的结果。 -
Number.MAX_VVALUE和Number.MIN_VALUE,它们定义了Number值集合的外边界。 - 如果生成的数值结果大于
Number.MAX_VALUE时,将被赋予值Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY,表示不再有Number值。生成的数值小于Number.MIN_VALUE,会被赋予值Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY,表示不再有Number值。 - 有表示无穷大的值为
Infinity。 -
Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY的值为Infinity,Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY的值为-Infinity。
使用
isFinite()方法判断参数值是否是有穷的。
- 特殊的
NaN,表示非数。与无穷大一样,NaN也不能用于算术计算。注意,NaN与自身不相等。
示例:
console.log(NaN == NaN) // false
console.log(isNaN("66")); // false复制代码-
String类型,是唯一没有固定大小的原始类型,字符串字面量是用双引号或者单引号声明。
类型判断
-
typeof操作符,用于获取一个变量或者表达式的类型。
返回值:
undefined,变量是Undefined类型 boolean,变量是Boolean类型的 number,变量是Number类型的 string,变量是String类型的 object,变量是一种引用类型或者Null类型复制代码
示例:
console.log(typeof 12); // number复制代码
typeof运算符对null的值返回Object。
-
instanceof操作符,用于判断一个引用类型属于哪种类型。
示例:
<script>
var a = new Array();
if(a instanceof Array) {
console.log('a是一个数组类型');
}else{
console.log('a不是一个数组类型');
}
</script>复制代码类型转换
-
Number变量,将变量转化为数字类型。 -
String变量,将变量转化为字符串类型。 -
Boolean变量,将变量转化为布尔值类型。 -
parseFloat变量,将变量转化为浮点类型。 -
parseInt变量,将变量转化为整数类型。
运算符
- 运算符:赋值运算符,算数运算符,比较运算符,逻辑运算符,一元运算符,二元运算符,三元运算符。
| 名称 | 操作符 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 赋值 | x = y | x = y |
| 加法赋值 | x += y |
x = x + y |
| 减法赋值 | x -= y |
x = x - y |
| 乘法赋值 | x *= y |
x = x * y |
| 除法赋值 | x /= y |
x = x / y |
| 求余赋值 | x %= y |
x = x % y |
| 求幂赋值 | x **= y |
x = x ** y |
| 左移位赋值 | x <<= y | x = x << y |
| 右移位赋值 | x >>= y |
x = x >> y |
| 无符号右移位赋值 | x >>>= y |
x = x >>> y |
| 按位与赋值 | x &= y |
x = x & y |
| 按位异或赋值 | x ^= y |
x = x ^ y |
示例:
赋值运算符的符号为= 算数运算符:+,-,*,/,% 比较运算符:>,>=,<,<=,!=,==,===,!== 逻辑运算符: &&,逻辑与,表示表达式前后全为true才能返回true ||,逻辑或,表示表达式前后只要有一个true就返回true !,逻辑取反,表示表达式后若为true,则返回false,否则反之。复制代码
++自增长,每执行一次自身加1,--自减,每执行一次自身减1.i++,值先参与外部表达式的运算,然后再将自身的值加1。++i,i先自身的值加1,再参与外部表达式的运算。+=,a+=3等于a=a+3。同理类似。- 三元运算符的表达式格式为:条件?正:假
- 运算符优先级:算数运算符>比较运算符>逻辑运算符>赋值运算符。
- 算数运算符
- 比较运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 赋值运算符
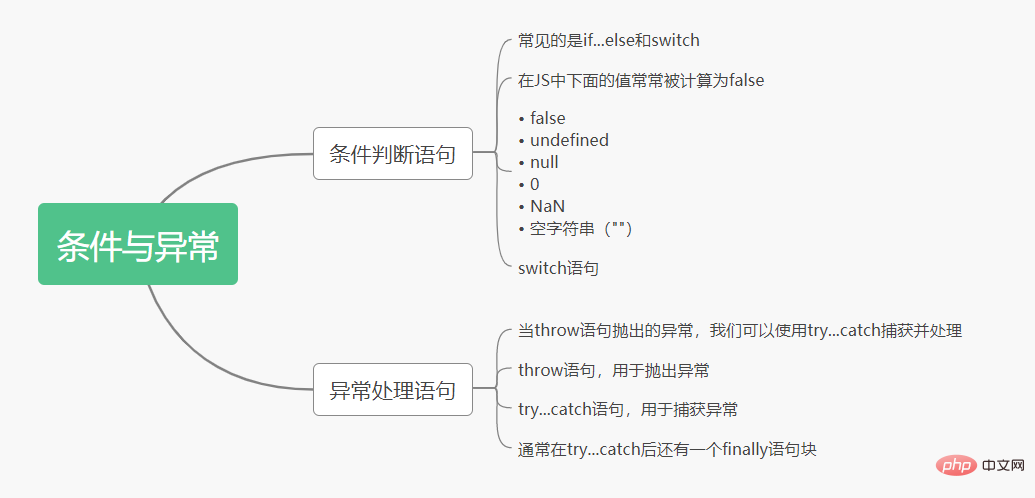
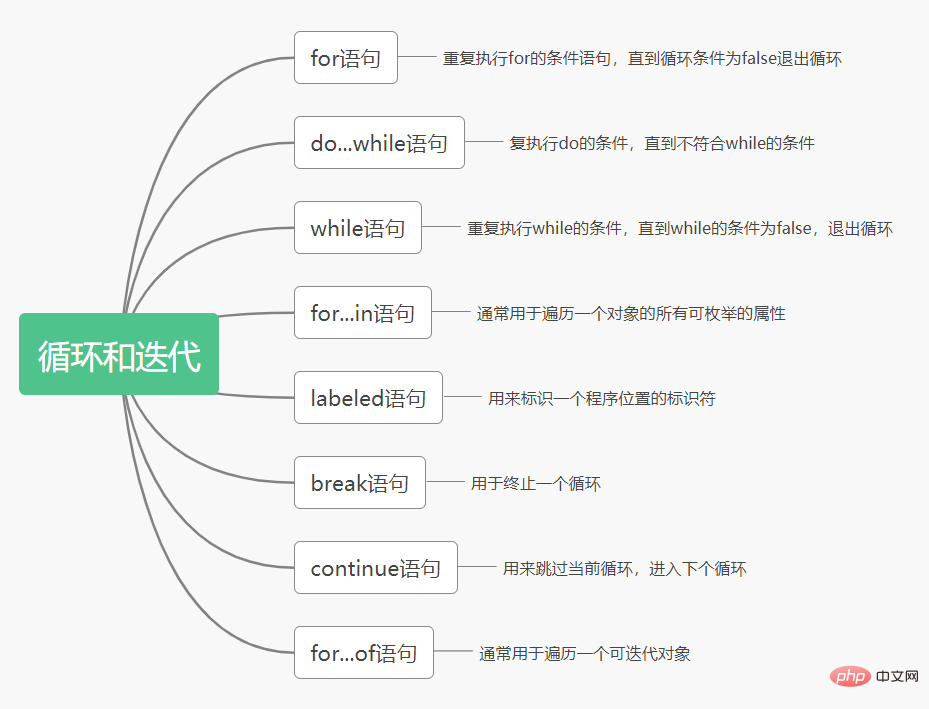
分支循环
-
if-else条件判断语句 -
switch-case选择语句 -
for循环语句 -
for-in遍历语句 -
while循环语句 -
do-while循环语句
示例:
if(条件 1) { 当条件1为true时执行的代码 }else if(条件 2){ 当条件2为true时执行的代码 }else{ 当条件1和条件2都不为true时执行的代码 }复制代码Copy after login示例:
switch(n){ case1: 执行代码块1 break; case2: 执行代码块2 break; default: ... }复制代码Copy after login示例:
for(语句1;语句2;语句3){ 被执行的代码块 }复制代码Copy after login-
continue表示为越过本次循环,继续下一次循环 -
break表示跳出整个循环,循环结束
遍历
-
for in语句循环遍历对象的属性,多用于对象,数组等复合类型,以遍历其中的属性和方法。
示例:
for(键 in 对象) { 代码块 }复制代码Copy after login-
while,只有表达式为真,就可以进入循环。
示例:
while(表达式){ 代码块 }复制代码Copy after logindo-while
示例:
do { 代码 }while(表达式)复制代码Copy after login数组
数组的属性和方法:
方法 说明 concat()连接两个或者更多的数组,并返回结果 join()把数组的所有元素放入一个字符串,元素通过指定的分隔符进行分隔 pop()删除并返回数组的最后一个元素 push()向数组的末尾添加一个或者多个元素,并返回新的长度 reverse()颠倒数组中元素的顺序 shift()删除并返回数组的第一个元素 slice()从某个已有的数组返回选定的元素 sort()对数组的元素进行排序 splice()删除元素,并向数组添加新元素 toSource()返回该对象的源代码 toString()将数组转换为字符串,并返回结果 toLocalString()将数组转换为本地数组,并返回结果 unshift()向数组的开头添加一个或者更多元素,并返回新的长度 valueOf()返回数组对象的原始值 indexOf()在数组中搜索指定元素并返回第一个匹配的索引 lastIndexOf()在数组中搜索指定元素并返回最后一个匹配的索引 concat()
连接两个或更多的数组,并返回一个新数组。
语法:
arr.concat(a1, a2, ..., an)复制代码
Copy after login参数:
-
arr:目标数组 -
a1,a2,...,an:需要合并的元素
join()使用指定分隔符,连接两个或多个数组的元素,返回一个字符串。
数组定义
- 使用
new关键字创建一个array对象,可以在内存中创建一个数组空间,添加元素。 - 使用
new关键字创建一个array对象的同时为数组赋予n个初始值。 - 不用
new,直接用[]声明一个数组,可以直接赋予初始值。
数组操作
- 添加元素
- 删除元素,pop方法,shift方法,splice方法。
- 遍历数组
- 插入元素,unshift方法,splice方法插入。
- 合并数组
- 数组转字符串
- 数组元素倒序
-
pop方法,从尾部删除,删除后元素从数组上剥离并返回。 -
shift方法,从头部删除元素,并返回。 -
splice方法,从指定位置删除指定的元素。 -
unshift方法,从头部插入。 -
splice方法,从指定位置插入指定个数的元素。 -
concat方法将多个数组连接成一个数组。 -
join方法将数组中的元素合并成一个用指定分隔符合并起来的字符串。 -
reverse方法可以将数组中的元素倒序排列,而且直接改变原来的数组,不会创建新的数组。 -
sort方法可以将数组中的元素按照一定的规则自动排序(默认的是按照字符的ASCII码顺序排序)。
pop()和push()
- pop(): 删除并返回数组最后一个元素,改变原数组。
- push(item): 向数组末尾添加一个或多个元素,改变原数组,返回新的数组长度。
shift()和unshift()
- shift(): 删除并返回数组第一个元素,改变原数组。
- unshift(item): 向数组头部添加一个或多个元素,改变原数组,返回新的数组长度。
示例:
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 5, 6]; let a1 = arr.slice(2); // [3, 5, 6] let a2 = arr.slice(2,3); // [3] let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; let a = arr.splice(1, 2, "web", "a"); // a => [2, 3] // arr => [1, "web", "a", 4]复制代码
Copy after loginforEach()
代码:
let a = [1,3,5,7]; a.forEach(function(val, index, arr){ arr[index] = val * 2 }) a ; // [2, 6, 10, 14]复制代码Copy after login代码:
arr.every(callback) 测试数组的所有元素是否都通过了指定函数的测试。 some() 测试数组中的某些元素是否通过由提供的函数实现的测试。复制代码
Copy after loginfilter()
示例:
let a = [1, "", "aa", 2, 6]; let res = a.filter(function(val, index, arr){ return typeof val == "number"; }) res;//[1, 2, 6]复制代码Copy after loginmap()
对每个元素执行此方法,并返回一个执行后的数组。
示例:
let a = [1, 3, 5]; let b = a.map(function(val, index, arr){ return val + 1; }) b; //[2, 4, 6]复制代码Copy after login拓展运算符
拓展运算符使用
(...)示例:
console.log(...[1, 2, 3]); // 1 2 3 console.log(1, ...[2,3], 4); // 1 2 3 4复制代码
Copy after login// 通常情况 浅拷贝 let a1 = [1, 2]; let a2 = a1; a2[0] = 3; console.log(a1,a2); // [3,2] [3,2] // 拓展运算符 深拷贝 let a1 = [1, 2]; let a2 = [...a1]; // let [...a2] = a1; // 作用相同 a2[0] = 3; console.log(a1,a2); // [1,2] [3,2]复制代码
Copy after loginlet [a, ...b] = [1, 2, 3, 4]; // a => 1 b => [2,3,4] let [a, ...b] = []; // a => undefined b => [] let [a, ...b] = ["abc"]; // a => "abc" b => []复制代码
Copy after loginfill()
- 用于用指定值填充一个数组
- 用来初始化空数组,并抹去数组中已有的元素
- fill()的第二个和第三个参数指定填充的起始位置和结束位置
new Array(3).fill('a'); // ['a','a','a'] [1,2,3].fill('a'); // ['a','a','a'] [1,2,3].fill('a',1,2);// [1, "a", 3]复制代码Copy after loginentries(),keys(),values()
-
entries()对键值对遍历 -
keys()对键名遍历 -
values()对键值遍历。
includes()
-
includes()用于表示数组是否包含给定的值 - 第二个参数为起始位置,默认为0,如果负数,则表示倒数的位置,如果大于数组长度,则重置为0开始。
代码:
[1,2,3].includes(3,3); // false [1,2,3].includes(3,4); // false [1,2,3].includes(3,-1); // true [1,2,3].includes(3,-4); // true复制代码
Copy after loginflat(),flatMap()
示例:
var arr1 = [1, 2, [3, 4]]; arr1.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4] var arr2 = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]]; arr2.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]] var arr3 = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]]; arr3.flat(2); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]复制代码
Copy after loginvar arr4 = [1, 2, , 4, 5]; arr4.flat(); // [1, 2, 4, 5]复制代码
Copy after login语法
var new_array = arr.flatMap(function callback(currentValue[, index[, array]]) { // return element for new_array }[, thisArg])复制代码Copy after loginvar arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]; arr1.map(x => [x * 2]); // [[2], [4], [6], [8]] arr1.flatMap(x => [x * 2]); // [2, 4, 6, 8] // only one level is flattened arr1.flatMap(x => [[x * 2]]); // [[2], [4], [6], [8]]复制代码
Copy after loginlet arr1 = ["it's Sunny in", "", "California"]; arr1.map(x => x.split(" ")); // [["it's","Sunny","in"],[""],["California"]] arr1.flatMap(x => x.split(" ")); // ["it's","Sunny","in", "", "California"]复制代码Copy after loginArray.prototype.reduce()
reduce()方法对数组中的每个元素执行一个由您提供的reducer函数(升序执行),将其结果汇总为单个返回值。var sum = [0, 1, 2, 3].reduce(function (accumulator, currentValue) { return accumulator + currentValue; }, 0); // 和为 6 var total = [ 0, 1, 2, 3 ].reduce( ( acc, cur ) => acc + cur, 0 );复制代码Copy after login语法
arr.reduce(callback(accumulator, currentValue[, index[, array]])[, initialValue]) initialValue可选 作为第一次调用 callback函数时的第一个参数的值。 如果没有提供初始值,则将使用数组中的第一个元素。 在没有初始值的空数组上调用 reduce 将报错。复制代码
Copy after login字符串对象属性
字符串对象属性
属性 说明 constructor对创建该对象的函数的引用 length字符串的长度 prototype允许向对象添加属性和方法 String object method
String object method
Attribute Description anchor()Create HTML anchor ##big() Display the string in large fontblink() Display the flashing stringbold() Use bold to display stringscharAt() Returns the character at the specified positioncharCodeAt() Returns the Unicode encoding of the character at the specified positionconcat() Connection string##fixed() Display the string as typewriter textfontcolor() Display the string using the specified colorfontsize() Display the string using the specified sizefromCharCode() Create a string from character encodingindexOf() Check the stringitalics() Use italics to display stringslastIndexOf() from after Search forward for stringlink() Display string as linklocaleCompare() Compares two strings in locale-specific ordermatch() Find a match for one or more regular expressionsreplace() Replace the substring that matches the regular expressionsearch() Retrieve values matching the regular expressionslice( ) Extract a fragment of the string and return the extracted part in a new stringsmall() Use small font size to display the stringsplit() Split the string into a string arraystrike() Use strikethrough to display stringsub() Display the string as a subscriptsubstr() Extract the specified string from the starting index number Number of characterssubstring() Extract the characters between the two specified index numbers in the stringsup() Display string as superscripttoLocaleLowerCase() ##toLocaleUpperCase()Convert the string to lowercaseConvert the string to uppercaseConvert the string to lowercaseConvert the string to uppercase##toString() Return the string valueOf() Returns the original value of a string object toSource() Represents the source code of the object 字符串搜索
indexOf(),lastIndexOf(),search()和match()。-
indexOf(),indexOf(搜索词,起始索引位置),第2个参数不写则默认从0开始搜索。indexOf()用于检索指定的字符串值在字符串中首次出现的位置。 -
lastIndexOf(),lastIndexOf(搜索词,起始索引位置),从后向前检索,返回的是一个指定的子字符串值最后出现的位置。 -
search(),语法为字符串,search(搜索词)或者字符串search(正则表达式)。 -
match(),语法为字符串。match()可在字符串内检索指定的值,或者找到一个或者多个正则表达式的匹配。没有匹配到结果,就返回null。有匹配到,会返回一个数组,数组的第0个元素存放的是匹配文本。
字符串截取
3种字符串截取方法:
substring(),slice(),substr()-
substring(),语法为字符串,substring(截取开始位置,截取结束位置),substring()是常用的字符串截取方法,接收两个参数,不能为负值,将返回一个新的字符串。 -
slice(),语法为字符串,slice(截取开始位置,截取结束位置),slice()中的参数可以为负值,如果参数是负值,则该参数从字符串的尾部开始算起的位置。-1是指字符串的最后一个字符。 -
substr(),substr(截取开始位置,length),在字符串中抽取从截取开始位置下标开始的指定数目的字符。返回一个字符串如果截取的开始位置为负数,则表示从字符串尾部开始算起。
字符串替换
replace(),replace(正则表达式/要被替换的字符串,要替换成为的子字符串)。字符串切割
split()用于将一个字符串分割成字符串数组,语法为字符串。split(用于分割的子字符串,返回数组的最大长度),返回数组的最大长度一般情况下不设置。JS事件三个阶段
事件流:
- 事件冒泡流
- 事件捕获流
事件的处理过程主要有三个阶段:捕获阶段,目标阶段,冒泡阶段 事件流包含三个阶段:事件捕获阶段,处于目标阶段和事件冒泡阶段。
- 捕获,事件由页面元素接收,逐级向下,到具体的元素
- 目标,具体的元素本身
- 冒泡,元素本身,逐级向上,到页面元素
- 事件捕获,当使用事件捕获时,父级元素先触发,子元素后触发。
- 事件冒泡,当使用事件冒泡时,子级元素先触发,父元素后触发。
事件冒泡和事件捕获
- 事件发生会产生事件流
-
DOM事件流:DOM结构是一个树形结构,当一个HTML元素产生一个事件时,该事件会在元素节点与根节点之间按特定的顺序传播,路径所经过的节点都会收到该事件。 - 事件流顺序有两种类型:事件冒泡和事件捕获。
事件触发方式
代码:
addEventListener("click","doSomething","true")复制代码Copy after login第三个参数为true,表示采用事件捕获,若false,表示采用事件冒泡。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> html,body{ width:100%; height:100%; } </style> <script> window.onload=function(){ d1 = document.getElementById("d1"); d2 = document.getElementById("d2"); d3 = document.getElementById("d3"); // true 表示在捕获阶段响应 // false 表示在冒泡阶段响应 d1.addEventListener("click",function(event){ console.log("d1") },"true"); d2.addEventListener("click",function(event){ console.log("d2") },"true") d3.addEventListener("click",function(event){ console.log("d3") },"true") } </script> </head> <body> <p id="d1" style="background: #0000ff; width: 500px; height: 500px"> <p id="d2" style="background: #00ff00; width: 400px; height: 400px"> <p id="d3" style="background: #ff0000; width: 200px; height: 200px"> </p> </p> </p> </body> </html>复制代码Copy after loginaddEventListener网页,点击跳转:addEventListener.html
事件委托
一个响应事件委托到另一个元素。
<ul id="btn"> <li id="btn1">按钮1</li> <li id="btn2">按钮2</li> <li id="btn3">按钮3</li> </ul> var btn1 = document.getElementById('btn1'); var btn2 = document.getElementById('btn2'); var btn3 = document.getElementById('btn3'); webbtn.myAddFun(btn1, 'click', function(event){ alert('1点击'); }); webbtn.myAddFun(btn2, 'click', function(event){ alert('2点击'); }); webbtn.myAddFun(btn3, 'click', function(event){ alert('3点击'); });复制代码Copy after login添加一个事件处理函数,来做事件委托
var btn = document.getElementById('btn'); webbtn.myAddFun(btn, 'click', function(event){ event = webbtn.getMyEvent(event); var target = webbtn.getMyTarget(event); switch(target.id){ case "btn1": alert('1点击'); break; case "btn2": alert('2点击'); break; case "btn3": alert('3点击'); break; } });复制代码Copy after login键盘事件
键盘事件就是有关键盘操作所触发的世界。
键盘事件:
方法 说明 keydown当用户按下键盘上的任意键时触发。按住不放,会重复触发 keypress当用户按下键盘上的字符键时触发。按住不放,会重复触发 keyup当用户释放键盘上的键时触发 鼠标拖拽效果
鼠标绑定
onmousedown(),onmousemove(),onmouseup()事件。mouse网页,点击跳转:mouse.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>mouse</title> <style> html,body{ width: 100%; height: 100%; } #dd { width: 120px; height: 120px; background: #00ff00; position: absolute; } </style> <script> var dd; var mflag = false; function ondown() { dd = document.getElementById('dd'); mflag = true; } function onmove(e){ if(mflag) { dd.style.left = e.clientX - 60 + "px"; dd.style.top = e.clientY - 60 + "px"; } } function onup() { mflag = false; } </script> </head> <body onmousemove="onmove(event)"> <p id="dd" onmousedown="ondown()" onmouseup="onup()" style="left: 80px;top: 120px;" </body> </html>复制代码Copy after login鼠标事件
鼠标事件:
方法 说明 click用户单击鼠标左键或者按下 Enter键触发dbclick用户双击鼠标触发 mousedown在用户按下任意鼠标按钮时触发 mouseenter在鼠标光标从元素外部首次移动到元素范围内时触发,不冒泡 mouseleave元素上方的光标移动到元素范围之外时触发,不冒泡 mousemove光标在元素的内部不断移动时触发 mouseover用户指针位于一个元素外部,然后用户将首次移动到另一个元素边界之内时触发 mouseout用户将光标从一个元素上方移动到另一个元素时触发 mouseup在用户释放鼠标时触发 mousewheel滚轮滚动时触发 示例:
function web(e) { mouseX = e.clientX; mouseY = e.clientY; console.log("x:"+mouseX + "," + "y:"+mouseY) } <body onclick="web(event)">复制代码Copy after login- 鼠标悬停是
onmouseover - 鼠标离开是
onmouseout
窗口事件
窗口事件:
loadunloadaborterrorselectresizescroll
load事件,表示当页面完全加载完之后,就会触发window上面的load事件。包含所有的图像,js文件,css文件等外部资源。示例:
window.onload=function(){}复制代码Copy after login当页面完全加载完之后执行其中的函数。
示例:
<script> window.onload = function() { var myp = document.getElementById("myp"); console.log(myp.innerText); } </script> <body> <p id="myp"></p> </body>复制代码Copy after login示例:
function imgLoad() { myimg = document.getElementById("myimg"); // 图片加载完成后,给图片加载框 myimg.style.border = "9px solid $00ff00"; } <img id="myimg src="" onload="imgLoad()">复制代码Copy after loginresize事件
- 当调整浏览器的窗口到一个新的宽度或者高度时,会触发
resize事件。
示例:
document.body.clientWidth和document.body.clientHeight获得窗口的宽和高。html,body { width: 100%; height: 100%; } <script> function winChange() { winWidth = document.body.clientWidth; winHeight = document.body.clientHeight; } </script> <body onresize="winChange()"> </body>复制代码Copy after loginscrol事件,文档或者浏览器窗口被滚动时触发scroll事件示例:
<script> function scrollChange() { srpos = document.getElementById("srpos"); srpos.innerText = document.documentElement.scrollTop; srpos.style.top = docuemnt.documentElement.scrollTop+"px"; } </script> <body onscroll="scrollChange()"> <p style="height:300%;"> <br/> <font id="srpos" style="position: relative;top: 0px">滚动条滚动到0px</font> </p> </body>复制代码Copy after login焦点事件
方法 说明 blur在元素失去焦点时触发,所有浏览器都支持 focus在元素获得焦点时触发,所有浏览器都支持 示例:
<script> var note; function myfocus(fname,notename) { note = document.getElementById(notename); note.innerText = fname+'获得焦点'; } function myblur(fname,notename) { note = document.getElementById(notename); note.innerText = fname + '失去焦点'; } </script> <body> <form name="myform"> <input type="text" name="uname" onfocus="myfocus('uname','unote')" onblur="myblur('uname','unote')"/><font id="unote"></font> <br/> <input type="text" name="pwd" onfocus="myfocus('pwd','pnot')" onblur="myblur('pwd','pnote')"/><font id="pnote"></font> </form> </body>复制代码Copy after login事件介绍
事件方法
方法 说明 onabort图像加载被中断 onblur元素失去焦点 onchange用户改变域的内容 onclick鼠标单击某个对象 ondblclick鼠标双击某个对象 onerror当加载文档或图像时发生某个错误 onfocus元素获得焦点 onkeydown某个键盘的键被按下 onkeypress某个键盘的键被按下或者按住 onkeyup某个键盘的键被松开 onload某个页面或者图像被完成加载 onmousedown某个鼠标按键被按下 onmousemove鼠标被移动 onmouseout鼠标从某元素移开 onmouseover鼠标被移到某元素之上 onmouseup某个鼠标按键被松开 onreset重置按钮被单击 onresize窗口或者框架被调整尺寸 onselect文本被选定 onsubmit提交按钮被单击 onunload用户退出页面 窗口事件
-
load事件 -
resize事件 -
scroll事件 - 焦点事件
鼠标事件
- 获取鼠标单击位置
- 鼠标悬停和离开
- 鼠标拖拽
键盘事件与事件冒泡,获取
JavaScript内置对象
-
window对象 -
document对象 -
location对象 -
navigator对象 -
screen对象 -
history对象
JavaScript的DOM操作,包含获取节点,获取,设置元素的属性值,创建,添加节点,删除节点,属性操作。DOM对象- 当网页被加载时,浏览器会创建页面的文档对象模型,
Document Object Model,文档对象模型属于BOM的一部分,用于对BOM中的核心对象document进行操作。 -
html dom模型被构造为对象的树。
DOM操作获取节点的方法:
- 标签
id获取:
document.getElementById(idName)复制代码
Copy after login- 标签
name属性获取:返回元素数组
document.getElementsByName(name)复制代码
Copy after login- 类别名称获取:返回元素数组
document.getElementsByClassName(className)复制代码
Copy after login- 标签名称获取:返回元素数组
document.getElementsByTagName(tagName)复制代码
Copy after login获取,设置元素的属性值
-
getAttribute(attributeName)方法,//括号出入输入名,返回对应属性的属性值 -
setAttribute(attributeName,attributeValue)方法,//传入属性名以及设置的值
示例:
<script> window.onload=function(){ mytable = document.getElementById('mytable'); // 获取mytable中标签名为tr的字节点 trs = mytable.getElementsByTagName("tr"); len = trs.length; flag = true; for(i=0;i<len;i++){ if(flag){ trs[i].setAttribute('bgcolor','#cccccc'); flag = false; }else{ flag = true; } } ww = mytable.getAttribute('width'); } </script> <body> <table id="mytable' align='center' width="80%" border="1"> <tr bgcolor = "#cccccc"> <td>aaa</td> <td>bbb</td> <td>ccc</td> </tr> </table> </body>复制代码Copy after login创建,添加节点
- 创建节点:
代码:
// 创建节点: document.createElement("h1"); document.createTextNode(String); document.createAttribute("class");复制代码Copy after login- 添加节点:
代码:
element.appendChild(Node); element.insertBefore(newNode, existingNode);复制代码
Copy after login- 删除节点
代码:
element.removeChild(Node)复制代码
Copy after login属性操作:获取当前元素的父节点,获取当前元素的子节点,获取当前元素的同级元素,获取当前元素的文本,获取当前节点的节点类型,设置样式。
- 获取当前元素的父节点
代码:
element.parentNode复制代码
Copy after login- 获取当前元素的子节点
代码:
element.chlidren复制代码
Copy after login- 获取当前元素的同级元素
代码:
element.nextElementSibling element.previousElementSibling复制代码
Copy after login- 获取当前元素的文本
代码:
element.innerHTML element.innerText复制代码
Copy after login- 获取当前节点的节点类型
代码:
node.nodeType复制代码
Copy after loginBOM对象
-
BOM对象,称为内置对象,是浏览器对象模型,也是JavaScript的重要组成部分。 -
window-》document,location,navigator,screen,history -
window对象表示浏览器窗口 -
window.innerHeight获取浏览器窗口的内部高度,window.innerWidth获取浏览器窗口的内部宽度。 -
document.documentElement.clientHeight,document.documentElement.clientWidth;document.body.clientHeight,document.body.clientWidth。 - 打开新窗口,
window.open(url)。 - 关闭当前窗口,
window.close()。 - 调整当前窗口的尺寸,
window.resizeTo(宽,高)
document对象
document属性和方法:Properties and methods Description ##document.bgColor Set the page background colordocument.fgColor Set the foreground colordocument.linkColor Unclicked link color##document.alinkCOlor Activate Link colordocument.vlinkColor Clicked link colordocument.URL Set the url attribute to open another web page in the same windowdocument.cookie ##document.write()Set or readDynamicly write content to the page##document.createElement(Tag) Create an HTML tag object document .getElementById(ID) Get the object with the specified idvalueGet the object with the specified namevalueSpecify the beginning of the document body and end document.location.href fullurl document. location.reload() Refresh the current web page document.location.reload(url) Open New web page ##location object location
Properties and methods:
Properties and methodsDescription
##location.href ##navigator Objectnavigator
Object contains information about the browser
Properties
Description
screenappName appVersionReturns the platform and version information of the browser cookieEnabledReturns to indicate whether the browser is enabled platform Returns the operating system platform on which the browser is runningattribute of each
scrrenwindow
object references a- object.
-
screenThe object stores information about displaying the browser screen.screen - Object properties:
Properties
DescriptionavailHeight availWidthReturn the width of the display screen ##bufferDepthSet or return the bit depth of the palette HeightReturns the height of the monitor screen WidthReturns the monitor The width of the screen history objecthistory
Object properties:Description
history.length Returns the number of urls in the browser history list history.back() Loadinghistory The previous url in the listhistory.forward()Loadinghistory##history.go()Load a specific page in the historylistBuilt-in functions
- String function
- Array function
- Mathematical function
- Date function
Mathematical function
Attribute Description ceilThe smallest integer greater than or equal to the number, rounded up floorLess than Or the largest integer equal to the number, rounded down min(parameter 1, parameter 2)Return the minimum value max(parameter 1, parameter 2)Return the maximum value pow(parameter 1, Parameter 2)Returns the value 1 to the power 2 ##random() Return Random numberround(numeric value) Roundingsqrt(numeric value) Square rootDate function
- set
: Used to set the date and time value of theDateobject. - get
: Used to obtain the date and time value of theDateobject. - to
: Used to return the value in string format of theDateobject. - parse and UTC
: used to parseDatestrings.
Attribute Description ##getFullYear() Get the complete yeargetMonth() Get the current monthgetDate() ##getDay()Get the current dayGet the current day of the weekGet the current time (starting from 1970.1.1)Get the current hoursGet Current scoreGet the current number of secondsGet the current dateGet the current timeGet date and time- 秒/分: 0 - 59;
- 时: 0 - 23;
- 星期: 0(周日) - 6(周六)
- 日期: 1 - 31
- 月份: 0(一月) - 11(十二月)
- 年份: 从1900开始的年数
定时器函数
-
setInterval(),按照指定的周期调用函数或者计算表达式。 -
setTimeout(),在指定的毫秒数后调用函数或者计算表达式。 - 区别:
setTimeout()只运行一次,setInterval()是循环执行的。
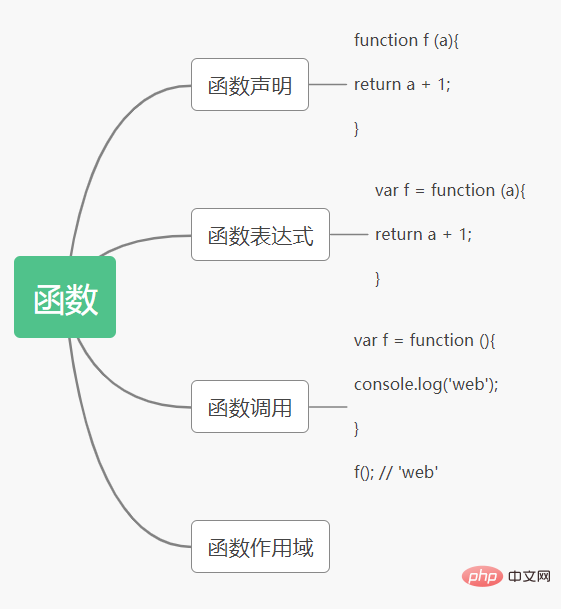
函数
- 函数由函数名,参数,函数体,返回值4部分组成的。
代码:
function 函数名(参数){ 函数体 return 返回值 }复制代码Copy after login- 函数声明3种:通过函数名声明,在程序调用时才能执行;通过将匿名函数赋值给变量,调用时可以执行;通过new的方式来声明,不需要调用,直接执行。
代码:
function web1 () { document.write("1"); } web1(); var web2 = function(){ document.write("2") } web2(); // 无须调用,直接执行,此方法不常用 var web3 = new function( document.write("3") );复制代码Copy after login- 函数返回值,函数执行完可以有返回值,也可以没有。
- 函数的调用:传值调用,传址调用,传函数调用。
闭包函数
- 内部函数只能在外部函数中访问
- 内部函数形成闭包
- 可以访问外部函数的参数和变量
- 外部函数却不能使用这个内部函数的参数和变量
- 闭包可以给内部函数的变量提供一定的安全保障
在js中一个函数在另一个函数中定义,就可以访问到父函数的成员,内部的函数就称为闭合函数。
闭合是词法闭包的简称,是引用了自由变量的函数。
闭包函数的特点:
- 闭包作为与函数成对的数据,在函数执行过程中属于激活状态。
- 闭包运行结束后,保持运行过程中的最终数据状态
- 闭包(英语:Closure),又称词法闭包(Lexical Closure)或函数闭包(function closures)
- 闭包在实现上是一个结构体,它存储了一个函数(通常是其入口地址)和一个关联的环境(相当于一个符号查找表)。
- 词法作用域
代码:
function init() { var name = "web"; // name 是一个被 init 创建的局部变量 function displayName() { // displayName() 是内部函数,一个闭包 alert(name); // 使用了父函数中声明的变量 } displayName(); } init();复制代码Copy after logininit()创建了一个局部变量name和一个名为displayName()的函数。displayName()是定义在init()里的内部函数,并且仅在init()函数体内可用。displayName()没有自己的局部变量。然而,因为它可以访问到外部函数的变量,所以displayName()可以使用父函数init()中声明的变量name。displayName()函数内的alert()语句成功显示出了变量name的值(该变量在其父函数中声明)。这个词法作用域的例子描述了分析器如何在函数嵌套的情况下解析变量名。
词法指,词法作用域根据源代码中声明变量的位置来确定该变量在何处可用。嵌套函数可访问声明于它们外部作用域的变量。
闭包是一个拥有许多变量和绑定了这些变量的环境的表达式(通常是一个函数),因而这些变量也是该表达式的一部分。
JavaScript中所有的function都是一个闭包。不过一般来说,嵌套的function所产生的闭包更为强大,也是大部分时候我们所谓的“闭包”。闭包的作用
在a执行完并返回后,闭包使得Javascript的垃圾回收机制GC不会收回a所占用的资源,因为a的内部函数b的执行需要依赖a中的变量。
- 函数的执行环境(excution context)
- 活动对象(call object)
- 作用域(scope)
- 作用域链(scope chain)

定时器和闭包
代码如下:
for(var i = 0 ; i<10; i++){ setTimeout(function(){ console.log(i); },100); }复制代码Copy after login返回的是10个10。
解决:
- 使用ES6新增的let。
- 使用闭包
for(var i = 0; i<10 ; i++){ (function(i){ setTimeout(function(){ console.log(i); }, i*100); })(i); }复制代码Copy after loginES6之前,使用var声明变量会变量提升问题:
for(var i = 0 ; i<10; i++) { console.log(i) }; console.log(i); // 变量提升 返回10复制代码Copy after login对象
- 声明一个对象有两种方法:通过
new Object()和{}实现。
示例:
// 1 var Person = function(id,name){ this.id = di; this.name = name; } var user1 = new Person(1,"web"); // 2 var web1 = {id:1,name:"web"}; var web2 = Object.create({id:2,name:"web"});复制代码Copy after login正则表达式太难了
创建正则表达式
使用一个正则表达式字面量:
let reg = /ab+c/; let reg = /^[a-zA-z]/gi;复制代码
Copy after login- 记不住,记不住,记不住。
- 正则表达式是由普通字符以及特殊字符组成的文字模式。
- 正则表达式中包含匹配符,定位符,限定符,转义符等。
- 正则表达式中有两种方法:字符串方法,正则对象方法。
字符串方法
属性 说明 search()检索与正则表达式相匹配的值 match()找到一个或者多个正则表达式的匹配 replace()替换与正则表达式的字符串 split()把字符串分割为字符串数组 正则对象方法
RegExp对象方法
属性 说明 test()用于检测一个字符串是否匹配某个模式 exec()该方法用于检索字符串中的正则表达式的匹配,该函数返回一个数组 [a-z] 匹配小写字母从a到z中的任意一个字符复制代码
Copy after login[A-Z] 匹配大写字母从a到z中的任意一个字符复制代码
Copy after login[0-9] 匹配数字0到9中任意一个字符,等于 \d复制代码
Copy after login[0-9a-z] 匹配数字0到9或者小写字母a到z中任意一个字符。复制代码
Copy after login[0-9a-zA-Z] 匹配数字0到9或小写a到z或大写A到Z中任意一个字符复制代码
Copy after login[abcd] 匹配字符abcd中的任意一个字符复制代码
Copy after login[^a-z] 匹配除小写字母a到z外的任意一个字符复制代码
Copy after login[^0-9] 匹配除数字0到9外的任意一个字符复制代码
Copy after login[^abcd] 匹配除abcd外的任意一个字符复制代码
Copy after login元字符是拥有特殊含义的字符:
. 查找单个字符,除了换行和行结束符。复制代码
Copy after login\w 查找单词字符。复制代码
Copy after login\W 查找非单词字符。复制代码
Copy after login\d 查找数字。复制代码
Copy after login\D 查找非数字字符。复制代码
Copy after login\s 查找空白字符。 \S 查找非空白字符。复制代码
Copy after login\0 查找 NUL 字符。 \n 查找换行符。 \f 查找换页符。 \r 查找回车符。 \t 查找制表符。 \v 查找垂直制表符。复制代码
Copy after login\xxx 查找以八进制数 xxx 规定的字符。 \xdd 查找以十六进制数 dd 规定的字符。 \uxxxx 查找以十六进制数 xxxx 规定的 Unicode 字符。复制代码
Copy after login量词
量词描述
量词 描述 n+至少一个 n 的字符串。 n*零个或多个 n 的字符串。 n?零个或一个 n 的字符串。 n{X}X 个 n 的序列的字符串。 n{X,Y}X 至 Y 个 n 的序列的字符串。 n{X,}至少 X 个 n 的序列的字符串。 n$匹配任何结尾为 n 的字符串。 ^n匹配任何开头为 n 的字符串。 ?=n匹配任何其后紧接指定字符串 n 的字符串。 ?!n匹配任何其后没有紧接指定字符串 n 的字符串。 .定位符 定位符可以将一个正则表达式固定在一行的开始或者结束,也可以创建只在单词内或者只在单词的开始或者结尾处出现的正则表达式。复制代码
Copy after login^ 匹配输入字符串的开始位置复制代码
Copy after login$ 匹配输入字符串的结束位置复制代码
Copy after login\b 匹配一个单词边界复制代码
Copy after login\B 匹配非单词边界复制代码
Copy after login/^[\d]{4}-[\d]{1,2}-[\d]{1,2}${1,2}$]/ 日期字符复制代码Copy after login转义符 使用转义符(反斜杠\)进行转义复制代码
Copy after loginnew RegExp(str[, attr])接收2个参数,str是一个字符串,指定正则表达式匹配规则,attr可选,表示匹配模式,值有g(全局匹配),i(区分大小写的匹配)和m(多行匹配)。表达式:g,i,m g 表示全局模式 应用于所有字符串,而非在发现第一个匹配项就停止 i 表示不区分大小写模式 m 表示多行模式 继续查找下一行中是否存在模式匹配的项复制代码
Copy after login修饰符 描述 i执行对大小写不敏感的匹配。 g执行全局匹配。 m执行多行匹配。 arguments对象
函数的实际参数会被保存在一个类数组对象 arguments 对象中,通过索引访问具体的参数:
var a = arguments[i]复制代码
Copy after login- 使用
arguments.length来获取实际传入参数的数量 -
arguments对象来获取每个参数
文本框失去焦点事件、获得焦点事件
onBlur:当失去输入焦点后产生该事件
onFocus:当输入获得焦点后,产生该文件
Onchange:当文字值改变时,产生该事件
Onselect:当文字加亮后,产生该文件
记忆力最好的三个时间段
- 睡觉前2个小时
- 起床后的一个小时
- 上午8-10点
相关免费学习推荐:javascript(视频)
The above is the detailed content of Consolidate your JavaScript knowledge system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions for Front-end Thermal Paper Ticket Printing In Front-end Development, Ticket Printing is a common requirement. However, many developers are implementing...
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object in JavaScript? When processing data, we often encounter the need to have the same ID...
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
In-depth discussion of the root causes of the difference in console.log output. This article will analyze the differences in the output results of console.log function in a piece of code and explain the reasons behind it. �...
 TypeScript for Beginners, Part 2: Basic Data Types
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:10 AM
TypeScript for Beginners, Part 2: Basic Data Types
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:10 AM
Once you have mastered the entry-level TypeScript tutorial, you should be able to write your own code in an IDE that supports TypeScript and compile it into JavaScript. This tutorial will dive into various data types in TypeScript. JavaScript has seven data types: Null, Undefined, Boolean, Number, String, Symbol (introduced by ES6) and Object. TypeScript defines more types on this basis, and this tutorial will cover all of them in detail. Null data type Like JavaScript, null in TypeScript
 How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Discussion on the realization of parallax scrolling and element animation effects in this article will explore how to achieve similar to Shiseido official website (https://www.shiseido.co.jp/sb/wonderland/)...
 Can PowerPoint run JavaScript?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
Can PowerPoint run JavaScript?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
JavaScript can be run in PowerPoint, and can be implemented by calling external JavaScript files or embedding HTML files through VBA. 1. To use VBA to call JavaScript files, you need to enable macros and have VBA programming knowledge. 2. Embed HTML files containing JavaScript, which are simple and easy to use but are subject to security restrictions. Advantages include extended functions and flexibility, while disadvantages involve security, compatibility and complexity. In practice, attention should be paid to security, compatibility, performance and user experience.





